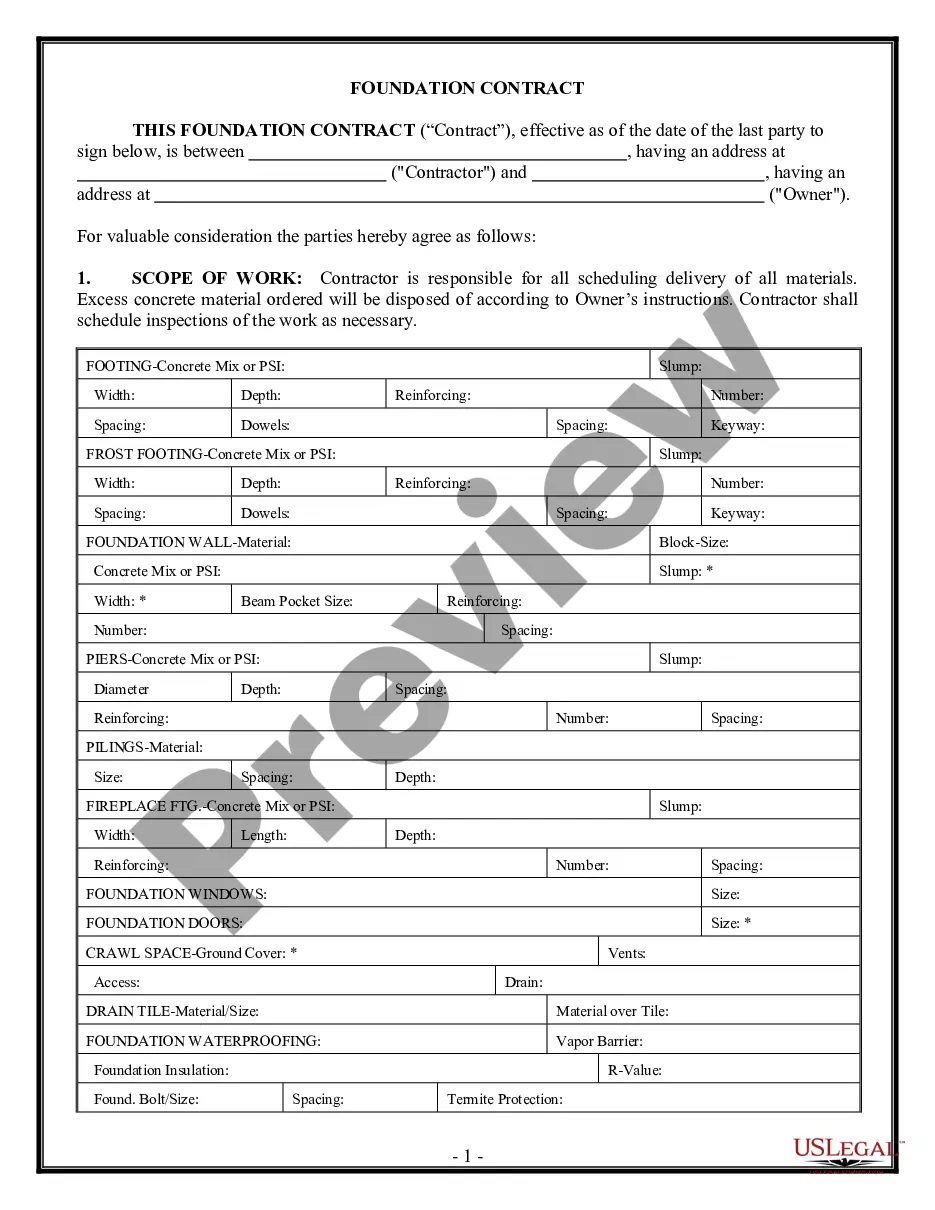
Libel With Actual Malice In Virginia
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Conversely, a defamatory statement is published with actual malice if, and only if, the publisher (1) knew that it was false when they published it or (2) exhibited a reckless disregard as to the truth or falsity of the statement when they published it.
The Vital Time Limit In defamation law, timing is crucial. Both libel and slander claims must be initiated within 12 months from the date of the statement's publication.
The Sullivan court stated that "actual malice" means that the defendant said the defamatory statement "with knowledge that it was false or with reckless disregard of whether it was false or not." The Sullivan court also held that when the standard is actual malice, the plaintiff must prove actual malice by " clear and ...
To be successful with defamation claims under Virginia Law, plaintiffs need to show the following elements: Factual assertion: The statement should be a claim of fact, not an opinion, a joke, or a hyperbole. False: It should be a false statement. It is not slander if the statement is the truth or substantially true.
Your reputation must suffer harm — The false and defamatory statement at issue must actually damage the reputation of the subject of the statement to support a lawsuit for defamation. The burden is on the plaintiff (the person bringing the lawsuit) to prove such damage — often a difficult task.
With the exception of punitive damages, there is no set limit on damages in Virginia defamation cases. Punitive damages are limited to $350,000. Easy or early settlements are rarer than you may expect. Cases resolved early are often heavily discounted.
Similarly, if the statement is true, it cannot be defamatory, even if it harms your reputation. In Virginia, you have one year from the date of publication of the defamatory statement to file a lawsuit for libel or slander. If you wait too long, you may lose your right to pursue legal action.