Hawaii Carbon Dioxide Storage Unit Agreement
Description
How to fill out Carbon Dioxide Storage Unit Agreement?
If you wish to comprehensive, download, or print legitimate document web templates, use US Legal Forms, the largest assortment of legitimate varieties, that can be found online. Utilize the site`s simple and handy search to get the paperwork you will need. Various web templates for organization and specific uses are categorized by classes and states, or keywords and phrases. Use US Legal Forms to get the Hawaii Carbon Dioxide Storage Unit Agreement in just a handful of click throughs.
In case you are currently a US Legal Forms client, log in to the bank account and click the Download option to obtain the Hawaii Carbon Dioxide Storage Unit Agreement. You can even gain access to varieties you in the past saved inside the My Forms tab of your own bank account.
Should you use US Legal Forms the first time, follow the instructions beneath:
- Step 1. Make sure you have chosen the shape to the right metropolis/region.
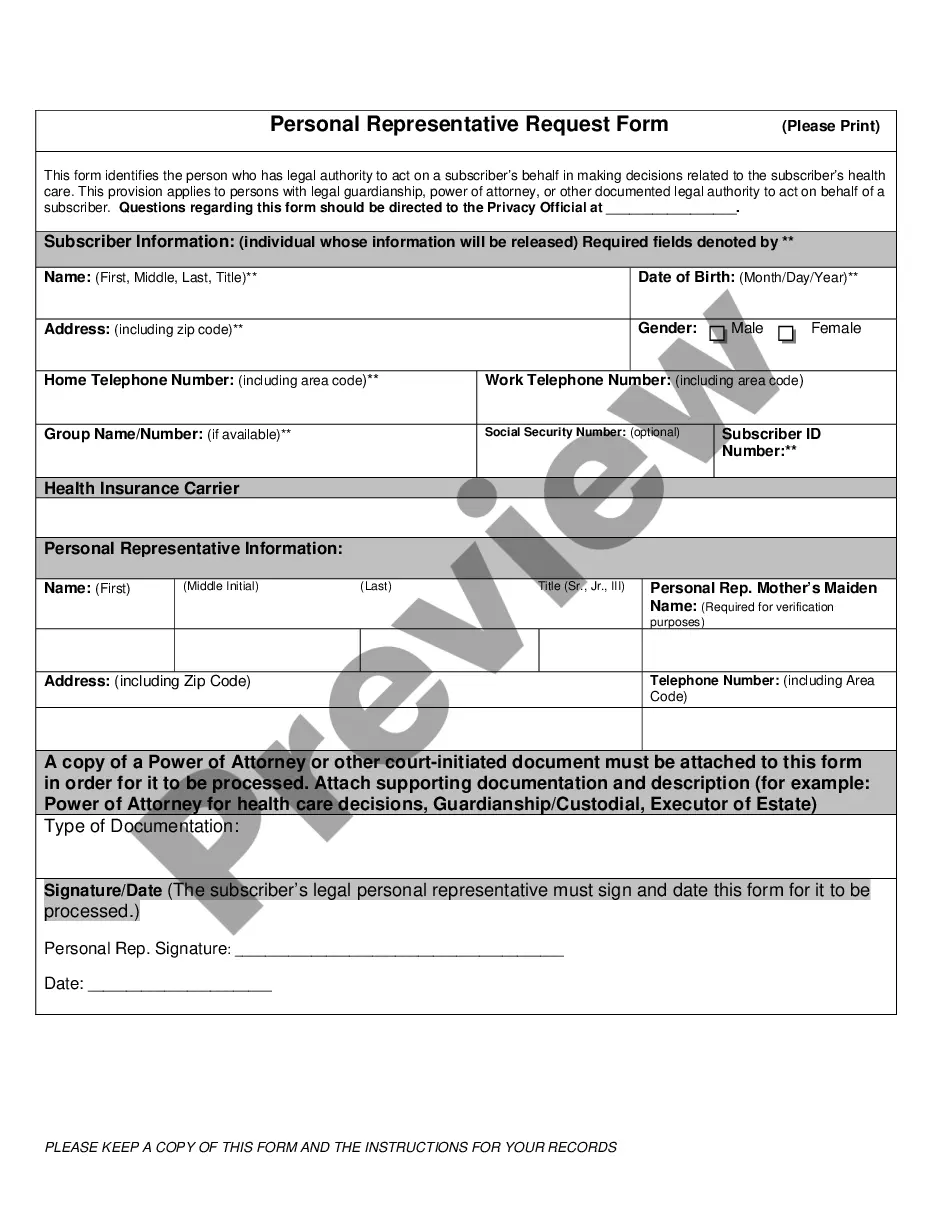
- Step 2. Take advantage of the Preview choice to check out the form`s articles. Do not neglect to learn the outline.
- Step 3. In case you are unhappy with all the type, use the Search industry towards the top of the monitor to locate other variations from the legitimate type template.
- Step 4. Once you have found the shape you will need, click the Purchase now option. Select the costs prepare you like and put your references to sign up for the bank account.
- Step 5. Process the deal. You should use your credit card or PayPal bank account to finish the deal.
- Step 6. Select the format from the legitimate type and download it in your device.
- Step 7. Complete, modify and print or signal the Hawaii Carbon Dioxide Storage Unit Agreement.
Every single legitimate document template you get is your own property forever. You possess acces to each type you saved with your acccount. Select the My Forms section and choose a type to print or download once more.
Contend and download, and print the Hawaii Carbon Dioxide Storage Unit Agreement with US Legal Forms. There are thousands of professional and status-particular varieties you can use for the organization or specific needs.
Form popularity
FAQ
CO2 transport and storage costs vary regionally. Key variabilities are distance, scale, monitoring, geology, and pipeline costs. We find CO2 transport and storage costs range from $4 to 45/tCO2. CCS deployment is more sensitive to transport and storage costs in some regions.
Estimated costs for sequestering up to 500 million tons of carbon per year?an amount that would offset up to one-third of current annual U.S. carbon emissions?range from $30 to $90 per ton.
The cost of carbon capture and storage (CSS) and carbon dioxide removal (CDR) solutions varies by approach and technology. It is estimated that CCS costs ranged between 15 and 130 U.S. dollars per metric ton of carbon dioxide (tCO?), while the costs for direct air CCS ranged between 100 and 345 U.S. dollars per tCO?.
Washington, DC - The United States has at least 2,400 billion metric tons of possible carbon dioxide (CO2) storage resource in saline formations, oil and gas reservoirs, and unmineable coal seams, ing to a new U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) publication.
They range between $100-$5,000. This greatly depends on the type and size as explained below. The CO2 tank by CryoFX can be sold in either steel or aluminum with or without siphon tubes. The CO2 tanks are offered in a variety of shapes and sizes which include: 20 lb., 35 lb., 50 lb., 75 lb., 100lb and 135lb.
The analysis suggests coal-sourced CO2 emissions can be stored in this region at a cost of $52?$60 ton?1, whereas the cost to store emission from natural-gas-fired plants ranges from approximately $80 to $90. Storing emissions offshore increases the lowest total costs of CCS to over $60 per ton of CO2 for coal.