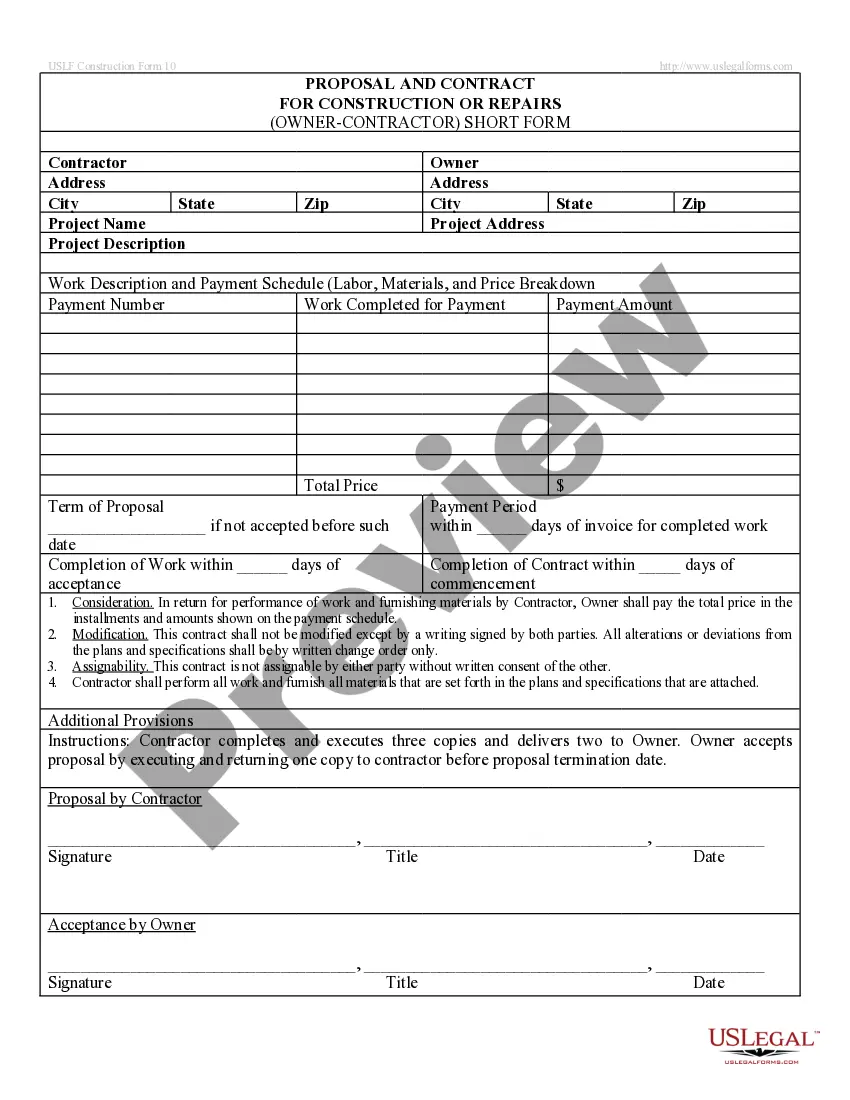
Loan Payoff Letter Example Format In Contra Costa
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Fill out the Summons (form SUM-100) and a Complaint. Also, fill out a Civil Case Cover Sheet (form CM-010). Since you are the one filing a lawsuit, you're called the plaintiff. The person or company you're suing is the defendant.
To file or defend a case in small claims court, you must be (a) at least 18 years old or legally emancipated, and (b) mentally competent. A person must be represented by a Guardian ad Litem if he or she is under 18 and not legally emancipated, or has been declared mentally incompetent by a court.
The Small Claims Hearing When submitting evidence, you must complete form LASC CIV 278 and use LASC CIV 279 mailing labels. You will have to provide proof that the other parties were sent copies of your evidence. You can get this from the Post Office at the time you mail these forms.
Start a case Form NameForm NumberGuide Plaintiff's Claim and Order to Go to Small Claims Court SC-100 Fill out forms to start a small claims case Other Plaintiffs or Defendants (Attachment to Plaintiff's Claim and ORDER to Go to Small Claims Court) SC-100A Fictitious Business Name (Small Claims) SC-103 3 more rows
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) Type your letter. Concisely review the main facts. Be polite. Write with your goal in mind. Ask for exactly what you want. Set a deadline. End the letter by stating you will promptly pursue legal remedies if the other party does not meet your demand. Make and keep copies.
A letter of intent to sue is used to notify an individual or business that legal action may be taken against them if the demands included in the letter are not met. By sending an intent to sue letter, you may be able to resolve the dispute without having to initiate a costly lawsuit.
In California, you're typically required to send a small claims demand letter to the defendant before filing a small claims case.
A letter of intent is a document outlining the intentions of two or more parties to do business together; it is often non-binding unless the language in the document specifies that the companies are legally bound to the terms.
Despite its preliminary nature, under certain circumstances, an LOI can be binding. If the document includes all the elements of a contract—offer, acceptance, and consideration—it might legally hold the parties to its terms.