Defamation Without Naming In Florida
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
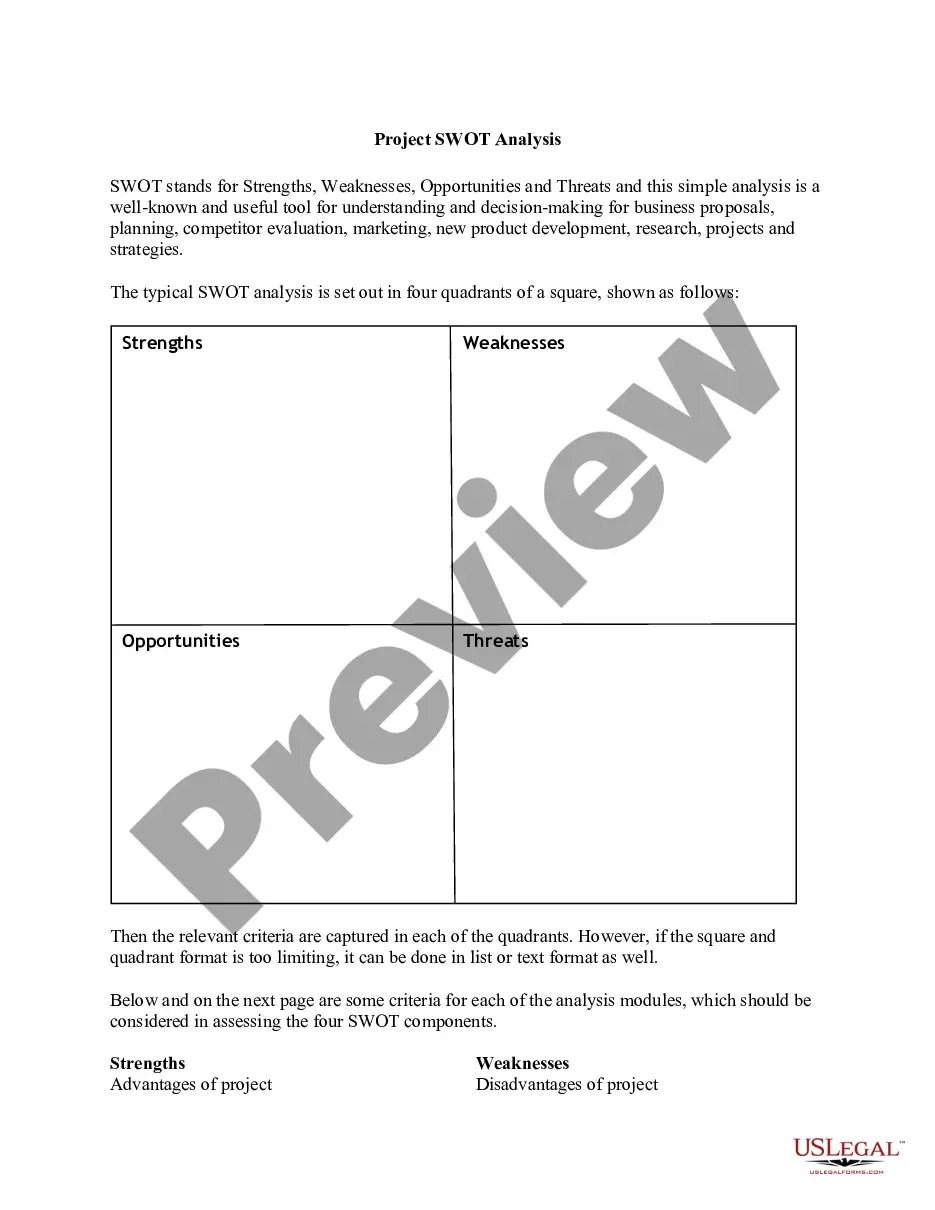
In general, pursuing a defamation lawsuit may be worthwhile if: The defamatory statement(s) are demonstrably false and have caused significant harm to your reputation or career. You have strong evidence to support your claim. The potential damages are substantial enough to justify the costs and risks of litigation.
Stat. § 768.73(1)(a) (2023).) As defamation per se inherently causes evident reputational harm, Florida law may award “presumed” damages in certain cases. These presumed damages are typically nominal, such as $1 or $100, and can be granted even if you can't prove specific economic or noneconomic losses.
Truth, or substantial truth, is a complete defense to a claim of defamation.
To prove defamation, a plaintiff generally must show: • A false statement purporting to be fact; • Publication or communication of that statement to a third person; • Fault amounting to at least negligence; and • Damages – that is, some harm caused to the plaintiff's reputation.
To prove defamation, a plaintiff generally must show: • A false statement purporting to be fact; • Publication or communication of that statement to a third person; • Fault amounting to at least negligence; and • Damages – that is, some harm caused to the plaintiff's reputation.
What is required to prove a case of defamation in Florida? To state a claim for defamation in Florida, a plaintiff must allege that (1) the defendant published or said a false statement; (2) about the plaintiff; (3) to a third party; and (4) the falsity of this statement caused injury to the plaintiff.
770.01 Notice condition precedent to action or prosecution for libel or slander. 770.02 Correction, apology, or retraction by newspaper or broadcast station.