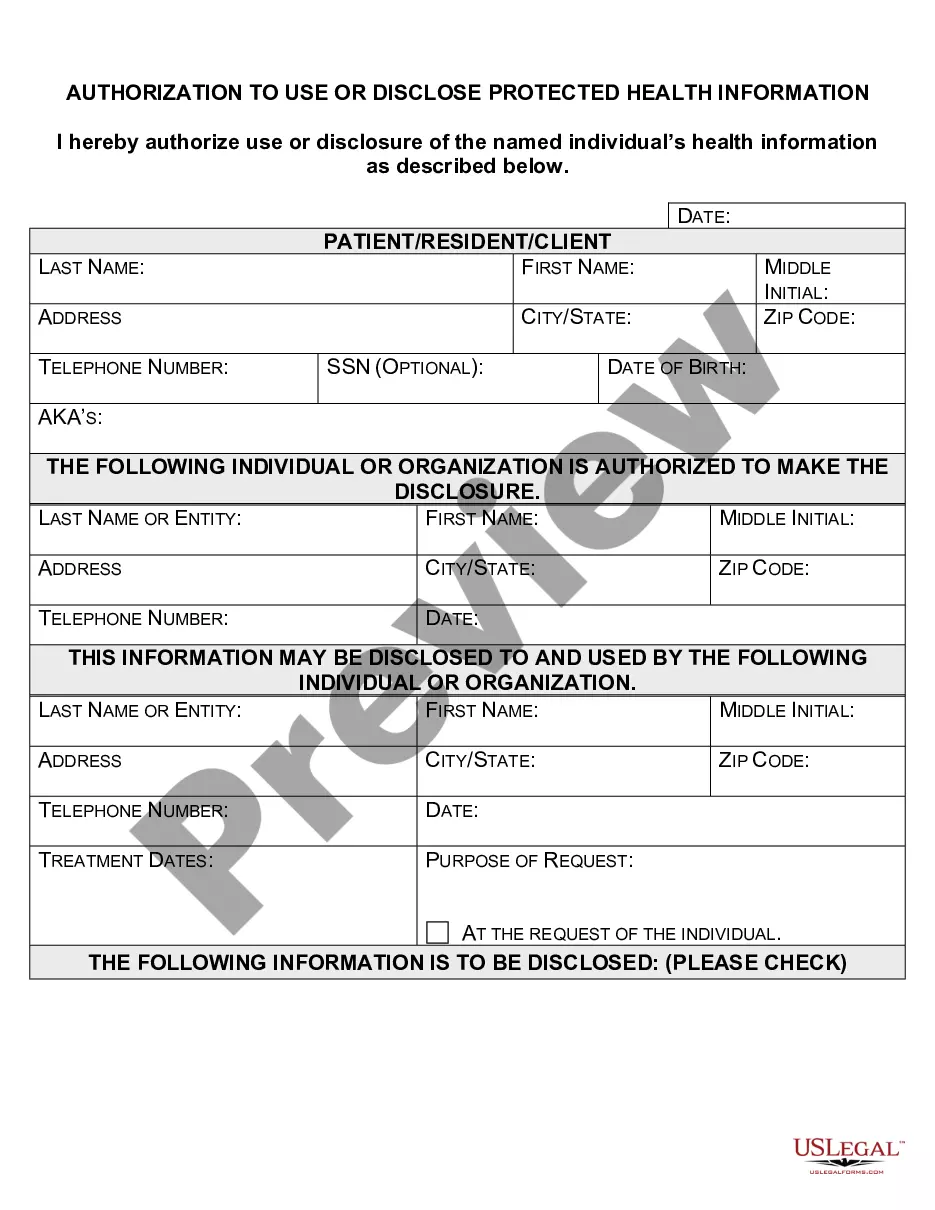
Nebraska Permission To Disclose Health Billing Information
Description
How to fill out Permission To Disclose Health Billing Information?
Are you in a situation where you will require documents for either business or personal reasons nearly every workday? There are numerous legal document templates available online, but locating ones you can trust isn’t simple. US Legal Forms offers a vast array of form templates, including the Nebraska Permission To Disclose Health Billing Information, which are designed to comply with state and federal regulations.
If you are already familiar with the US Legal Forms website and have an account, simply Log In. After that, you can download the Nebraska Permission To Disclose Health Billing Information template.
If you do not have an account and wish to start using US Legal Forms, follow these steps: Find the form you need and ensure it is for the correct city/county. Use the Preview option to check the form. Review the details to confirm you have selected the correct form. If the form isn’t what you are looking for, utilize the Search field to find the form that meets your needs and requirements. Once you find the right form, click Get now. Choose the pricing plan you need, enter the required information to create your account, and purchase your order using your PayPal or credit card. Select a convenient file format and download your copy.
- Access all the document templates you have purchased in the My documents section. You can download an additional copy of Nebraska Permission To Disclose Health Billing Information at any time, if needed. Just click the desired form to download or print the document template.
- Utilize US Legal Forms, the most extensive collection of legal forms, to save time and avoid mistakes. The service offers professionally crafted legal document templates that you can use for various purposes. Create your account on US Legal Forms and start making your life easier.
Form popularity
FAQ
Filling out the authorization to use and disclose health information is a straightforward process. First, gather your personal information, such as your name, address, and contact details. Next, clearly specify the health information you want to be disclosed, and identify the person or organization that will receive this information. By using the US Legal platform, you can access templates specifically designed for the Nebraska Permission To Disclose Health Billing Information, making the process even easier and ensuring your compliance with legal standards.
Covered entities may disclose protected health information that they believe is necessary to prevent or lessen a serious and imminent threat to a person or the public, when such disclosure is made to someone they believe can prevent or lessen the threat (including the target of the threat).
A covered entity must disclose protected health information in only two situations: (a) to individuals (or their personal representatives) specifically when they request access to, or an accounting of disclosures of, their protected health information; and (b) to HHS when it is undertaking a compliance investigation or
There are a few scenarios where you can disclose PHI without patient consent: coroner's investigations, court litigation, reporting communicable diseases to a public health department, and reporting gunshot and knife wounds.
Protected health information (PHI), also referred to as personal health information, is the demographic information, medical histories, test and laboratory results, mental health conditions, insurance information and other data that a healthcare professional collects to identify an individual and determine appropriate
Under the HIPAA Privacy Rule, a covered entity must disclose protected health information in only two situations: (a) to individuals (or their personal representatives) specifically when they request access to, or an accounting of disclosures of, their protected health information; and (b) to the Department of Health
PHI may be disclosed as necessary to prevent or lessen a serious and imminent threat to the health and safety of a person or the public based on the health care provider's professional judgment under 45 CFR 164.512(j).
Covered entities must obtain patient authorization before they use or disclose PHI for marketing purposes. Under the Privacy Rule, "marketing" means communicating about a product or service in a way that encourages a recipient to purchase or use the product or service.
Covered entities may use and disclose protected health information without individual authorization as required by law (including by statute, regulation, or court orders).
When a patient is not present or cannot agree or object because of some incapacity or emergency, a health care provider may share relevant information about the patient with family, friends, or others involved in the patient's care or payment for care if the health care provider determines, based on professional