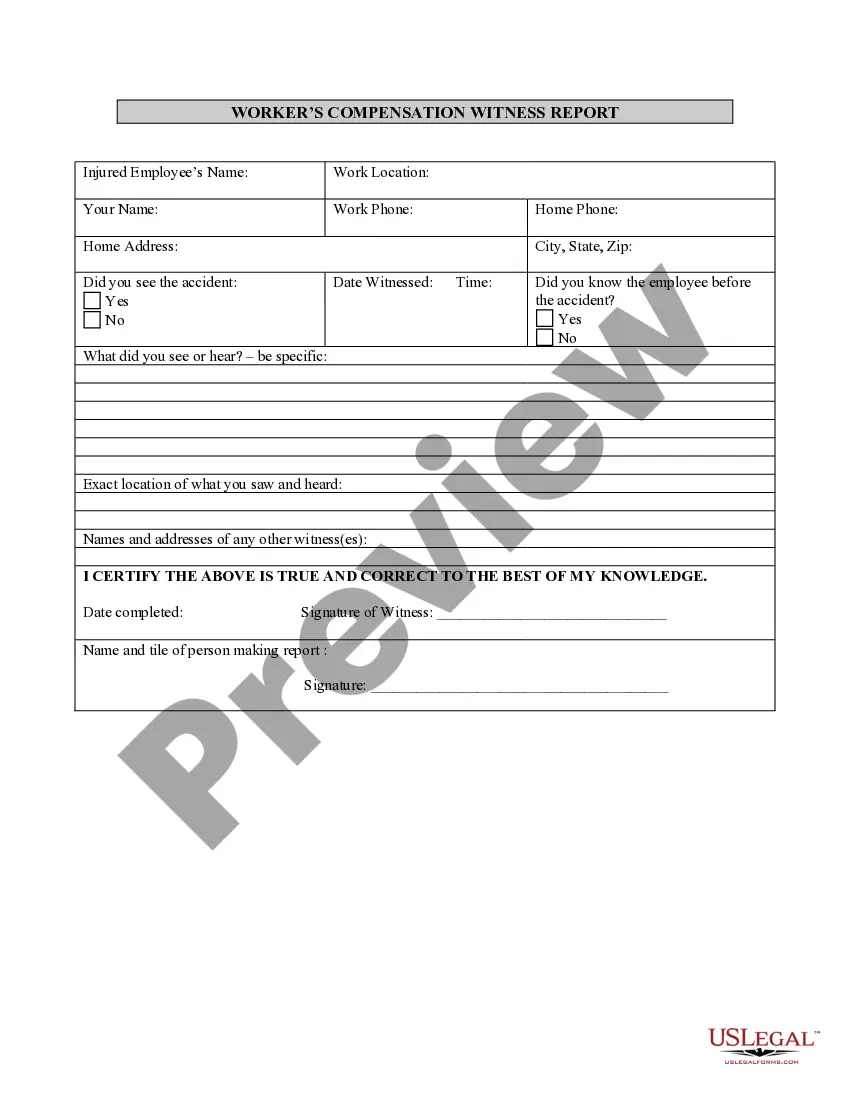
Joint Tenancy Definition With Right Of Survivorship In Virginia
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Joint tenants (JT), or joint tenants with rights of survivorship (JTWROS), are the forms of ownership most commonly used by married couples.
For instance, if you're married, the most common way to title your home is Tenancy by the Entirety (TBE).
Pro: Right of Survivorship. In Virginia, when a property is owned in joint tenancy or tenancy by the entirety, it belongs 100% to all or both people, so when one owner dies, there is still another person(s) left who owns 100% of the house or property.
Joint tenancy is most common among married couples because it helps property owners avoid probate. Without joint tenancy, a spouse would have to wait for their partner's Last Will to go through a legal review process—which can take months or even years.
Virginia recognizes the ability of two or more individuals to hold concurrent interests in a property. There are four types of co-ownership structures recognized under the Virginia law: (1) tenancy in common, (2) joint tenancy, (3) tenancy by entirety, and (4) coparcenary.
Utilizing a revocable trust is the best way for a married couple to take title. Titling property in your trust avoids probate upon the death of both the initial and surviving spouses and preserves the capital gains step up for the entire property on the first death.
To challenge the right of survivorship, the party contesting the right must file a lawsuit and prove their case in court with the help of a lawyer.
If all the joint owners of an asset intended that when one of them died their share would pass to the other joint owner(s), then this is a survivorship asset. This type of asset is always owned equally and the deceased's share of the asset passes to the other joint owner(s) by survivorship.
Community Property with Right of Survivorship For example, let's say that married couple Joe and Jane own a inium as community property with the Right of Survivorship. If Jane dies, Joe automatically becomes the sole owner of the condo without going through the probate process.