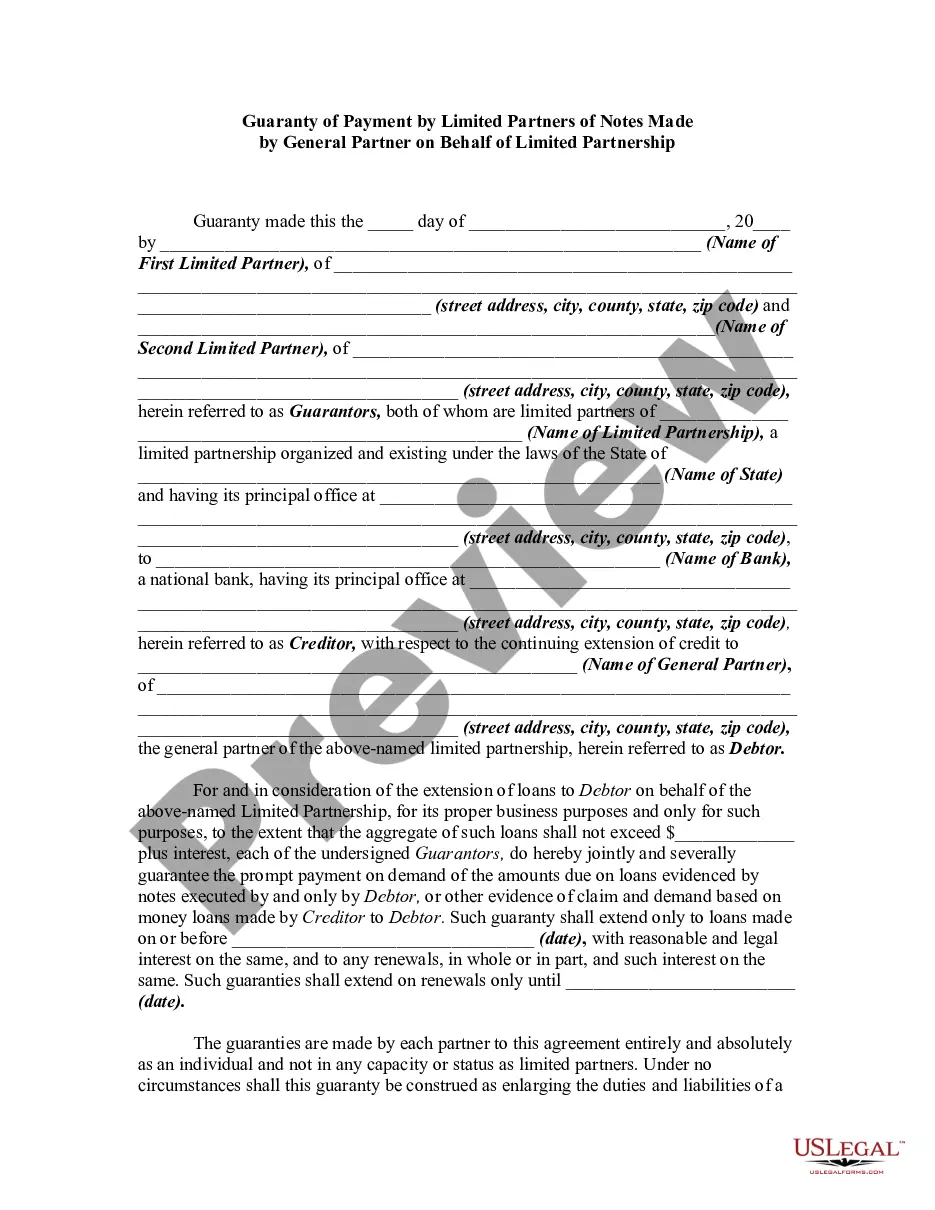
A guaranty is an undertaking on the part of one person (the guarantor) that is collateral to an obligation of another person (the debtor or obligor), and which binds the guarantor to performance of the obligation in the event of default by the debtor or obligor. A guaranty agreement is a type of contract. Thus, questions relating to such matters as validity, interpretation, and enforceability of guaranty agreements are decided in accordance with basic principles of contract law.
Oregon Continuing Guaranty of Business Indebtedness with Guarantor Having Limited Liability
Description
How to fill out Continuing Guaranty Of Business Indebtedness With Guarantor Having Limited Liability?
If you desire to acquire, download, or create authentic document templates, use US Legal Forms, the largest assortment of official forms available online.
Utilize the site's easy and user-friendly search to find the documents you need.
Various templates for business and personal purposes are categorized by groups and jurisdictions, or keywords.
Step 4. After identifying the form you need, click the Purchase now button. Choose your preferred pricing plan and enter your credentials to register for an account.
Step 5. Complete the transaction. You can use your credit card or PayPal account to finalize the purchase.
- Use US Legal Forms to obtain the Oregon Continuing Guaranty of Business Indebtedness with a Guarantor Having Limited Liability with just a few clicks.
- If you are already a US Legal Forms user, Log In to your account and click on the Acquire button to locate the Oregon Continuing Guaranty of Business Indebtedness with Guarantor Having Limited Liability.
- You can also access forms you previously downloaded from the My documents section of your account.
- If you are using US Legal Forms for the first time, follow the instructions outlined below.
- Step 1. Make sure you have selected the form for the correct city/state.
- Step 2. Take advantage of the Review feature to check the form’s details. Be sure to read the information carefully.
- Step 3. If you are not satisfied with the form, utilize the Search field at the top of the screen to find alternative templates in the legal forms catalog.
Form popularity
FAQ
The three primary types of guarantees are absolute guarantees, limited guarantees, and contingent guarantees. Within the framework of the Oregon Continuing Guaranty of Business Indebtedness with Guarantor Having Limited Liability, these guarantees play crucial roles in shaping business financial relationships. Absolute guarantees commit the guarantor to repay the entire debt, while limited guarantees restrict liability to specific amounts or circumstances. Contingent guarantees depend on certain events occurring, highlighting the importance of choosing the right type for your business context.
A limited guarantor is one who agrees to take responsibility for a specific portion of the debt, rather than the entire amount. In relation to the Oregon Continuing Guaranty of Business Indebtedness with Guarantor Having Limited Liability, this arrangement can protect the guarantor's personal assets. This structure provides a safety net, allowing business owners to secure financing while minimizing personal risk. It's often a strategic choice for individuals seeking to balance risk and business needs.
In the context of the Oregon Continuing Guaranty of Business Indebtedness with Guarantor Having Limited Liability, various types of guarantors exist. These include personal guarantors, corporate guarantors, and limited liability company (LLC) guarantors. Each type interacts differently with the obligations and risks associated with business debts. Understanding these distinctions can help you make informed decisions when entering into guaranty agreements.
The term 'limited' generally refers to limitations on the liabilities or obligations of the guarantor, while 'limited by guarantee' signifies a specific structure where the company itself limits its liability. In the context of the Oregon Continuing Guaranty of Business Indebtedness with Guarantor Having Limited Liability, understanding this difference can help businesses and guarantors navigate their financial responsibilities and ensure compliance with agreements.
A guarantor has the right to understand the terms of the obligation they are guaranteeing, including any limitations on their liability. They can also seek to enforce the terms of the guarantee through negotiation or legal action if necessary. In regard to the Oregon Continuing Guaranty of Business Indebtedness with Guarantor Having Limited Liability, a guarantor must be aware of their rights to protect themselves and make informed decisions about their involvement.
An unlimited continuing guaranty means the guarantor agrees to be fully responsible for all debts incurred by the borrower, without any cap on liability. This type of guaranty is riskier for the guarantor but provides lenders with a high level of security. With an Oregon Continuing Guaranty of Business Indebtedness with Guarantor Having Limited Liability, businesses typically prefer the limited options, as they provide a better balance of security and risk.
An example of a limited guarantee could involve a company borrowing $100,000 with a guarantee stating the guarantor will cover only up to $50,000 if the company defaults on payments. This type of arrangement provides reassurance to lenders while maintaining a manageable risk for the guarantor. In the context of the Oregon Continuing Guaranty of Business Indebtedness with Guarantor Having Limited Liability, this structured approach ensures the guarantor's financial exposure remains controlled.
A limited guarantee is a promise by a guarantor to cover a specified amount or type of obligation, rather than all potential liabilities. This means that the guarantor's liability is restricted to certain terms laid out in the agreement, making it less risky for the guarantor. When you're looking at the Oregon Continuing Guaranty of Business Indebtedness with Guarantor Having Limited Liability, the limited guarantee allows a business to secure financing while protecting the guarantor from overwhelming debt.
A limited warranty often protects the buyer against specific defects in a product, like a new appliance. For instance, if you buy a refrigerator, a limited warranty might cover repairs for the first year but exclude damage from mishandling or common wear and tear. In the context of the Oregon Continuing Guaranty of Business Indebtedness with Guarantor Having Limited Liability, it would specify the exact nature and extent of the obligations of the guarantor.
Filling out a letter of guarantee involves including your details, the borrower’s information, and the specifics of the guaranteed obligation. Clearly state the terms of the guarantee and your liability limits. For those navigating the Oregon Continuing Guaranty of Business Indebtedness with Guarantor Having Limited Liability, ensuring clarity in this document is vital to protect your interests.