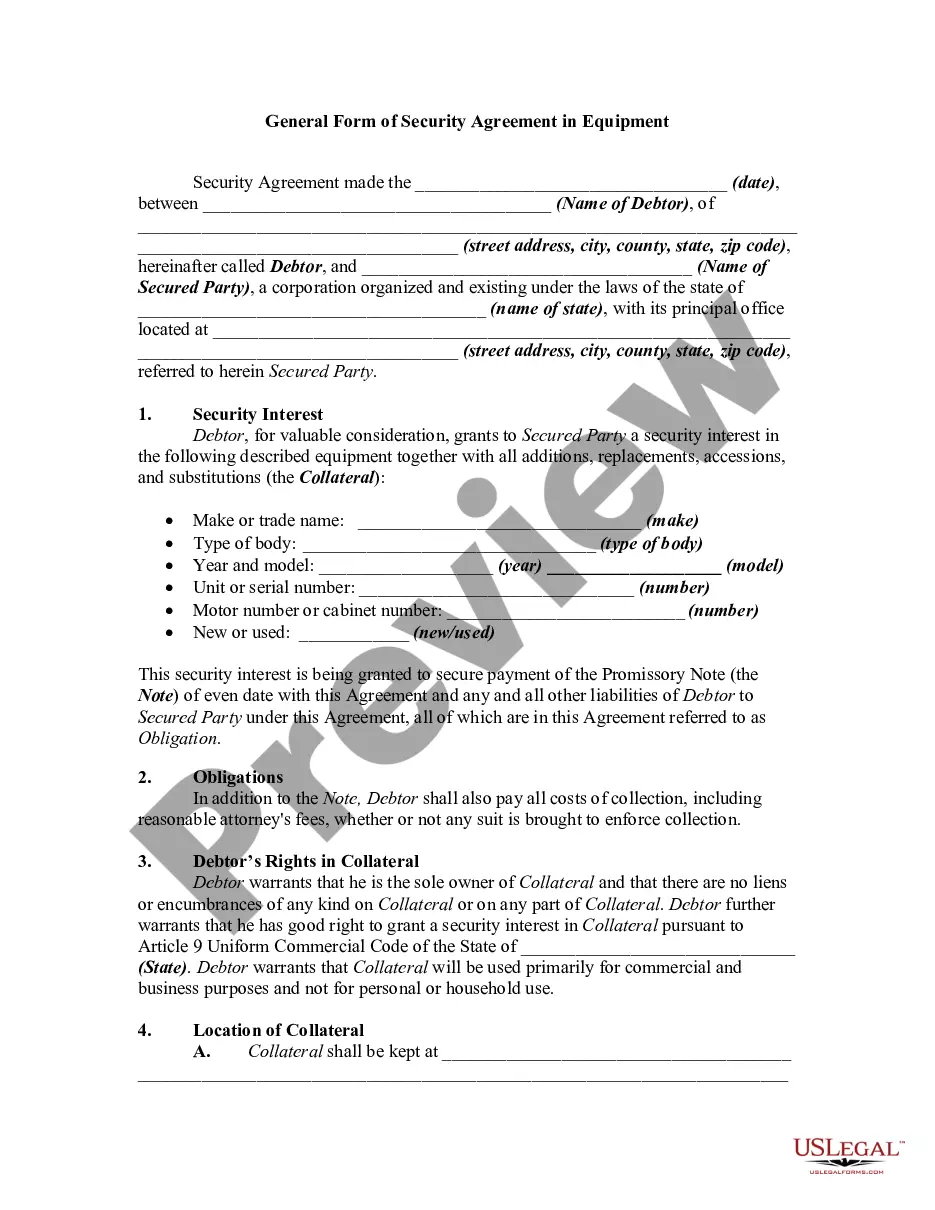
A secured transaction is created when a buyer or borrower (debtor) grants a seller or lender (creditor or secured party) a security interest in personal property (collateral). A security interest allows a creditor to repossess and sell the collateral if a debtor fails to pay a secured debt.
The Truth-in-Lending Act (TILA) is part of the Federal Consumer Credit Protection Act. The purpose of the TILA is to make full disclosure to debtors of what they are being charged for the credit they are receiving. The Act merely asks lenders to be honest to the debtors and not cover up what they are paying for the credit. Regulation Z is a federal regulation prepared by the Federal Reserve Board to carry out the details of the Act. TILA applies to consumer credit transactions. Consumer credit is credit for personal or household use and not commercial use or business purposes.