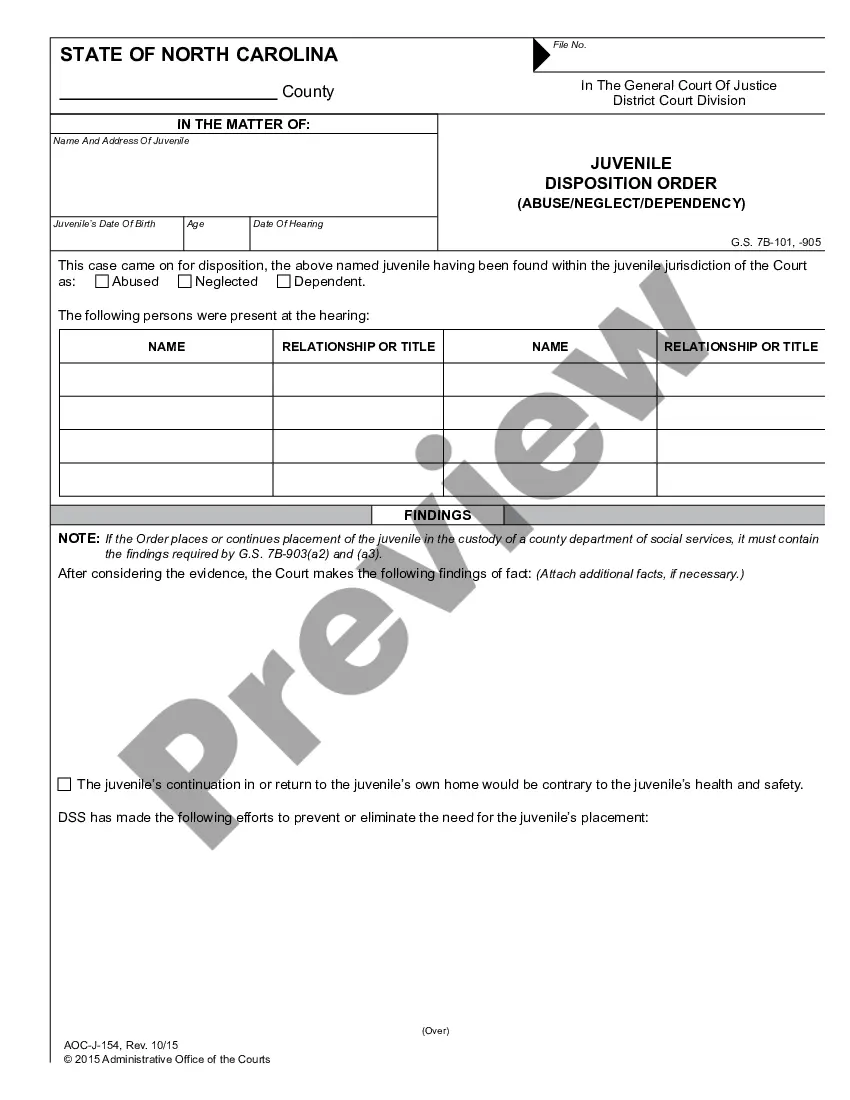
Juvenile Order: This is an official form from the North Carolina Administration of the Courts (AOC), which complies with all applicable laws and statutes. USLF amends and updates the forms as is required by North Carolina statutes and law.
North Carolina Juvenile Order
Description
Get your form ready online
Our built-in tools help you complete, sign, share, and store your documents in one place.
Make edits, fill in missing information, and update formatting in US Legal Forms—just like you would in MS Word.
Download a copy, print it, send it by email, or mail it via USPS—whatever works best for your next step.
Sign and collect signatures with our SignNow integration. Send to multiple recipients, set reminders, and more. Go Premium to unlock E-Sign.
If this form requires notarization, complete it online through a secure video call—no need to meet a notary in person or wait for an appointment.
We protect your documents and personal data by following strict security and privacy standards.
Make edits, fill in missing information, and update formatting in US Legal Forms—just like you would in MS Word.

Download a copy, print it, send it by email, or mail it via USPS—whatever works best for your next step.

Sign and collect signatures with our SignNow integration. Send to multiple recipients, set reminders, and more. Go Premium to unlock E-Sign.
If this form requires notarization, complete it online through a secure video call—no need to meet a notary in person or wait for an appointment.
We protect your documents and personal data by following strict security and privacy standards.
Looking for another form?
How to fill out North Carolina Juvenile Order?
Steer clear of expensive attorneys and discover the North Carolina Juvenile Order you seek at an affordable rate on the US Legal Forms website.
Utilize our straightforward groups feature to locate and acquire legal and tax documents. Review their descriptions and preview them before downloading.
Choose to download the form in PDF or DOCX format. Just click Download and locate your form in the My documents section. You may save the form to your device or print it out. After downloading, you can fill out the North Carolina Juvenile Order manually or with the aid of editing software. Print it out and reuse the template multiple times. Achieve more for less with US Legal Forms!
- Additionally, US Legal Forms offers clients detailed instructions on how to access and complete each form.
- US Legal Forms users simply need to Log In and download the specific form they require to their My documents section.
- Those who have not subscribed yet should adhere to the steps outlined below.
- Confirm that the North Carolina Juvenile Order is permissible for use in your area.
- If possible, examine the description and utilize the Preview function prior to downloading the templates.
- If you’re certain the template meets your requirements, click Buy Now.
- If the form is incorrect, utilize the search feature to find the correct one.
- Then, create your account and choose a subscription plan.
- Make payment via card or PayPal.
Form popularity
FAQ
The Supreme Court has not ruled on whether juveniles have the right to bail, the right to a speedy trial, or the right to self- representation under the United States Constitution, and the North Carolina General Assembly did not extend those rights to juveniles as part of the Juvenile Code. G.S. 7B- 2405.
2756 Petition: a formal document filed by a court counselor requesting that charges be brought against a juvenile.Juveniles are entitled to a probable cause hearing if they are charged with felonies. 2756 Probation: a court-2010ordered period of supervision for a juvenile who has been adjudicated as delinquent.
How are juvenile cases handled? In North Carolina, juvenile cases are sent to the state district courts for hearings. These courts have authority over delinquent and undisciplined juveniles.
The juvenile justice system underwent a process that has been described as the four Ds: (1) Decriminalization, that is, taking status offenders out from delinquency definitions and constraining court authority with these youths; (2) Diversion from the court of lesser offenders, including status offenders; (3) Due
The juvenile justice process involves nine major decision points: (1) arrest, (2) referral to court, (3) diversion, (4) secure detention, (5) judicial waiver to adult criminal court, (6) case petitioning, (7) delinquency finding/adjudication, (8) probation, and (9) residential placement, including confinement in a
Petition: A document filed in juvenile court alleging that a juvenile is a delinquent or a status offender and asking that the court assume jurisdiction over the juvenile or that an alleged delinquent be transferred to criminal court for prosecution as an adult.
The juvenile justice process involves nine major decision points: (1) arrest, (2) referral to court, (3) diversion, (4) secure detention, (5) judicial waiver to adult criminal court, (6) case petitioning, (7) delinquency finding/adjudication, (8) probation, and (9) residential placement, including confinement in a
Intake: The process used for every youth referred to juvenile court. Intake involves screening each youth to determine the appropriateness for release or referral to a diversionary program or agency for nonofficial or nonjudicial handling.