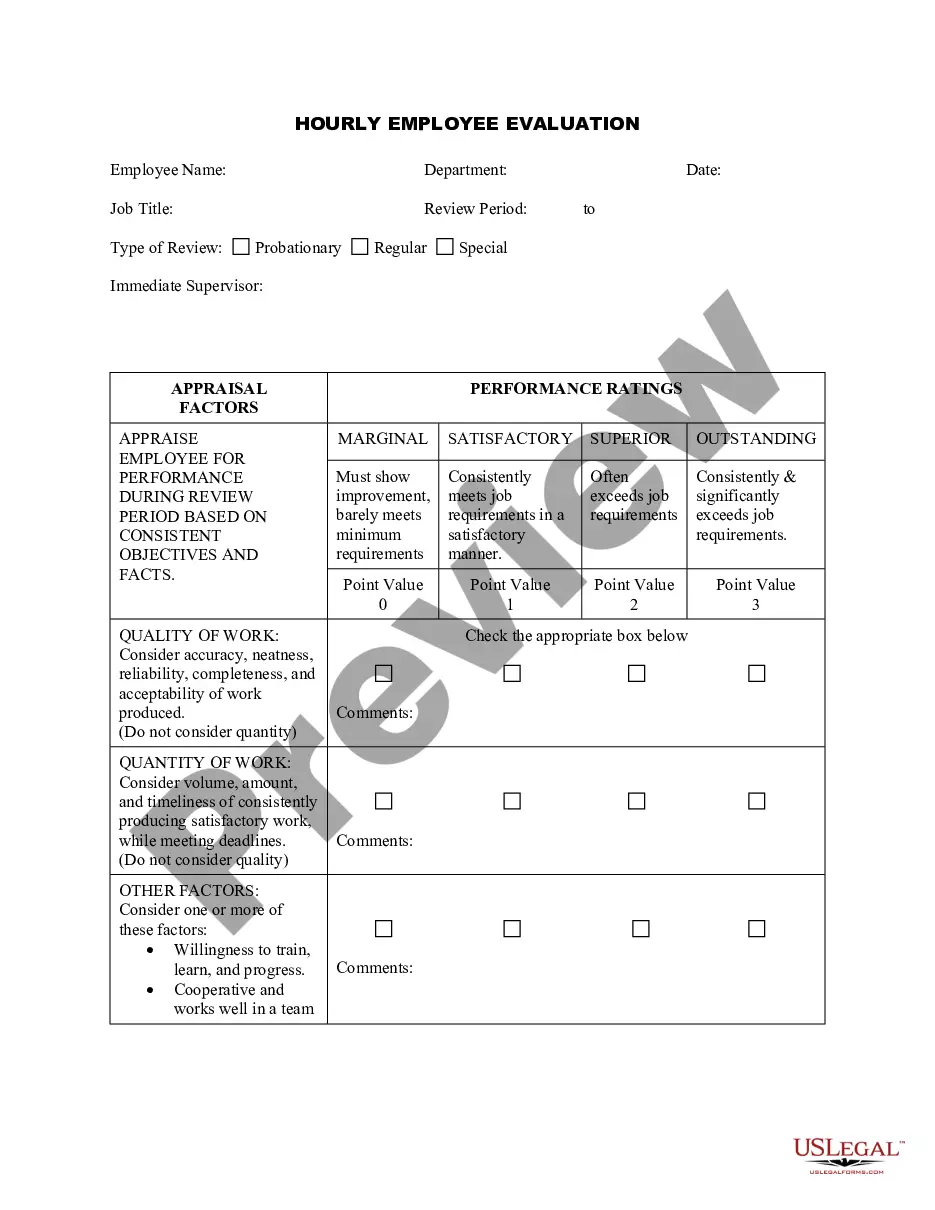
California Model Performance Evaluation - Appraisal Form for Hourly, Exempt, Nonexempt, and Managerial Employees
Description
How to fill out Model Performance Evaluation - Appraisal Form For Hourly, Exempt, Nonexempt, And Managerial Employees?
Selecting the appropriate legal document format can be a challenge.
Of course, there are numerous templates available online, but how can you locate the legal form you need.
Utilize the US Legal Forms website. The service offers a vast array of templates, including the California Model Performance Evaluation - Appraisal Form for Hourly, Exempt, Nonexempt, and Managerial Employees, which you may use for business and personal purposes.
If the form does not meet your requirements, use the Search field to find the appropriate form.
- All of the forms are reviewed by professionals and comply with state and federal regulations.
- If you are already a registered user, Log In to your account and click on the Download button to acquire the California Model Performance Evaluation - Appraisal Form for Hourly, Exempt, Nonexempt, and Managerial Employees.
- Utilize your account to browse through the legal forms you may have purchased in the past.
- Visit the My documents tab in your account and obtain another copy of the document you need.
- If you are a new user of US Legal Forms, here are simple instructions you can follow.
- First, ensure you have selected the correct form for your city/state. You can examine the form using the Preview button and review the form details to confirm it is suitable for you.
Form popularity
FAQ
To submit a self-appraisal using the California Model Performance Evaluation - Appraisal Form for Hourly, Exempt, Nonexempt, and Managerial Employees, first complete the form thoroughly. After filling it out, save your document and send it via email or your company's chosen platform. Make sure to inform your manager that the evaluation is available, as this can facilitate a more productive discussion.
The primary difference in status between exempt and non-exempt employees is their eligibility for overtime. Under federal law, that status is determined by the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). Exempt employees are not entitled to overtime, while non-exempt employees are.
The executive exemption usually is applied to managerial employees. However, managers still have to meet the requirements for the exemption. If they do not, they must be classified as nonexempt, unless they can meet one of the other exemptions.
With few exceptions, to be exempt an employee must (a) be paid at least $23,600 per year ($455 per week), and (b) be paid on a salary basis, and also (c) perform exempt job duties. These requirements are outlined in the FLSA Regulations (promulgated by the U.S. Department of Labor).
The FLSA includes these job categories as exempt: professional, administrative, executive, outside sales, and computer-related. The details vary by state, but if an employee falls in the above categories, is salaried, and earns a minimum of $684 per week or $35,568 annually, then they are considered exempt.
From time to time, employers may need to reclassify employees due to changes in job duties and responsibilities....Non-Exempt to Exempt:Apply federal and state tests first. Ensure the employee qualifies as exempt under federal and applicable state laws.Communicate the change in advance.Avoid improper deductions.
You select your own Federal tax exemptions, allowances and additional withholding (if any), and report it on the electronic W-4. You can change your W-4 exemptions and allowances any time by simply completing and submitting another electronic W-4 form in CLASS-Web.
Partial Exempted Personnel from Overtime Pay.Executive Exemption.Administrative Exemption.Computer Professionals Exemption.Professional Exemption.Outside Sales Exemption.Highly Compensated Employees.
How to Communicate a Change in FLSA Exemption Status to EmployeesStep 1: Explain Why the Change Is Occurring.Step 2: Discuss the Meaning of a Change in Status.Step 3: Apprise the Employee of Changes in Compensation.Step 4: Inform the Employee of Changes in Position.More items...
Tips For Drafting Job Descriptions for Exempt EmployeesAccuracy is King. The job description must be accurate.Accuracy Does Not Mean Exhaustion.Strong Verbs, Clear Impact.Focus on Exempt Functions.Don't Shy Away From Degree Requirements.Assist With Can Diminish a Role.Consider Requiring Acknowledgement.