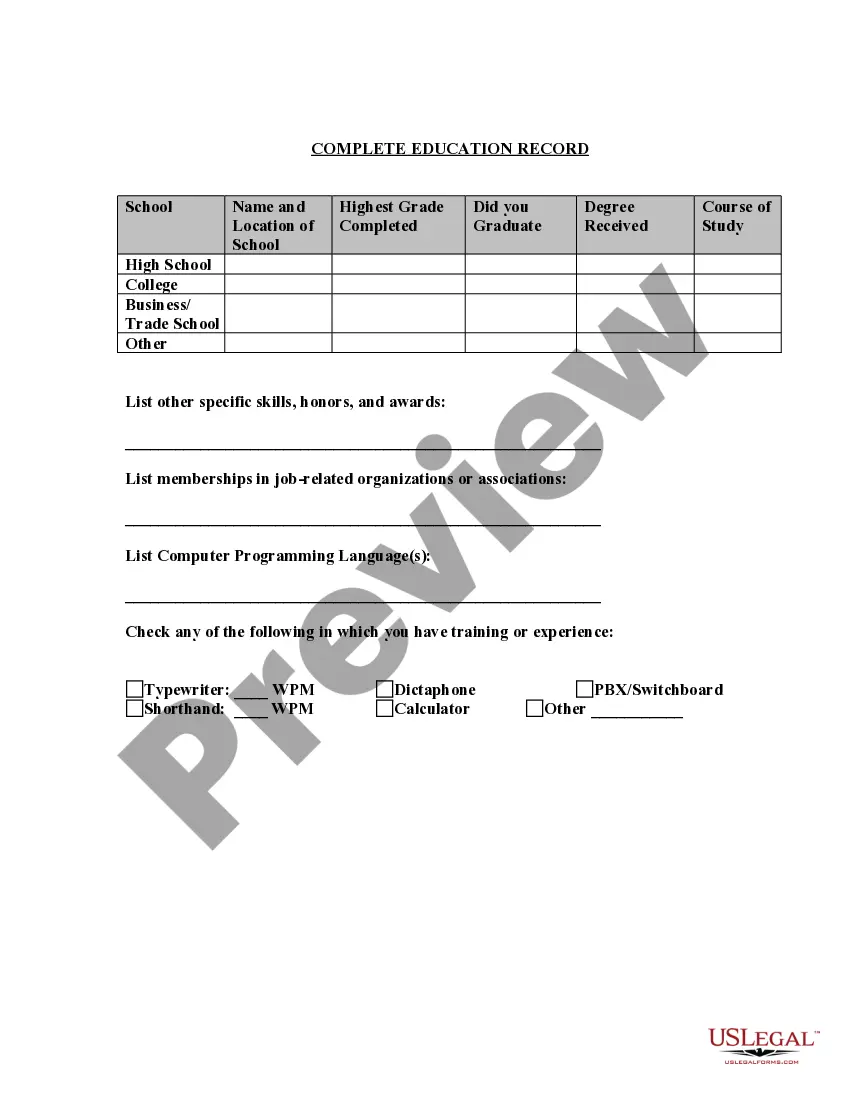
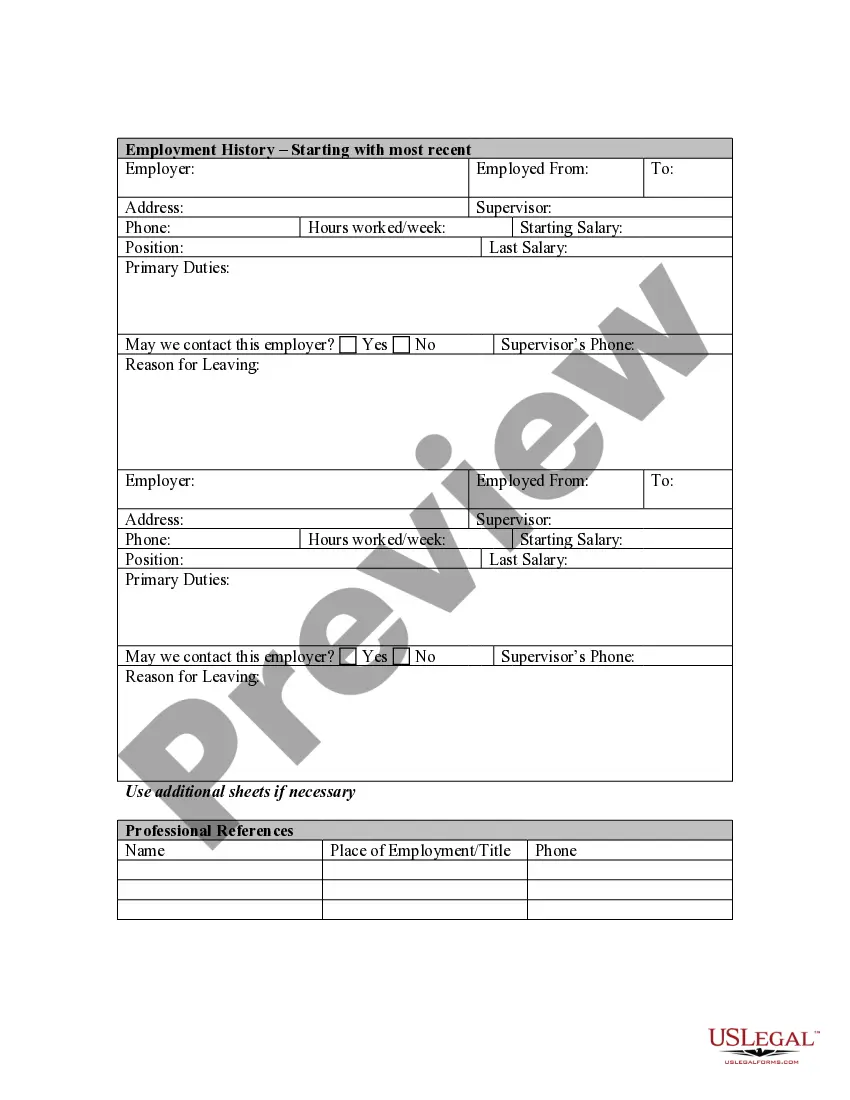
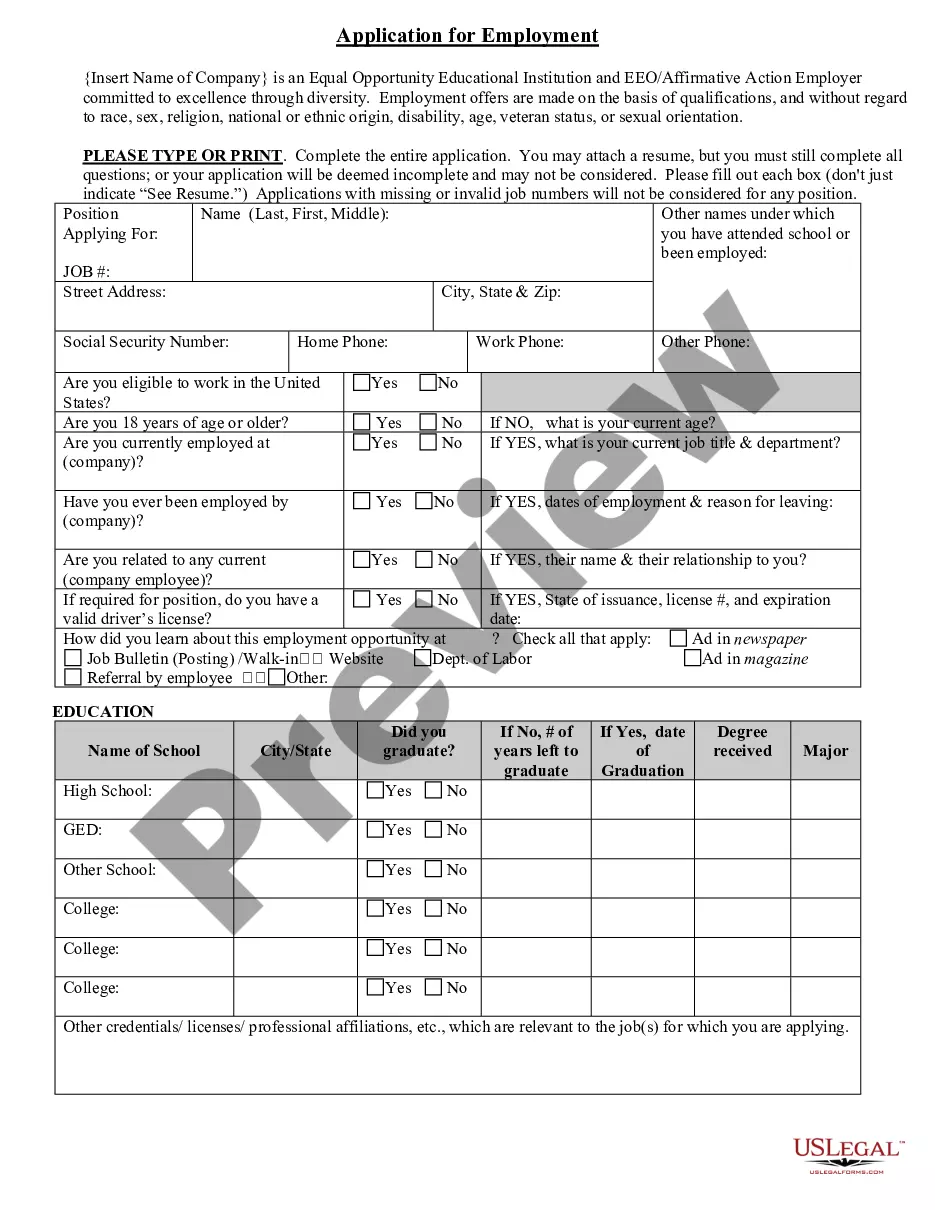
South Dakota Application for Work or Employment - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, or Nonexempt Position
Description
How to fill out Application For Work Or Employment - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, Or Nonexempt Position?
You can devote hours on the Web searching for the appropriate legal form that meets the state and federal requirements you will need.
US Legal Forms provides a vast array of legal templates that are vetted by experts.
It is easy to download or print the South Dakota Application for Work or Employment - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, or Nonexempt Position from the service.
If available, use the Review button to browse through the template as well.
- If you have a US Legal Forms account, you may Log In and click on the Obtain button.
- After that, you may complete, modify, print, or sign the South Dakota Application for Work or Employment - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, or Nonexempt Position.
- Each legal template you receive is yours indefinitely.
- To obtain an additional copy of a downloaded form, navigate to the My documents tab and click on the corresponding button.
- If you are using the US Legal Forms site for the first time, follow the simple instructions below.
- First, ensure that you have selected the correct template for the state/city that you choose.
- Check the form description to confirm you have selected the right form.
Form popularity
FAQ
In South Dakota, full-time employment typically consists of working at least 40 hours per week. However, some companies may define full-time hours differently, depending on their policies. If you’re searching for a full-time position, using the South Dakota Application for Work or Employment - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, or Nonexempt Position can clarify options and requirements.
Exempt positions are excluded from minimum wage, overtime regulations, and other rights and protections afforded nonexempt workers. Employers must pay a salary rather than an hourly wage for a position for it to be exempt.
Exempt or Nonexempt.Employees whose jobs are governed by the FLSA are either "exempt" or "nonexempt." Nonexempt employees are entitled to overtime pay. Exempt employees are not.
The FLSA includes these job categories as exempt: professional, administrative, executive, outside sales, and computer-related. The details vary by state, but if an employee falls in the above categories, is salaried, and earns a minimum of $684 per week or $35,568 annually, then they are considered exempt.
What does non-exempt mean? If employees are non-exempt, it means they are entitled to minimum wage and overtime pay when they work more than 40 hours per week.
Key Takeaways. An exempt employee is an employee who does not receive overtime pay or qualify for minimum wage. Exempt employees are paid a salary rather than by the hour, and their work is executive or professional in nature.
Nonexempt: An individual who is not exempt from the overtime provisions of the FLSA and is therefore entitled to overtime pay for all hours worked beyond 40 in a workweek (as well as any state overtime provisions). Nonexempt employees may be paid on a salary, hourly or other basis.
An exempt employee is not entitled overtime pay by the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). These salaried employees receive the same amount of pay per pay period, even if they put in overtime hours. A nonexempt employee is eligible to be paid overtime for work in excess of 40 hours per week, per federal guidelines.
Key Takeaways. An exempt employee is an employee who does not receive overtime pay or qualify for minimum wage. Exempt employees are paid a salary rather than by the hour, and their work is executive or professional in nature.