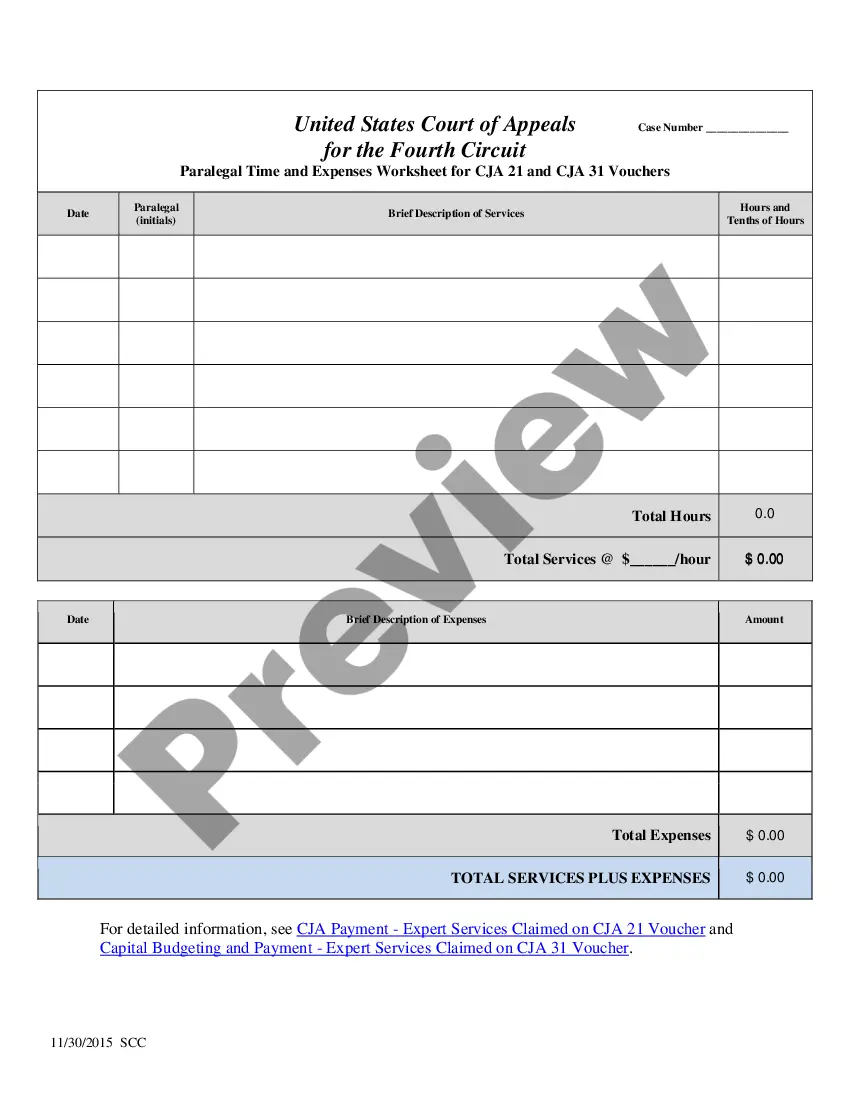
Indenture For Land In Travis
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
In real estate, an indenture is a deed in which two parties agree to continuing obligations. For example, one party may agree to maintain a property and the other may agree to make payments on it.
Real Estate Indenture An indenture is a deed that establishes ongoing responsibilities between two parties in real estate.
The Indenture pledges certain revenues as security for repayment of the Bonds. The Trustee agrees to act on behalf of the holders of the Bonds and to represent their interests.
In real estate, an indenture is a deed in which two parties agree to continuing obligations. For example, one party may agree to maintain a property and the other may agree to make payments on it.
An indenture is a particular formal contract or deed made between two or more parties. Beginning in medieval England, an indenture can be defined as a specific agreement within a contract noted with a specific duration or significance.
Real Estate Indenture An indenture is a deed that establishes ongoing responsibilities between two parties in real estate.
A contract between an Issuer and a Trustee (normally a commercial bank with trust powers) under which the Issuer issues Bonds and specifies their Maturities, Interest Rates, Redemption provisions, form, exchange provisions, security and other terms.
The term is used for any kind of deed executed by more than one party, in contrast to a deed poll which is made by one individual. In the case of bonds, the indenture shows the pledge, promises, representations and covenants of the issuing party.
The indenture typically: (1) clearly describes and defines the issued debt securities; (2) specifies the rights of the parties, including the duties of the trustee as a third-party administrator; (3) sets forth the borrower's obligation to make payments; and (4) outlines the remedies available to the noteholders if the ...