Hawaii Accredited Investor Qualification and Verification Requirements for Reg D, Rule 506(c) Offerings
Description
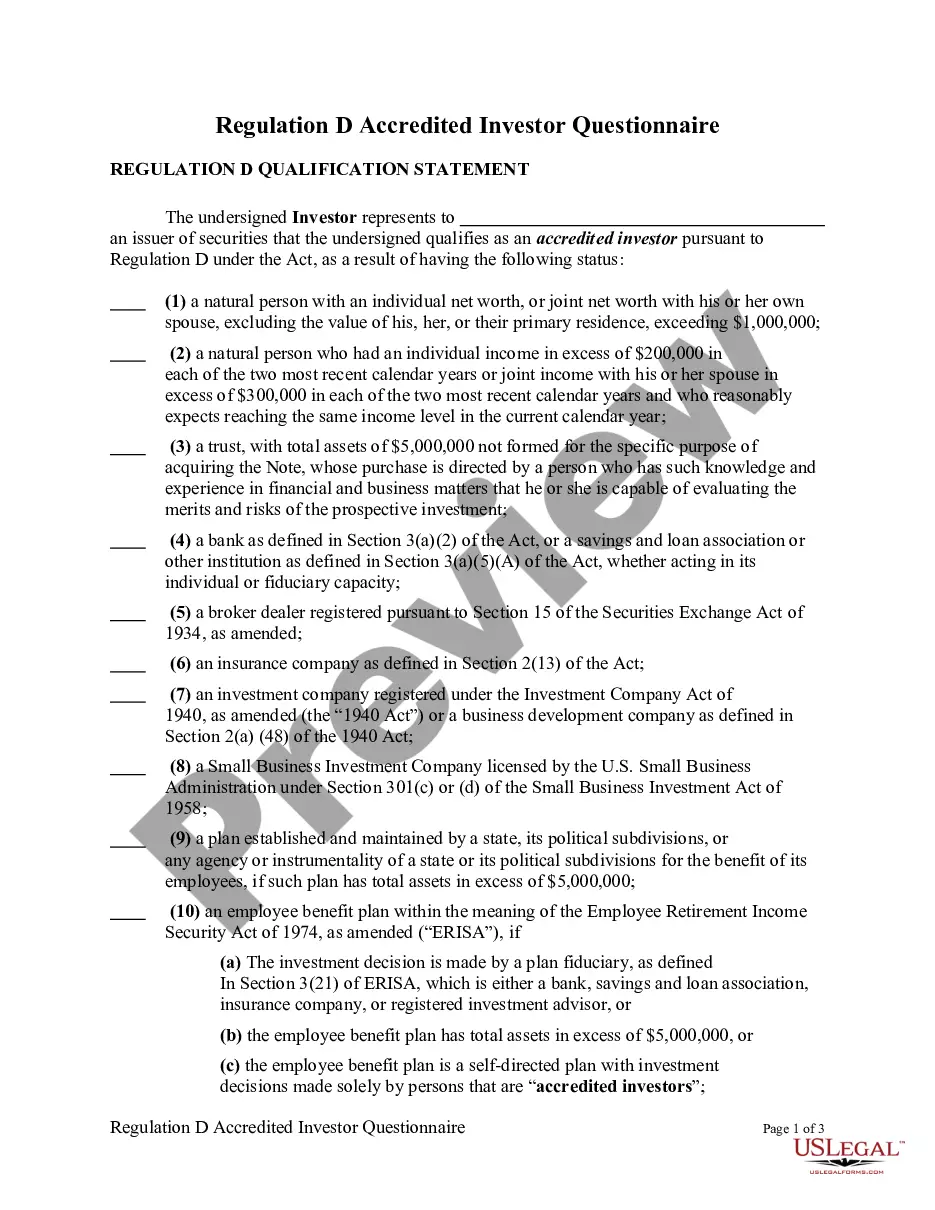
To become an accredited investor the (SEC) requires certain wealth, income or knowledge requirements. The investor must fall into one of three categories. Firms selling unregistered securities must put investors through their own screening process to determine if investors can be considered an accredited investor.
The Verifying Individual or Entity should take reasonable steps to verify and determined that an Investor is an "accredited investor" as such term is defined in Rule 501 of the Securities Act, and hereby provides written confirmation. This letter serves to help the Entity determine status, take Investor statements regarding information, and waiver of claims."
How to fill out Accredited Investor Qualification And Verification Requirements For Reg D, Rule 506(c) Offerings?
Choosing the best lawful record template can be quite a have difficulties. Needless to say, there are tons of themes available on the Internet, but how do you obtain the lawful form you want? Take advantage of the US Legal Forms site. The service gives thousands of themes, including the Hawaii Accredited Investor Qualification and Verification Requirements for Reg D, Rule 506(c) Offerings, that you can use for company and personal requires. Each of the types are examined by pros and fulfill state and federal demands.
When you are currently registered, log in to your profile and click the Download button to find the Hawaii Accredited Investor Qualification and Verification Requirements for Reg D, Rule 506(c) Offerings. Use your profile to appear from the lawful types you possess ordered in the past. Check out the My Forms tab of the profile and obtain another copy of the record you want.
When you are a whole new customer of US Legal Forms, listed below are easy guidelines that you should adhere to:
- First, make sure you have selected the right form to your area/state. You can look through the shape making use of the Review button and browse the shape information to make certain this is basically the right one for you.
- When the form fails to fulfill your preferences, utilize the Seach industry to get the proper form.
- Once you are positive that the shape is suitable, go through the Purchase now button to find the form.
- Choose the rates strategy you desire and enter the essential details. Build your profile and pay for the order making use of your PayPal profile or Visa or Mastercard.
- Choose the document formatting and download the lawful record template to your product.
- Comprehensive, edit and print and sign the received Hawaii Accredited Investor Qualification and Verification Requirements for Reg D, Rule 506(c) Offerings.
US Legal Forms is definitely the largest collection of lawful types in which you can see a variety of record themes. Take advantage of the service to download skillfully-created papers that adhere to condition demands.
Form popularity
FAQ
In a Rule 506(b) offering, the issuer may take the investor's word that he, she, or it is accredited, unless the issuer has reason to believe the investor is lying. In a Rule 506(c) offering, the issuer must take reasonable steps to verify that every investor is accredited.
Rule 506(c) allows companies to generally advertise their offerings to a potential investor using the internet, social media, websites, TV campaigns, radio ads, etc. This is in contrast to Rule 506(b) (which is the same as the old Rule 506 before the JOBS Act came in) which does not allow general solicitation at all.
The company cannot use general solicitation or advertising to market the securities. The company may sell its securities to an unlimited number of "accredited investors" and up to 35 other purchasers.
Reviewing bank statements, brokerage statements, and other similar reports to determine net worth. Obtaining written confirmation of the investor's accredited investor status from one of the following persons: a registered broker-dealer, an investment adviser registered with the SEC, a licensed attorney, or a CPA.
Under Rule 506(c), there are no limits to how much money fund managers can raise or how much each investor can invest. It simply depends on how much the VCs can?and want to?raise. This is no different than Rule 506(b).
To confirm their status as an accredited investor, an investor can submit official documents for net worth and income verification, including: Tax returns. Pay stubs. Financial statements. IRS forms. Credit report. Brokerage statements. Tax assessments.
Rule 506(c) sets out a principles-based method for accredited investor verification, requiring an objective determination by the issuer as to whether the steps taken in verification were ?reasonable? in context of the particular facts and circumstances of each purchaser and transaction.
Rule 506(c) permits issuers to broadly solicit and generally advertise an offering, provided that: all purchasers in the offering are accredited investors. the issuer takes reasonable steps to verify purchasers' accredited investor status and. certain other conditions in Regulation D are satisfied.