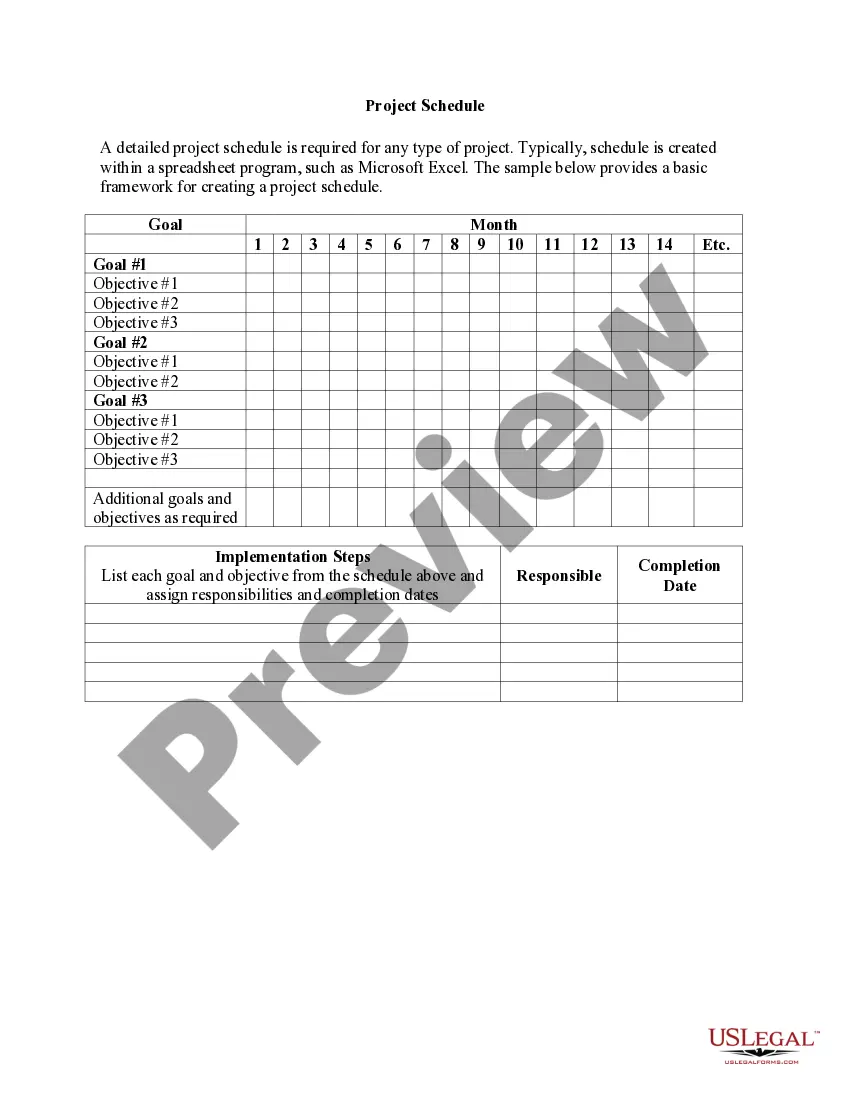
Sample Management Contract With Force Majeure In Collin
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Either Party shall be excused from performance and shall not be in default in respect of any obligation hereunder to the extent that the failure to perform such obligation is due to a Natural Force Majeure Event.
If force majeure continues to a point where performance would be radically different from that contemplated, the contract will be frustrated, and terminated, without recourse by either party.
Most clauses will provide that if the impact of the force majeure event is not lifted within a certain time, for example 6 or 12 months, then the parties will have the right to terminate the contract. The parties should also consider the knock-on effect on other provisions under the contract.
In contract law, force majeure (/ˌfɔːrs məˈʒɜːr/ FORSS mə-ZHUR; French: fɔʁs maʒœʁ) is a common clause in contracts which essentially frees both parties from liability or obligation when an extraordinary event or circumstance beyond the control of the parties, such as a war, strike, riot, crime, epidemic, or sudden ...
These may include earthquakes, floods, fire, plague, Acts of God (as defined in the contract or in applicable law) and other natural disasters. These are events which are not within the control of the Host Government.
Neither Party shall be liable for failure of or delay in performing obligations set forth in this Agreement, and neither shall be deemed in breach of its obligations, if such failure or delay is due to natural disasters or any causes beyond the 5 reasonable control of either Party.
Termination — In cases where the force majeure event is severe and long-lasting, the contract may allow for its termination, meaning the parties are released from their obligations entirely because the event has made it impossible or impractical to continue with the contract.
Contract end by performance. A contract can end when the parties have done all that the contract requires of them. Contract end by agreement. A contract can end when both parties agree to end it before the work is complete. Contract end by frustration. Contract end for convenience. Contract end due to a breach.
What is an example of a force majeure event? Typical force majeure events include natural disasters (fire, storms, floods), governmental or societal actions (war, invasion, civil unrest, labor strikes), and infrastructure failures (transportation, energy).
If a contract is silent on force majeure or if the event does not meet the definition of force majeure under the parties' contract, a party's performance may still be excused in certain circumstances under the doctrine of commercial impracticability.