After the filing of a bankruptcy petition, the debtor needs protection from the collection efforts of its creditors. Therefore, the bankruptcy law provides that the filing of either a voluntary or involuntary petition operates as an automatic stay which prevents creditors from taking action against the debtor. This is similar to an injunction against the creditors of the debtor. The automatic stay ends when the bankruptcy case is closed or dismissed or when the debtor is granted a discharge. Anyone who willfully violates the stay in the case of an individual debtor can be liable for actual damages caused by the violation and sometimes liable for punitive damages.
Kentucky Motion to Extend Automatic Stay and Notice of Motion
Description
How to fill out Motion To Extend Automatic Stay And Notice Of Motion?
Choosing the right authorized document format could be a have a problem. Obviously, there are tons of templates accessible on the Internet, but how will you discover the authorized develop you require? Make use of the US Legal Forms website. The services delivers a huge number of templates, such as the Kentucky Motion to Extend Automatic Stay and Notice of Motion, which can be used for enterprise and personal requires. Every one of the varieties are checked out by pros and satisfy state and federal demands.
Should you be previously authorized, log in to your bank account and click the Obtain switch to have the Kentucky Motion to Extend Automatic Stay and Notice of Motion. Make use of bank account to search throughout the authorized varieties you might have bought previously. Visit the My Forms tab of the bank account and have another version of the document you require.
Should you be a new user of US Legal Forms, listed below are straightforward instructions that you should comply with:
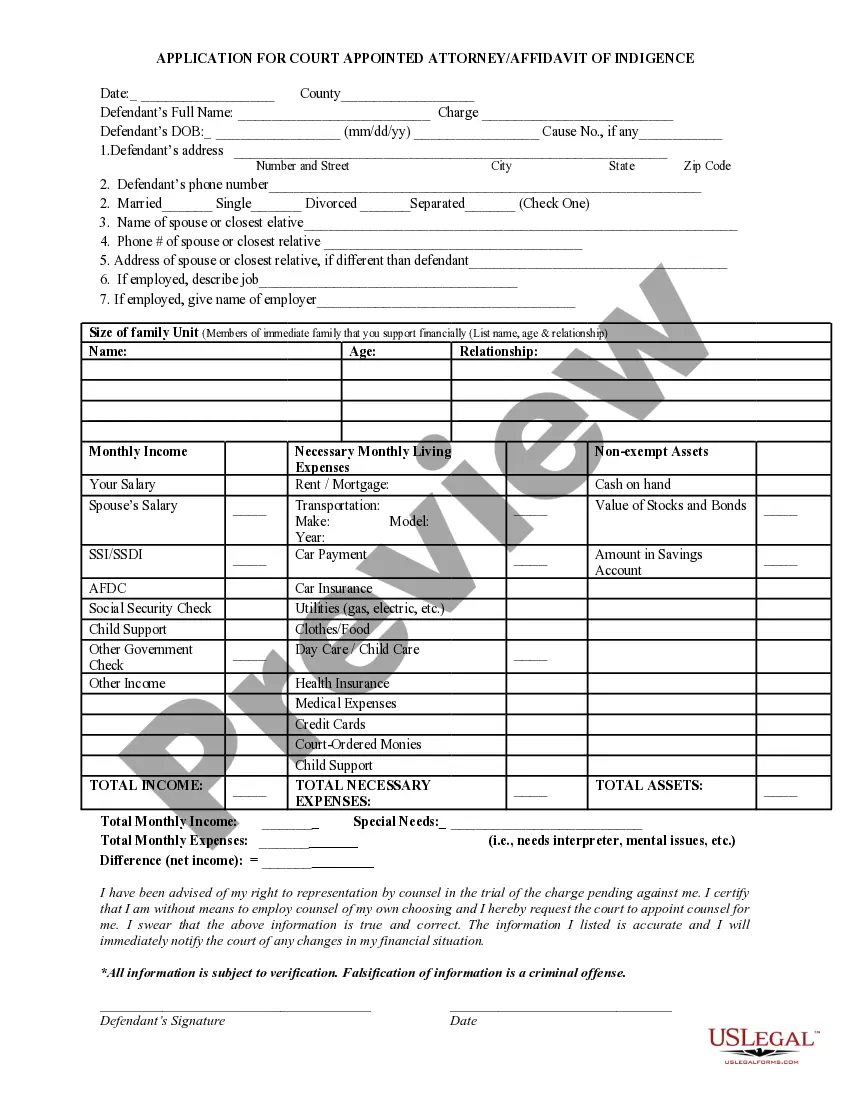
- First, be sure you have chosen the proper develop for your town/county. You can check out the shape utilizing the Preview switch and study the shape outline to guarantee this is basically the best for you.
- In case the develop is not going to satisfy your needs, utilize the Seach industry to obtain the proper develop.
- When you are sure that the shape is suitable, go through the Acquire now switch to have the develop.
- Select the pricing strategy you would like and type in the essential details. Build your bank account and pay for the transaction making use of your PayPal bank account or bank card.
- Pick the file file format and download the authorized document format to your system.
- Comprehensive, edit and print out and indicator the received Kentucky Motion to Extend Automatic Stay and Notice of Motion.
US Legal Forms may be the largest collection of authorized varieties that you will find various document templates. Make use of the company to download skillfully-made papers that comply with express demands.
Form popularity
FAQ
Key Takeaways. An automatic stay stops creditors from trying to collect debts from a debtor who has filed for bankruptcy until court proceedings are completed. Creditors, collection agencies, and others who violate the automatic stay can be sued by the debtor.
Two main methods exist for fighting a motion for relief from automatic stay. These types are ?procedural? and ?substantive? objections. Basically, procedural objections challenge the manner in which the motion was filed, while substantive objections challenge the actual substance of the motion.
In some situations, a creditor might file a motion to lift the automatic stay. This would allow them to resume collection actions. One situation would be if you were behind on your payments for a secured loan, such as a mortgage or car payment, and the loan amount was greater than the value of the home or car.
The automatic stay is one of the fundamental debtor protections provided by the bankruptcy laws. It gives the debtor a breathing spell from his creditors. It stops all collection efforts, all harassment, and all foreclosure actions.
When relief from stay is granted, it does not remove the property from the bankruptcy estate or grant the creditor ownership of the property. It simply removes the stay and restores the parties to their state law rights. Creditors can then enforce those rights to the extent that the relief from stay order permits.
Filing a Motion and Setting a Hearing Date -- A Motion for Relief from the Automatic Stay is commenced by filing the appropriate motion and setting the motion for a hearing date. To file a Motion for Relief from the Automatic Stay, the Local Bankruptcy Rules require parties to use mandatory forms.
What is a Motion for Relief From Stay? A motion for relief from automatic stay, also known as a stay relief motion, is something a creditor requests from the bankruptcy court. They essentially ask the court for permission to continue certain collection actions against you.
An order for relief invokes the automatic stay and brings down an iron curtain, separating the pre-bankruptcy from the post-bankruptcy debtor, creating a bankruptcy estate and prohibiting unauthorized transfers of the debtor's property.