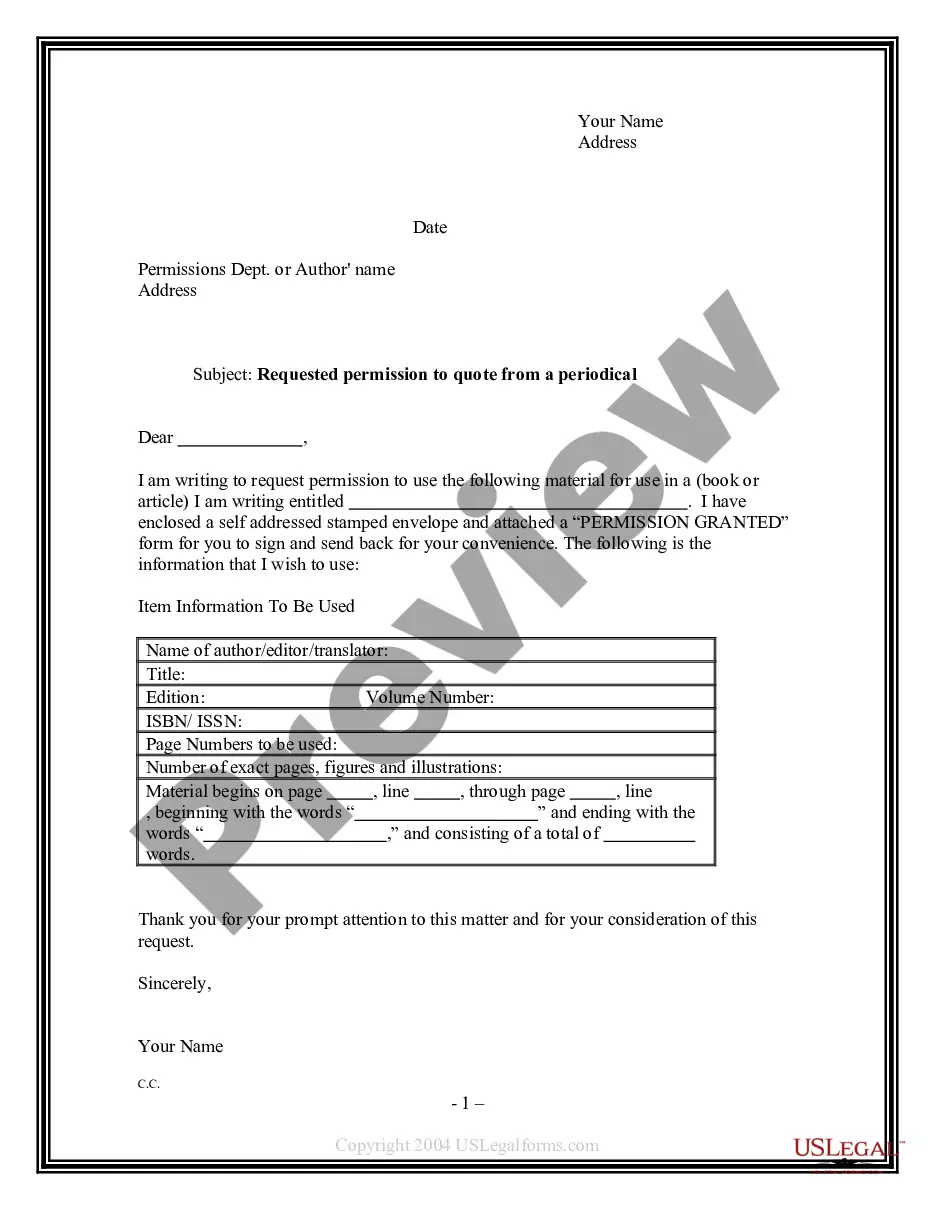
Alabama Requested Permission to Quote From a Periodical
Description
How to fill out Requested Permission To Quote From A Periodical?
US Legal Forms - one of the largest collections of legal documents in the United States - offers a range of legal document templates that you can download or create.
By using the website, you can access a vast array of forms for business and personal purposes, categorized by groups, states, or keywords. You can quickly obtain the latest versions of forms such as the Alabama Requested Permission to Quote From a Periodical.
If you have a monthly subscription, Log In and retrieve the Alabama Requested Permission to Quote From a Periodical from the US Legal Forms library. The Download option will be visible for every form you view. You have access to all previously downloaded forms in the My documents section of your account.
Make adjustments. Complete, modify, print, and sign the downloaded Alabama Requested Permission to Quote From a Periodical.
Every template you have added to your account has no expiration date and is permanently yours. Therefore, if you wish to download or print another copy, simply navigate to the My documents section and click on the form you desire. Access the Alabama Requested Permission to Quote From a Periodical with US Legal Forms, the largest library of legal document templates. Utilize a wide range of professional and state-specific templates that meet your business or personal needs.
- To use US Legal Forms for the first time, here are some simple instructions to help you get started.
- Ensure you have selected the correct form for your area/state. Click the Preview option to review the contents of the form. Check the form details to confirm you have chosen the right one.
- If the form does not meet your requirements, utilize the Search field at the top of the screen to find one that does.
- If you are satisfied with the form, confirm your selection by clicking the Buy now button. Then, choose your preferred pricing plan and provide your information to register for the account.
- Process the purchase. Use your credit card or PayPal account to complete the transaction.
- Select the format and download the form to your device.
Form popularity
FAQ
What is the amount and substantiality of the material used? The American Psychological Association allows authors to cite 400 words in single- text extracts, or 800 words in a series of text extracts, without permission (American Psychological Association, 2010).
To cite a newspaper article in MLA format, start by writing the author's last and first name, separated by a comma. Next, add the title of the article, ending with a period, and put the entire title in quotation marks. Then, include the name of the newspaper in italics and place a comma after it.
Step-by-Step Guide to Get Copyright PermissionsStep 1: Determine if you require permission to use or adapt the original work.Step 2: Identify the copyright holder.Step 3: Send a request to the owner for permission to use the work.Step 4: Cite the original work appropriately.
Quotes are considered intellectual property, which is protected under the law. This means that if you're not a quote's original author and you want to SELL something with the quote on it, one of two things must be true: 1. You have the author's written permission to use their words on your work.
There are no official limits to quotation length, though any quotations that are more than four lines should be formatted as a separate block quote. However, it is generally better to paraphrase the sources you cite rather than use direct quotations.
As a general guideline, if you're going to be quoting a lot of text, get permission. And if you're just quoting a single line but aren't certain it's okay to do it, get permission then too. You might think you don't need permission for short quotes from properly cited sources. But when in doubt, play it safe.
That means if you are using an author's exact phrasing or sequence of words to express an idea, then you need permission to cite more than what can be considered fair use. According to the fair-use rule, authors may make limited use of others' material without permission.
If you're seeking permission to quote from a book, look on the copyright page for the rights holder; it's usually the author. However, assuming the book is currently in print and on sale, normally you contact the publisher for permission. You can also try contacting the author or the author's literary agent or estate.
You DON'T need permission:To quote books or other works published before 1923. For news stories or scientific studies. Shorter quotes, references and paraphrasing is usually ok without permission. Copying large amounts of a story or study, however, may require permission from the writer or publisher.
Unfortunately, quoting or excerpting someone else's work falls into one of the grayest areas of copyright law. There is no legal rule stipulating what quantity is OK to use without seeking permission from the owner or creator of the material.