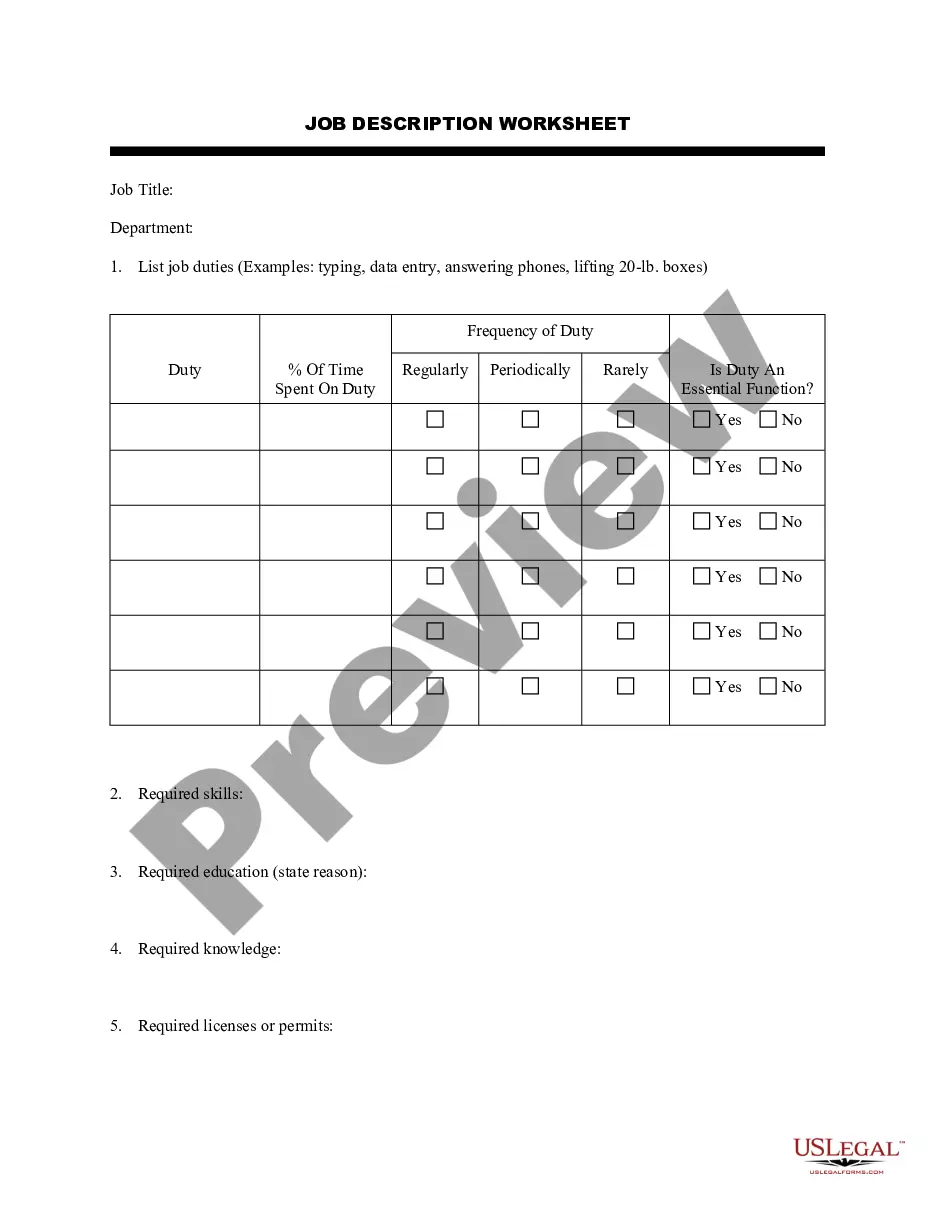
Authority Letter For Degree In Texas
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
You will need to contact your local department of education to find out their requirements for getting degree-granting privileges. You'll likely need to meet criteria such as meeting local standards for academic degrees, having sufficient funding to run your institution, and hiring qualified faculty.
Funding Overviews The state of Texas appropriates the majority of funds to state agencies and institutions of higher education through a biennial General Appropriations Act. The majority of those appropriations are allocated to institutions of higher education using funding formulas, which vary by sector.
Obtaining state authorization and licensing is a crucial step in establishing a university, but the process can be complex and time-consuming. The requirements and regulations vary significantly from state to state, and the timeline for approval depends on the type of programs you plan to offer.
Some states have specific nuances in their authorization processes. For example, in Texas, if you plan to offer degree programs, you must submit two separate applications to two different agencies: the Texas Workforce Commission (TWC) and the Texas Higher Education Coordinating Board (THECB).
The Steps to Starting a Private College Develop a clear vision and mission statement. Conduct market research. Obtain accreditation. Secure funding. Hire staff. Develop a curriculum. Market your college.
An application for registration, formerly called a certificate of authority, is filed by a foreign corporation, limited liability company, limited partnership, limited liability partnership, professional association, or other foreign entity as listed in section 9.001 of the Texas Business Organizations Code when the ...
These standards include: consideration of the school's goals and objectives; compliance with state and federal statutes; effective administration and governance; the teaching of a rigorous curriculum; hiring qualified instructional leaders with college degrees; student achievement; and quality of learning standards.