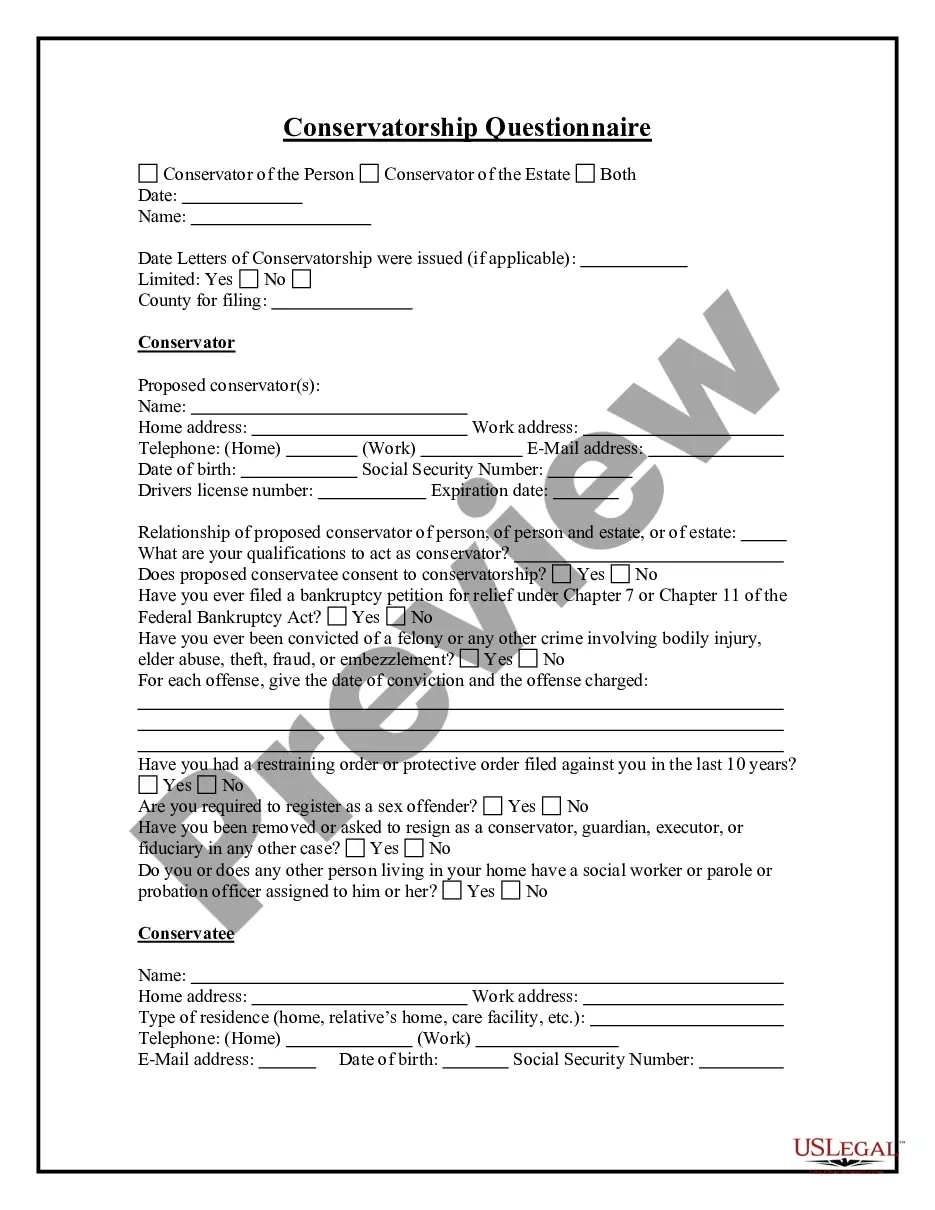
Covenant And Agreement In Chicago
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
The 2.5 miles radius would be reasonable. However, Illinois courts will not enforce a non-compete unless the employee received "something of value" in return. This is usually considered to be at least two years of employment or other benefits.
Thus, to be enforceable under Illinois law, an employee restrictive covenant must be (1) necessary to protect a legitimate business interest, (2) limited in terms of duration, geographic scope, and prohibited activity, (3) supported by sufficient consideration, and (4) ancillary to a valid employment agreement or sale ...
Illinois courts generally disfavor non-competes as a restraint of trade. However, Illinois courts enforce non-compete agreements if they are: ∎ Reasonable. ∎ Supported by adequate consideration.
Proving there was a breach of your employment contract is another way that you can defeat a non-compete agreement. If your employer did not fulfill the employment contract terms, they likely can't force you to stick to a non-compete agreement. This is known as a material breach.
Racially restrictive covenants and deed restrictions were legal instruments used to promote racial segregation in the first half of the twentieth century. They were first created and deployed by individuals, but then were embraced by real estate leaders and economists, who led national organizations based in Chicago.
It is possible to apply to the Lands Chamber of the Upper Tribunal to have a restrictive covenant “discharged or modified”, as the statute puts it, in order to get the covenant removed or changed so that development can take place or the use of the land can be changed.
My limited understanding is, restrictive covenants are only enforceable by a home owners association created among them. A local government isn't going to swoop in and enforce, or defend, a covenant that you created on your property. The local government is only concerned with land use ordinance's and state laws.
A covenant agreement is akin to a contractual agreement between parties. It often outlines terms and conditions where a party will perform a certain action or refrain from performing a certain action. Covenants are legally binding and enforceable.
Thus, to be enforceable under Illinois law, an employee restrictive covenant must be (1) necessary to protect a legitimate business interest, (2) limited in terms of duration, geographic scope, and prohibited activity, (3) supported by sufficient consideration, and (4) ancillary to a valid employment agreement or sale ...
From the early twentieth century, RRCs were used to prevent mostly African Americans (but also Hispanic/Latino Americans, Asian Americans, Jewish Americans, and Middle-easterners) from purchasing or living in homes located in white neighborhoods or subdivisions covered by the covenants.