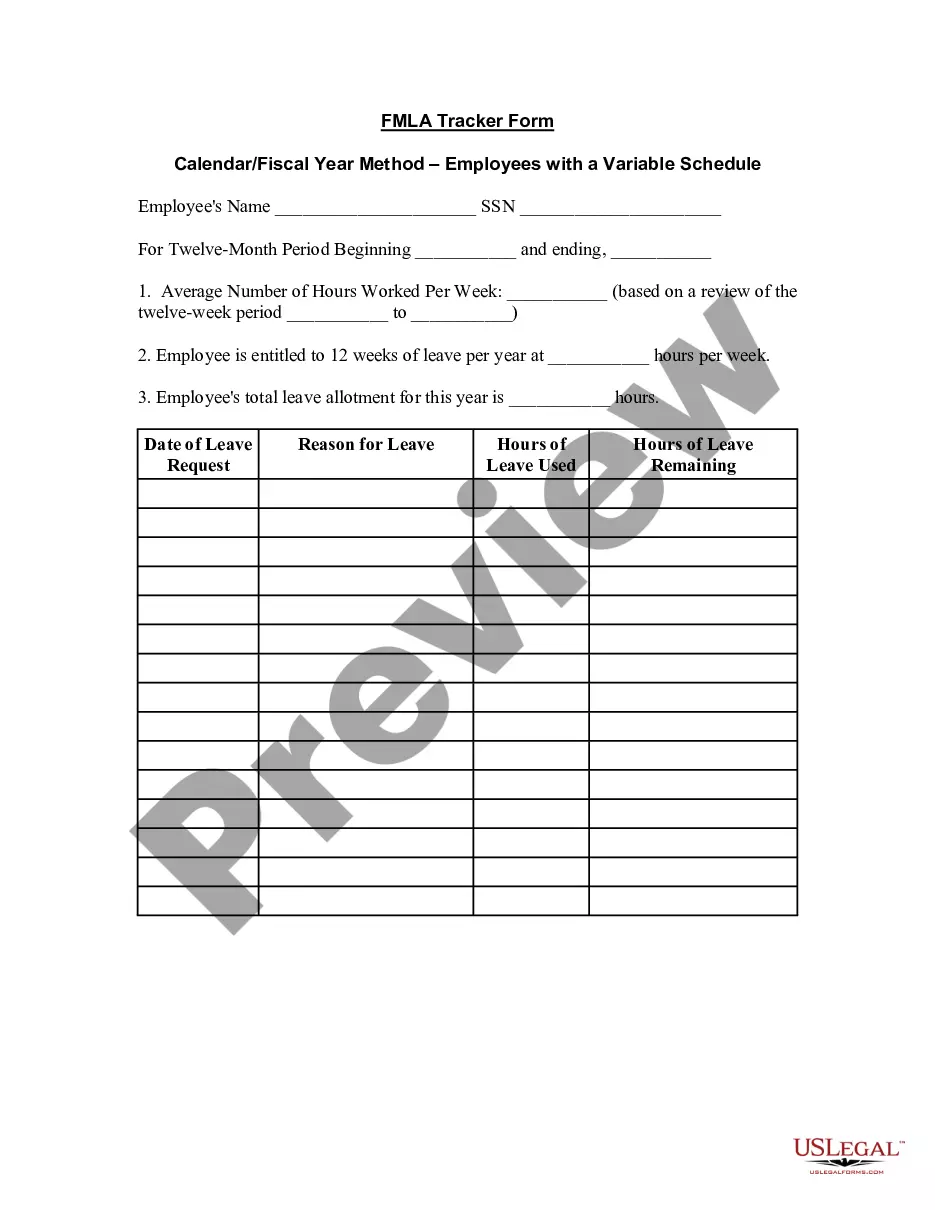
Settlement Against Estate Without Will In Cook
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Understanding the Deceased Estate 3-Year Rule The core premise of the 3-year rule is that if the deceased's estate is not claimed or administered within three years of their death, the state or governing body may step in and take control of the distribution and management of the assets.
Claims under the Inheritance Act must be made within 6 months of the date Probate was granted in the estate.
How long do creditors have to collect a debt from an estate? Creditors usually have six years from the date the debt became due to claim the debt. After this limitation period has expired, the creditor cannot take legal action to recover the debt in court, unless there are exceptional circumstances.
But what is the time limit for making an inheritance claim? Inheritance Act claims must be commenced within the limitation period, which is six months from the date of issue of the Grant of Probate or Letters of Administration.
Place a notice in The Gazette giving any creditors 2 months to claim anything they're owed. Do not distribute the estate's assets until the 2 months is up.
Steps to Become the Administrator of an Estate Without a Will Determine Your Eligibility. File a Petition with the Probate Court. Notify Heirs and Interested Parties. Attend the Probate Hearing. Obtain Letters of Administration. Identifying and Inventorying Assets. Paying Debts and Taxes. Distributing Assets.
Steps to Become the Administrator of an Estate Without a Will Determine Your Eligibility. File a Petition with the Probate Court. Notify Heirs and Interested Parties. Attend the Probate Hearing. Obtain Letters of Administration. Identifying and Inventorying Assets. Paying Debts and Taxes. Distributing Assets.
The decedent's property is given to the decedent's heirs during a probate court case. A decedent's relatives also get part of the estate. If someone is married and has no children, everything goes to the surviving spouse. If there is a spouse and two children, the spouse gets half of the assets of the estate.
When a person dies in Illinois, anyone who has a claim against a decedent's estate —whether it is a contract, tort, or statutory custodial claim—may file that claim with the estate representative or with the court.