Accident With Trauma In Orange
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
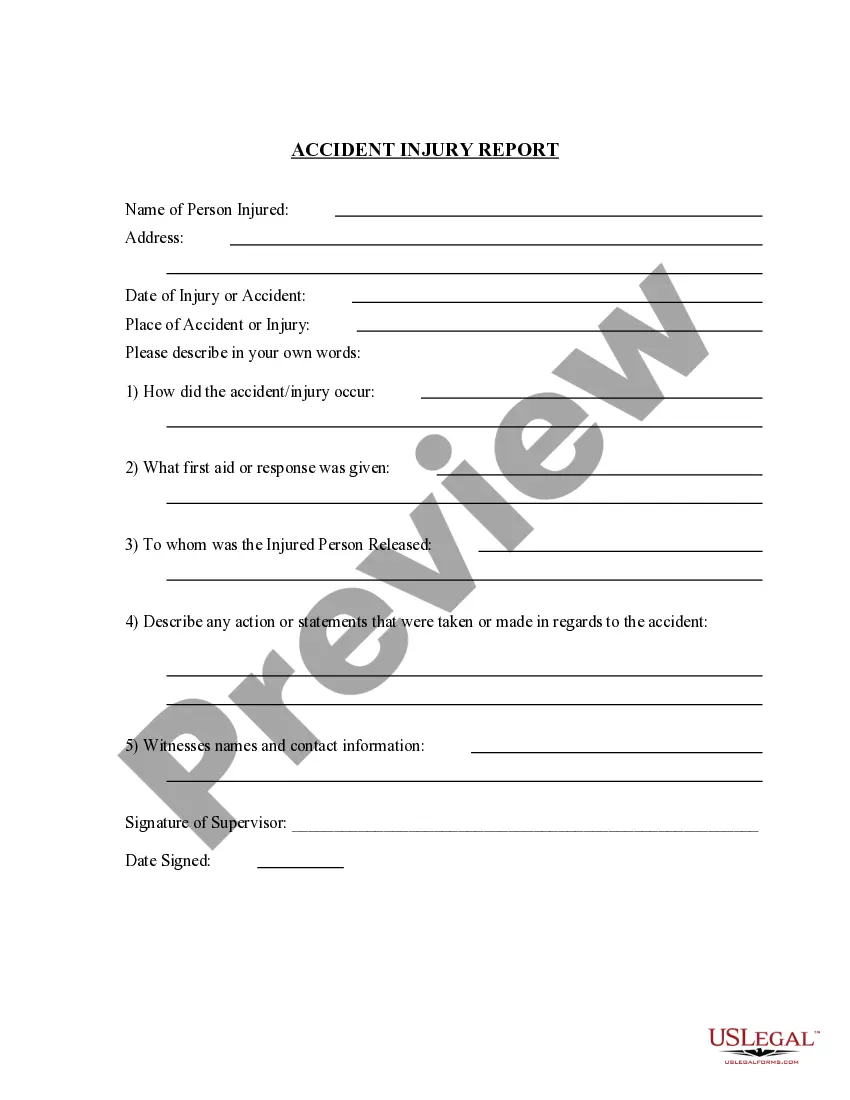
1. Basic Information Date and Time: When the accident occurred. 2. Parties Involved Driver Information: Name, address, phone number, driver's license number, and insurance details for each driver. 3. Witnesses 4. Accident Description 5. Law Enforcement 6. Additional Information 7. Conclusion 8. Attachments
Stick to the Facts Focus on the facts without adding opinions or assumptions. Describe what happened during the accident clearly and avoid discussing fault or other details. Never guess or estimate. If you don't know the answer to a question, admit that you don't know and move on.
These coping skills for trauma after a car crash can expedite the recovery process: Acknowledge Your Feelings. Talk About the Incident. Seek Professional Guidance. Stay Active. Practice Self-Care Techniques. Try Gradual Exposure.
“Incident (Accident) Investigations: A Guide for Employers” simplifies how to approach incident or accident investigations — providing helpful information on how to: Preserve and document the scene. Collect Data. Determine root causes. Implement corrective actions.
Acknowledge Your Feelings : It's important to recognize and accept your feelings of guilt. Understand that it's a natural response to a traumatic event. Reflect on the Situation : Try to analyze what happened. Were there factors beyond your control? Talk About It : Share your feelings with someone you trust.
Witnessing an accident can be traumatic for several reasons: Suddenness and Shock: Accidents often happen unexpectedly, leading to an immediate shock response. The brain may struggle to process the event in real time, which can heighten feelings of fear and confusion.
Provide your name, phone number, and address. If pressed for more, inform the adjuster of things like the date, time, and location. However, you are not required to discuss the nature of your injury, the treatment you received, and how the crash occurred.
Blunt force trauma frequently occurs in auto accidents. It is usually due to an impact with the steering wheel or other object within the vehicle and can cause damage to the head, lungs, abdomen and chest.
Absolutely. Report the severe PTSD to the insurance reps, get an official diagnosis and official treatment, and if you have to get an accident lawyer to do it, make sure all treatment, both physical and mental health, comes out of the insurance of the at fault person.
PTSD can develop immediately after the accident or even months or years later. Additionally, while some individuals find that their PTSD symptoms ease within a few days to a month, others might struggle with lasting effects that don't go away on their own and may need some help to work through.