Law On Construction 2014 In Wake
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Construction law Construction (Design and Management) Regulations 2015. Control of Substances Hazardous to Health Regulations (COSHH) 2002. Health and Safety (Consultation with Employees) Regulations 1996. Health and Safety at Work etc Act 1974. Lifting Operations and Lifting Equipment Regulations (LOLER) 1998.
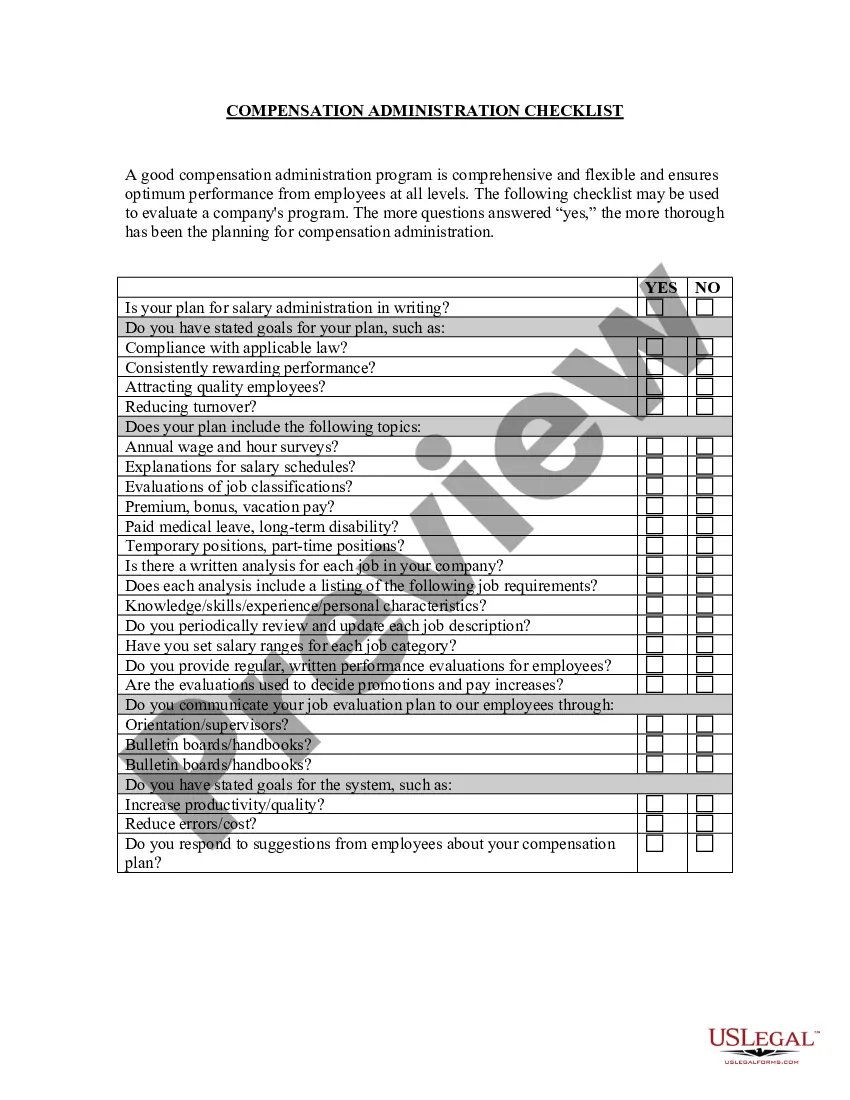
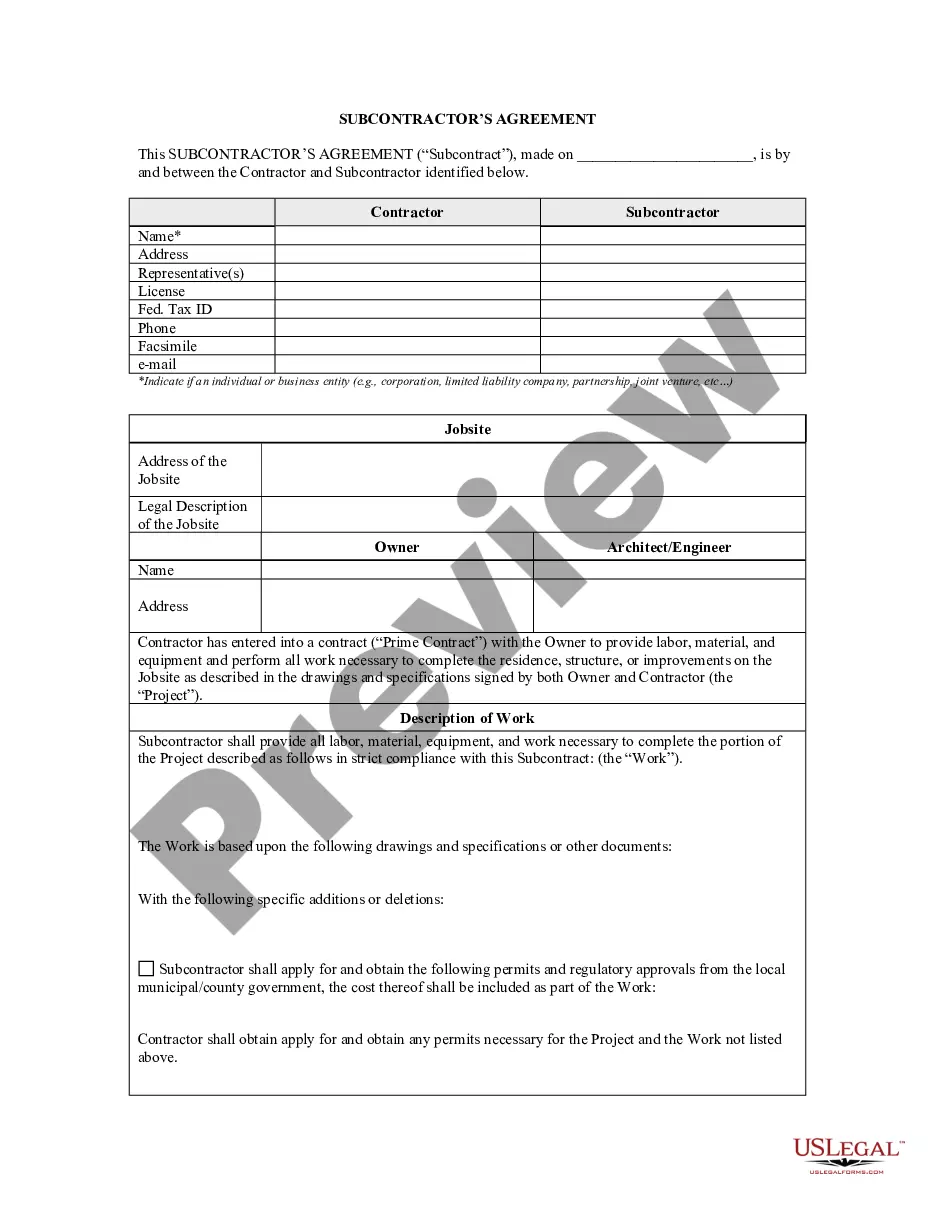
The area of construction law deals with matters such as infrastructure, housing, planning permissions and construction and engineering. The key to understanding construction law is that it has two main categories: non-contentious and contentious. Below is a brief overview of construction law and its branches.
Effective July 1, 2024, contractors will be required to certify Workers' Compensation classification codes when renewing their licenses. The requirement ensures proper Workers' Comp coverage and accurate worker classification. Review your current classifications to be sure you comply with the law.
The provisions of this chapter shall govern the conduct of all construction or demolition operations with regard to the safety of the public and property. For regulations relating to the safety of persons employed in construction or demolition operations, OSHA standards shall apply.
The Building Act 1984 is the primary legislation. Its stated purpose is to “secure the health, safety, welfare and convenience of persons in or about buildings and of others who may be affected by buildings or matters connected with buildings”.
Monthly construction output is estimated to have fallen by 0.4% in volume terms in October 2024; this follows an increase of 0.1% in September 2024. The decrease in monthly output came solely from a fall in repair and maintenance (1.3%) as new work grew by 0.2%.
Definition: A rule or principle that is accepted as fundamental. It is also known as the canon of construction. Example: When interpreting a law, the rule of construction is to give effect to the intention of the legislature.
A rule of construction is used to interpret a document in order to determine how its provisions operate as a whole to bring about the purpose of those who drafted it.
Here are the basic steps towards becoming a lawyer specializing in construction law. Step 1: Complete a Bachelor's Law Degree. Step 2: Take the LSAT. Step 3: Join an ABA-Approved Law School. Step 4: Intern at a Firm. Step 5: Earn Your Juris Doctor Degree. Step 6: Sit and Pass the Bar Exam.