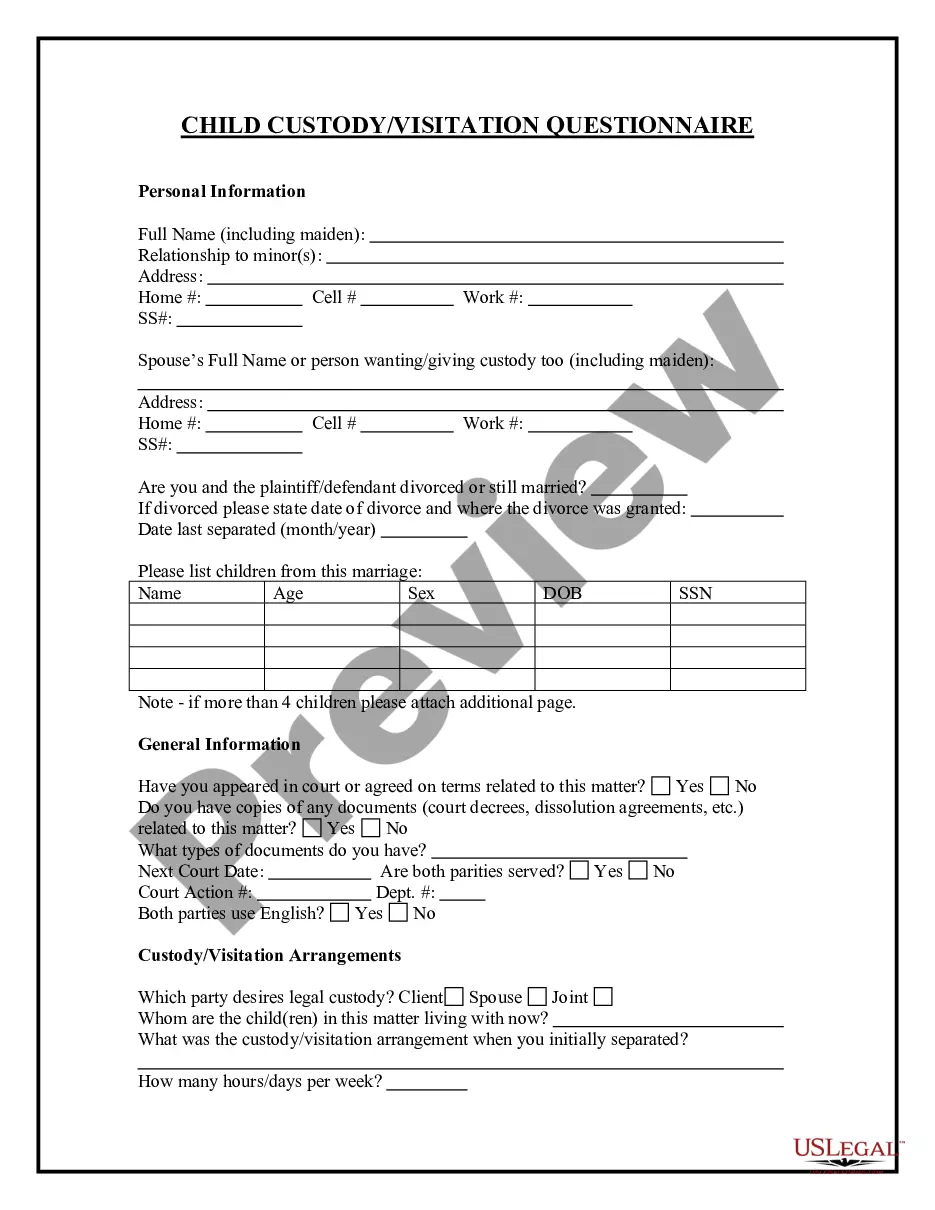
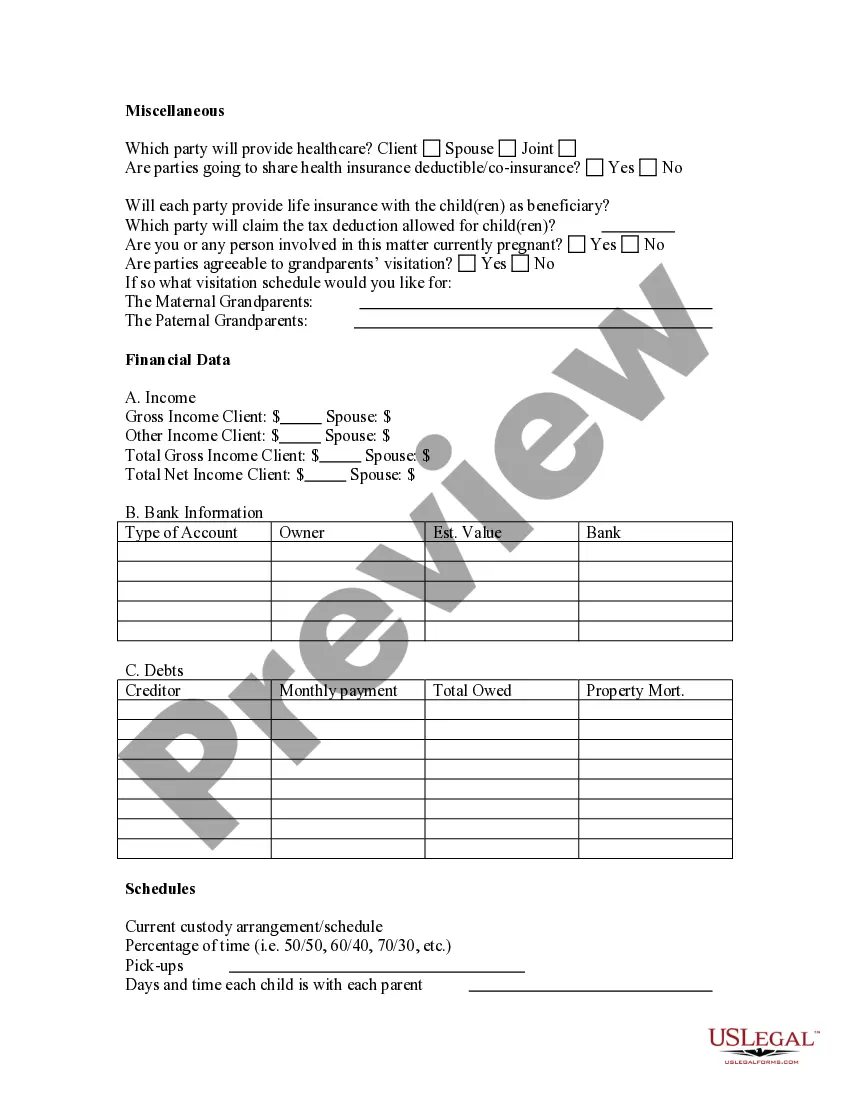
Child Custody And Order
Description
How to fill out Child Custody And Visitation Questionnaire?
It's clear that you cannot become a legal specialist instantly, nor can you swiftly learn how to assemble Child Custody And Order without possessing a specialized education.
Compiling legal documents is a lengthy endeavor necessitating particular training and expertise. So why not entrust the creation of the Child Custody And Order to the experts.
With US Legal Forms, one of the most extensive legal document repositories, you can discover anything from court forms to templates for office communications.
You can revisit your forms from the My documents tab at any time. If you are an existing client, you can simply Log In and find and download the template from the same tab.
Regardless of the purpose of your documentation—whether financial, legal, or personal—our platform has you supported. Give US Legal Forms a try now!
- Understand the document you require by utilizing the search feature at the top of the page.
- Examine it (if this feature is available) and review the accompanying description to ensure Child Custody And Order is what you need.
- Start your search again if you need any different template.
- Sign up for a complimentary account and select a subscription plan to acquire the form.
- Select Buy now. After the transaction is finalized, you can access the Child Custody And Order, complete it, print it, and deliver or send it to the necessary individuals or organizations.
Form popularity
FAQ
The new custody law in Missouri sets forth a rebuttable presumption that an award of equal, or nearly equal, parenting time is in the best interests of the child.
If there is clear evidence of potential harm or risk to the child, the court may order a father to completely stop seeing their children. Other options available to the court are: How long you can see them ? whether or not any overnight contact is awarded or the duration of the contact itself.
If your children are over 16, you should try and work out arrangements yourselves. A court won't usually make decisions about a child who's 16 or older. If you still can't agree and your children are under 16, you can go to court to sort out arrangements that you'll both have to stick to.
Fill in the C100 court form. You must show you've attended a meeting about mediation first - except in certain cases (there's been domestic abuse, for example) or when applying for a consent order. Send your original form and 3 copies of it to the nearest court that deals with cases involving children.
Most experts recommend that co-parents with toddlers use the 2-2-3 schedule. This schedule minimizes the time a toddler spends apart from either co-parent. In addition, this consistency provides the stability young children need and allows them to form meaningful relationships with both parents.