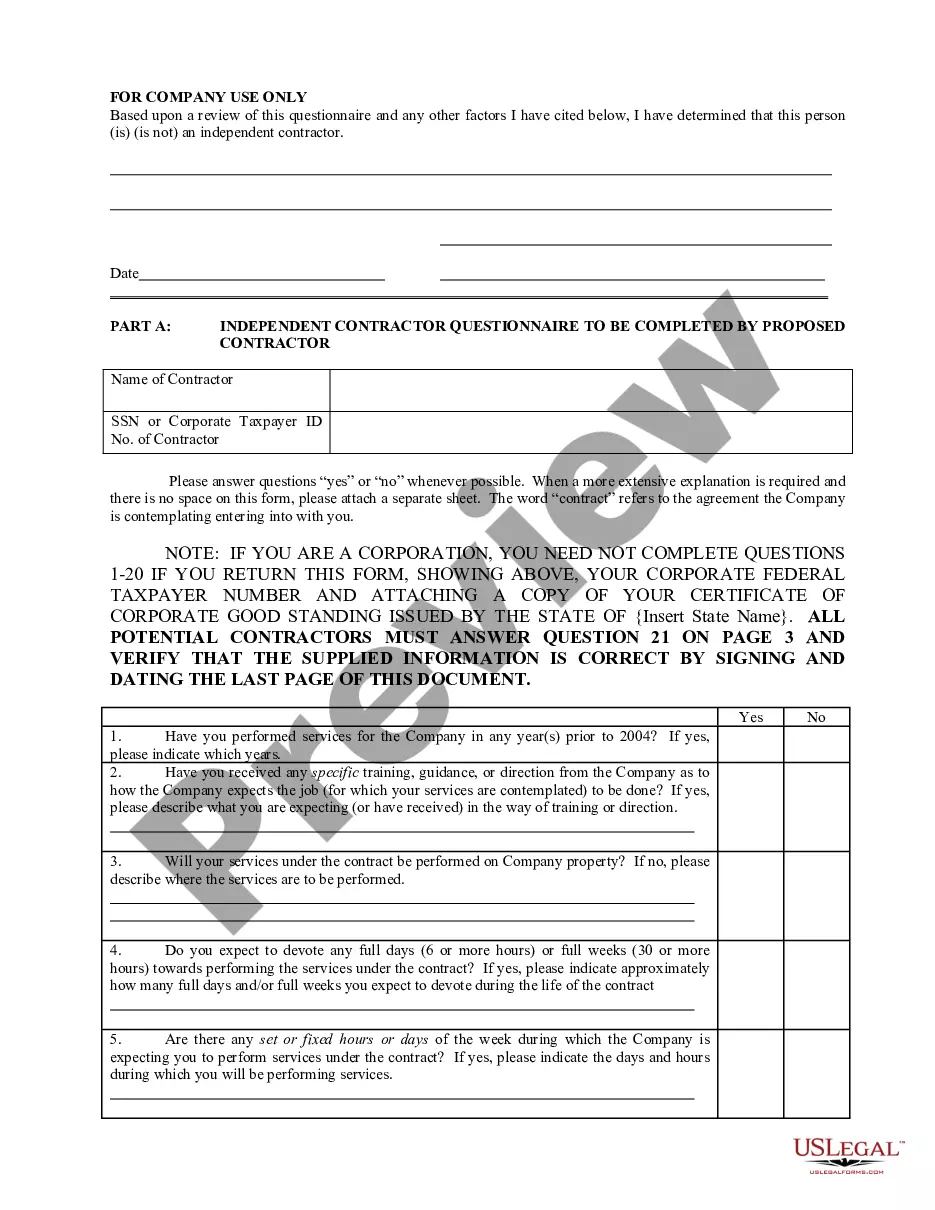
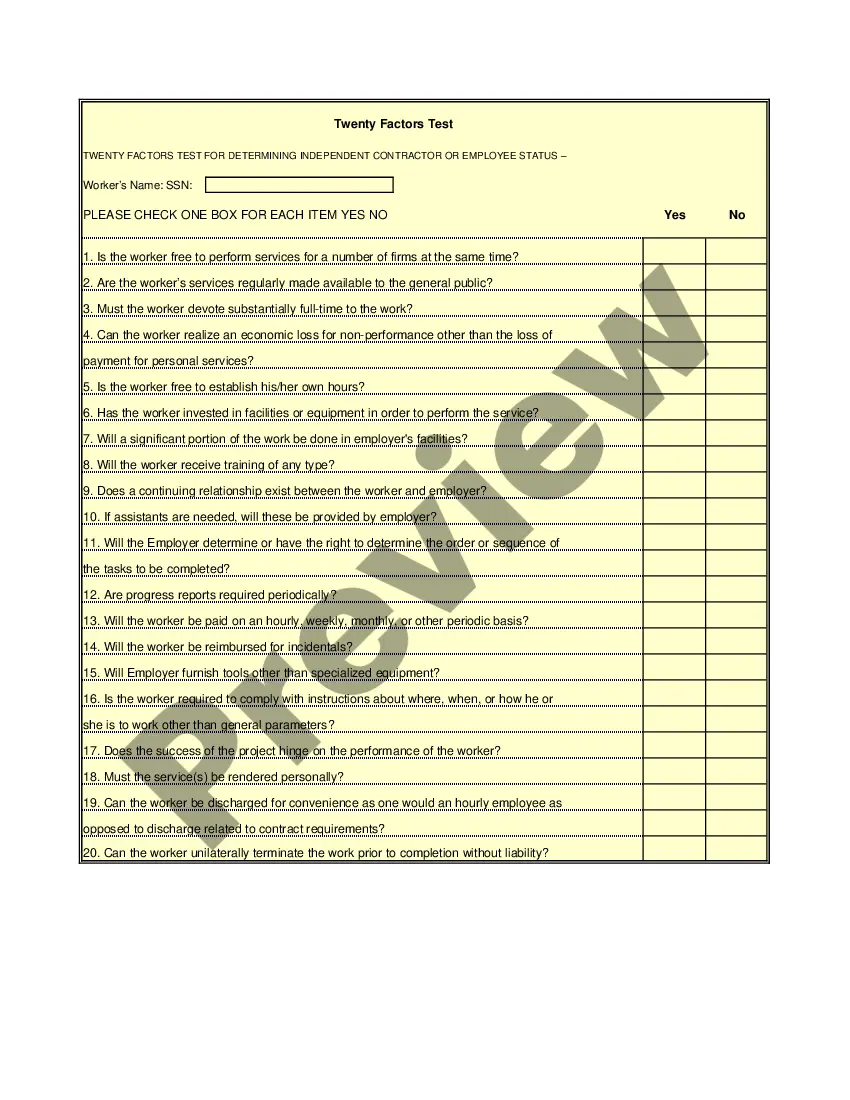
District of Columbia IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status
Description
How to fill out IRS 20 Quiz To Determine 1099 Vs Employee Status?
Finding the right legal document design might be a have difficulties. Needless to say, there are a variety of themes available online, but how do you find the legal kind you require? Use the US Legal Forms internet site. The service offers a large number of themes, for example the District of Columbia IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status, that you can use for company and personal requirements. All the varieties are checked by pros and meet up with state and federal needs.
In case you are presently authorized, log in in your account and click the Acquire option to obtain the District of Columbia IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status. Make use of your account to search through the legal varieties you may have purchased formerly. Proceed to the My Forms tab of the account and get yet another backup of your document you require.
In case you are a whole new customer of US Legal Forms, here are simple recommendations so that you can follow:
- Initial, be sure you have chosen the appropriate kind for your city/state. You may look through the shape making use of the Preview option and study the shape information to make certain it is the right one for you.
- In the event the kind is not going to meet up with your expectations, use the Seach field to obtain the correct kind.
- When you are certain the shape would work, click on the Acquire now option to obtain the kind.
- Choose the prices program you want and type in the essential details. Create your account and buy an order making use of your PayPal account or credit card.
- Select the data file structure and down load the legal document design in your product.
- Comprehensive, modify and print out and indication the received District of Columbia IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status.
US Legal Forms may be the greatest library of legal varieties where you will find a variety of document themes. Use the service to down load expertly-produced files that follow condition needs.
Form popularity
FAQ
To determine independent contractor status, consider asking about the level of control you have over the work. Specifically, inquire whether you dictate how, when, and where the work is completed. Additionally, ask about the financial arrangements. Are you providing your own tools, or does the company supply them? Finally, assess the relationship. Does the engagement create expectations for employee benefits, or is it distinctly contract-based? Understanding these aspects directly relates to the District of Columbia IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status, which can guide you in making the correct classification.
Determining whether someone is a W-2 employee or a 1099 independent contractor involves examining the relationship dynamics and tax obligations. W-2 employees generally receive benefits and have taxes withheld from their paychecks, while 1099 workers manage their own tax responsibilities. Engaging with the District of Columbia IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status can help clarify these distinctions and guide you towards accurate classifications.
To determine a person's status, consider the level of control the employer has over how work is performed, the financial arrangements, and any agreements made between the parties. Reviewing all contractual materials and past interactions can provide deeper insights. You can also take the District of Columbia IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status to gain clarity on this important distinction.
Several factors contribute to determining a person's status as an employee or an independent contractor, including the degree of control the employer exerts over the worker. Other aspects like benefits, tools provided, and the nature of the work relationship also play a pivotal role. Familiarity with these factors will help you navigate the District of Columbia IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status effectively.
The IRS employs three critical tests to ascertain a worker's status as an employee: the behavioral test, the financial test, and the relationship test. These tests examine the level of control an employer has, the financial arrangement, and how the parties perceive their relationship. Mastering these tests is essential for correctly navigating the complexities presented by the District of Columbia IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status.
The IRS assesses whether a worker is an independent contractor based on the amount of control the employer has over the work. They use specific guidelines, focusing on three main areas: behavioral, financial, and the relationship between the parties. An understanding of these categories will greatly enhance your abilities when engaging with the District of Columbia IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status.
The distinction between an employee and an independent contractor hinges on several factors, including the level of control over work, the nature of the relationship, and the degree of independence. Employers typically have more control over employees, dictating how tasks are completed. In contrast, independent contractors operate with greater autonomy in their work. Understanding this distinction is crucial when navigating the District of Columbia IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status.