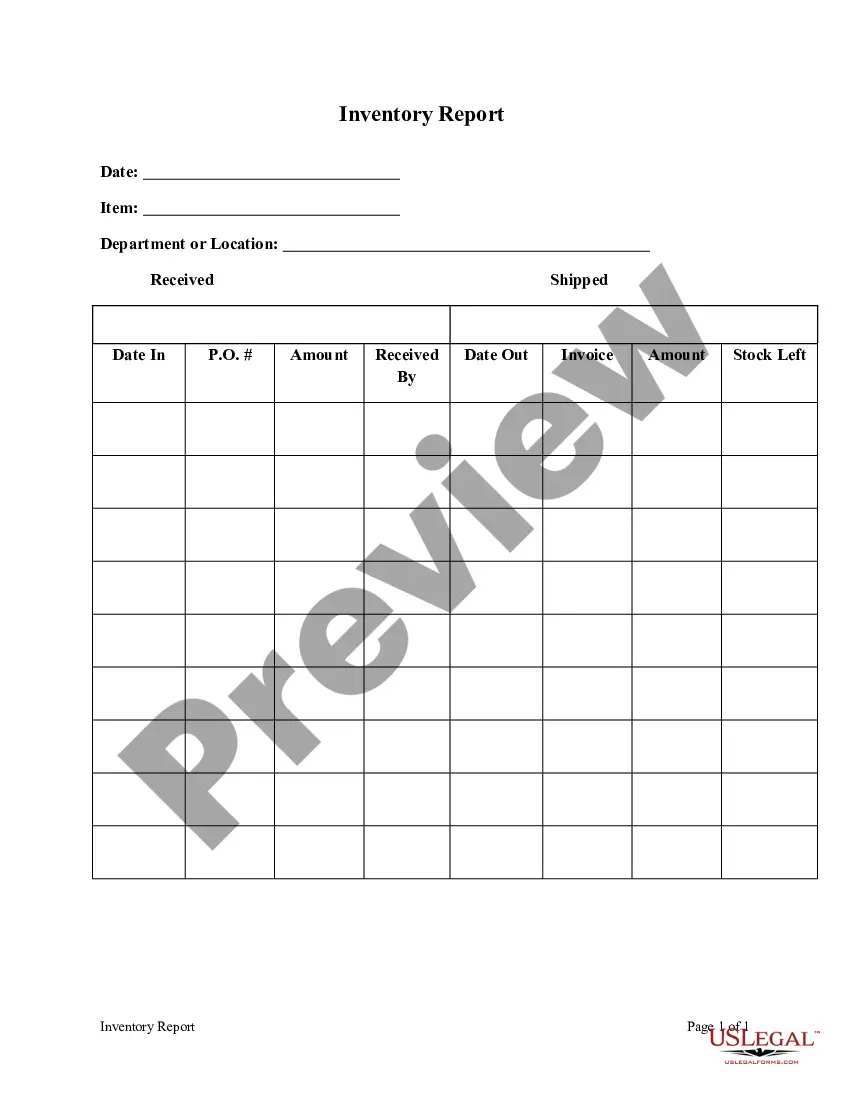
Contingency In Law Meaning In Allegheny
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
(a) "Contingency," as used in this subpart, means a possible future event or condition arising from presently known or unknown causes, the outcome of which is indeterminable at the present time.
Contingent means that an event may or may not occur in the future, depending on the fulfillment of some condition that is uncertain. This term is often used in contracts where the event will not take effect until the specified condition occurs.
Contingency refers to an event that may or may not occur in the future. In other words, it depends on fulfillment of a condition, which is uncertain or incidental.
Contingent adj 1 : likely but not certain to happen compare executory. 2 : intended for use in circumstances not completely foreseen a fund 3 : dependent on or conditioned by something else a claim a legacy on the marriage compare vested.
A contingency is an event you can't be sure will happen or not. The noun contingency describes something that might or might not happen. We use it to describe an event or situation that is a possible outcome but one that's impossible to predict with certainty.
Contingent means that an event may or may not occur in the future, depending on the fulfillment of some condition that is uncertain. This term is often used in contracts where the event will not take effect until the specified condition occurs.
A "contingent contract" is a contract to do or not to do something, if some event, collateral to such contract, does or does not happen.
The term "contingency" refers to the fact that the payment is dependent on the successful completion of the agreed-upon task, such as a court case or a business deal.
Contingency planning means preparing an organization to be ready to respond effectively in the event of an emergency. It is an important part of the IFRC's work supporting National Society preparedness.