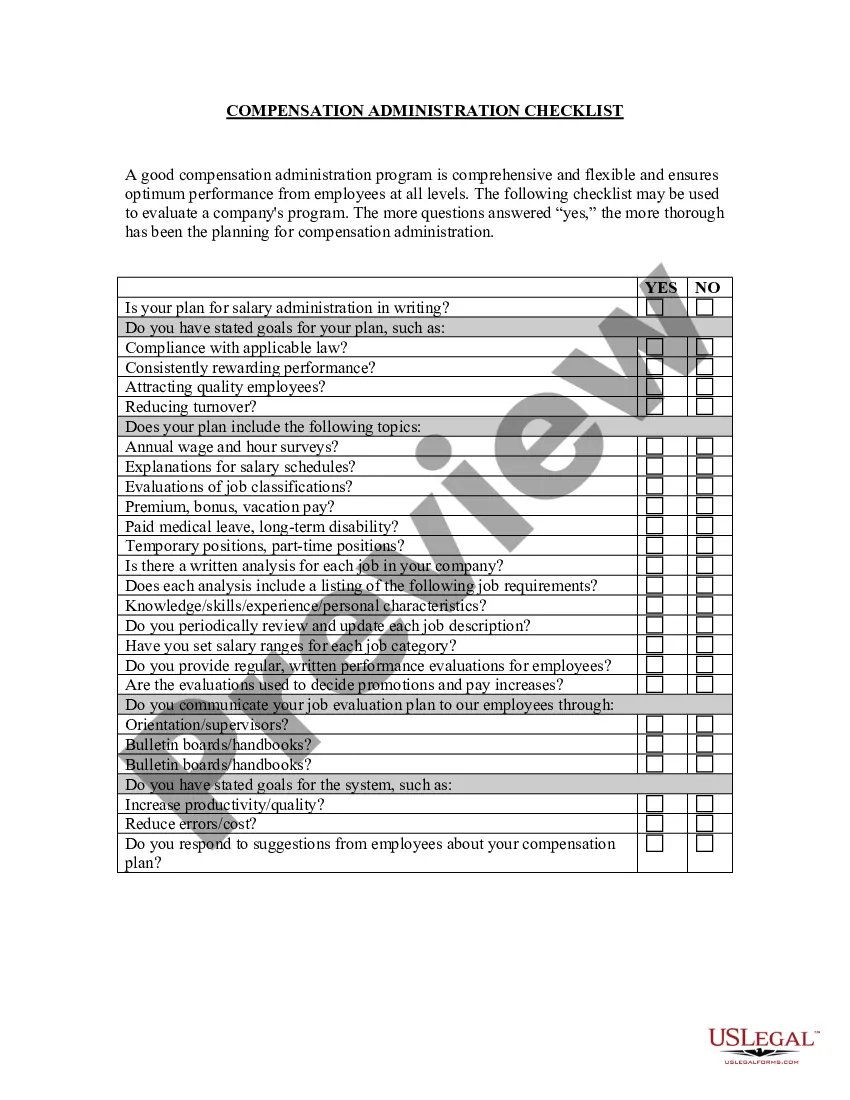
Hawaii Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist
Description
How to fill out Equal Pay - Administration And Enforcement Checklist?
It is feasible to devote numerous hours online seeking the legal document template that complies with the state and federal requirements you desire.
US Legal Forms offers a vast array of legal forms that have been vetted by professionals.
You can conveniently access or print the Hawaii Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist from their service.
If available, utilize the Review option to browse through the document template as well.
- If you already possess a US Legal Forms account, you can sign in and click the Download button.
- Then, you can complete, modify, print, or sign the Hawaii Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist.
- Every legal document template you purchase is yours permanently.
- To obtain an additional copy of any purchased form, navigate to the My documents tab and select the appropriate option.
- If you are using the US Legal Forms website for the first time, adhere to the straightforward instructions outlined below.
- First, ensure you've chosen the correct document template for the state/city of your choice.
- Review the document description to confirm you have selected the right form.
Form popularity
FAQ
Yes, you can sue for wrongful termination in Hawaii if you believe your dismissal violated state laws or public policy. Wrongful termination claims can arise from retaliation, discrimination, or breach of employment contracts. The Hawaii Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist can be a valuable resource for understanding your rights and options in such situations. Consulting with an attorney or using platforms like uslegalforms can guide you through the legal process effectively.
Yes, Hawaii has implemented a salary history ban. This law prevents employers from asking about a candidate's salary history during the hiring process. The aim is to promote fair compensation practices and support the Hawaii Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist. By focusing on the responsibilities of the job and the skills required, employers can ensure they provide equitable pay to all candidates.
The wage transparency law in Maryland aims to promote equal pay and reduce wage disparities based on gender and other factors. This law mandates that employers provide employees with information regarding wage ranges for certain positions. The law aligns with the principles in the Hawaii Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist, which emphasizes transparency in pay structures. By utilizing tools and templates from platforms like US Legal Forms, employers can effectively implement wage transparency practices and ensure compliance with these laws.
Overview Of Federal Sector EEO Complaint ProcessEEO Counselor.Filing A Formal Complaint.Agency Issues A Decision (Final Action)Requesting A Hearing.Filing An Appeal Of The Agency's Final Order.Request For Reconsideration Of The Appeal Decision.Filing A Lawsuit.
Yes, but only if there is an employment contract or bargaining agreement. If you do not have a contract, your employer can legally reduce your work hours or cut pay and you may not have any recourse.
For a pay cut to be imposed on any employee, their consent must first be given in order for the reduction to be legal. This means that a pay cut can only be unilaterally applied across a workforce if each staff member agrees to it.
What is the most common next step in the EEOC enforcement process after a person files an employment discrimination claim? The EEOC either accepts or refers the charge.
A pay cut cannot be enacted without the employee being notified. If an employer cuts an employee's pay without telling him, it is considered a breach of contract. Pay cuts are legal as long as they are not done discriminatorily (i.e., based on the employee's race, gender, religion, and/or age).
The first three stages, pre-complaint, formal complaint, and appeal, are all part of the EEOC's administrative process....The final stage starts the judicial process.Pre-Complaint Stage.Formal Complaint Stage.Mixed Cases Complaints.Class Complaints.Appeal Stage.Judicial Stage.
Note: Federal employees and applicants for federal employment have a different complaint process.Access Your Charge Information through the EEOC Public Portal.Mediation.Investigation.Adding to Your Charge.Subpoena.Requesting a Notice of Right to Sue.Possible Action After Investigation Completed.