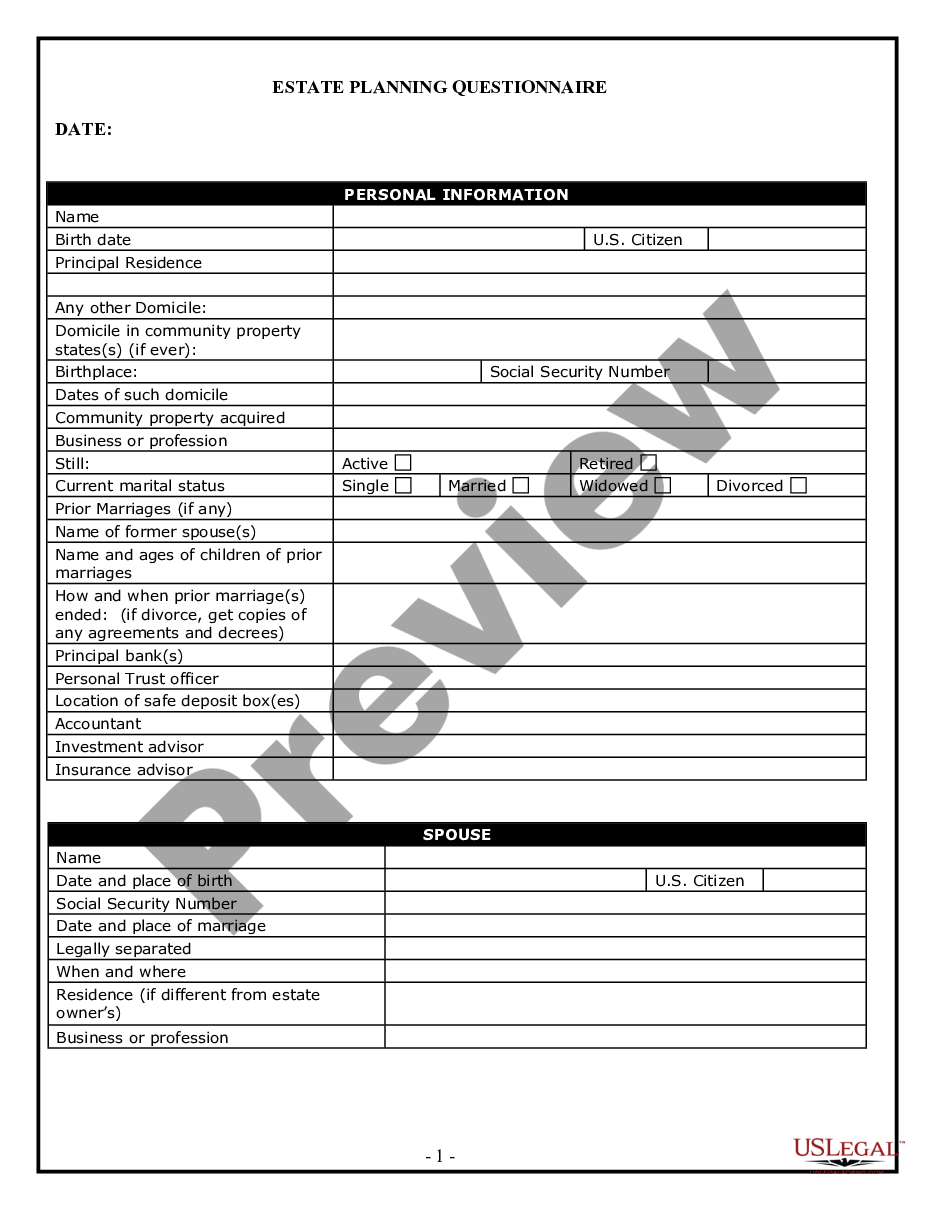
Contract Training For Non Lawyers In Allegheny
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Ten Top Law Schools College/UniversityInstitution TypeLocation Yale University Private, not-for-profit, 4-year New Haven, CT Stanford University Private, not-for-profit, 4-year Stanford, CA Columbia University Private, not-for-profit, 4-year New York, NY University of Chicago Private, not-for-profit, 4-year Chicago, IL6 more rows
The three major sources of contract law in the United States are the Common Law of Contracts, the Uniform Commercial Code (UCC), and case law. These sources provide legal frameworks for the creation and enforcement of contracts.
There are three essential components of any contract: the offer, the acceptance, and the consideration. If all three of these characteristics aren't present, a document is not considered a contract.
To be legally binding as a contract, a promise must be exchanged for adequate consideration. There are two different theories or definitions of consideration: Bargain Theory of Consideration and Benefit-Detriment theory of consideration.
At its core, social contract theory proposed that individuals give up the right to do anything they please in return for protection provided by government. Individuals surrender those rights they do not want others to use against them in order to enjoy the rest of their rights.
For a contract to be binding it needs to satisfy four principles, offer, acceptance, consideration, and the intention to create legal relations. Generally, the law believes that an agreement is made when one party makes an offer and the other party accepts it.
Contract law regulates the obligations established by agreement, whether express or implied, between private parties in the United States. The law of contracts varies from state to state; there is nationwide federal contract law in certain areas, such as contracts entered into pursuant to Federal Reclamation Law.
Understanding these seven essential elements of a contract — offer, acceptance, consideration, legally competent parties, meeting of the minds, terms of the contract, and legality of purpose — will help you check whether any agreement you enter into is a strong, legally binding contract.