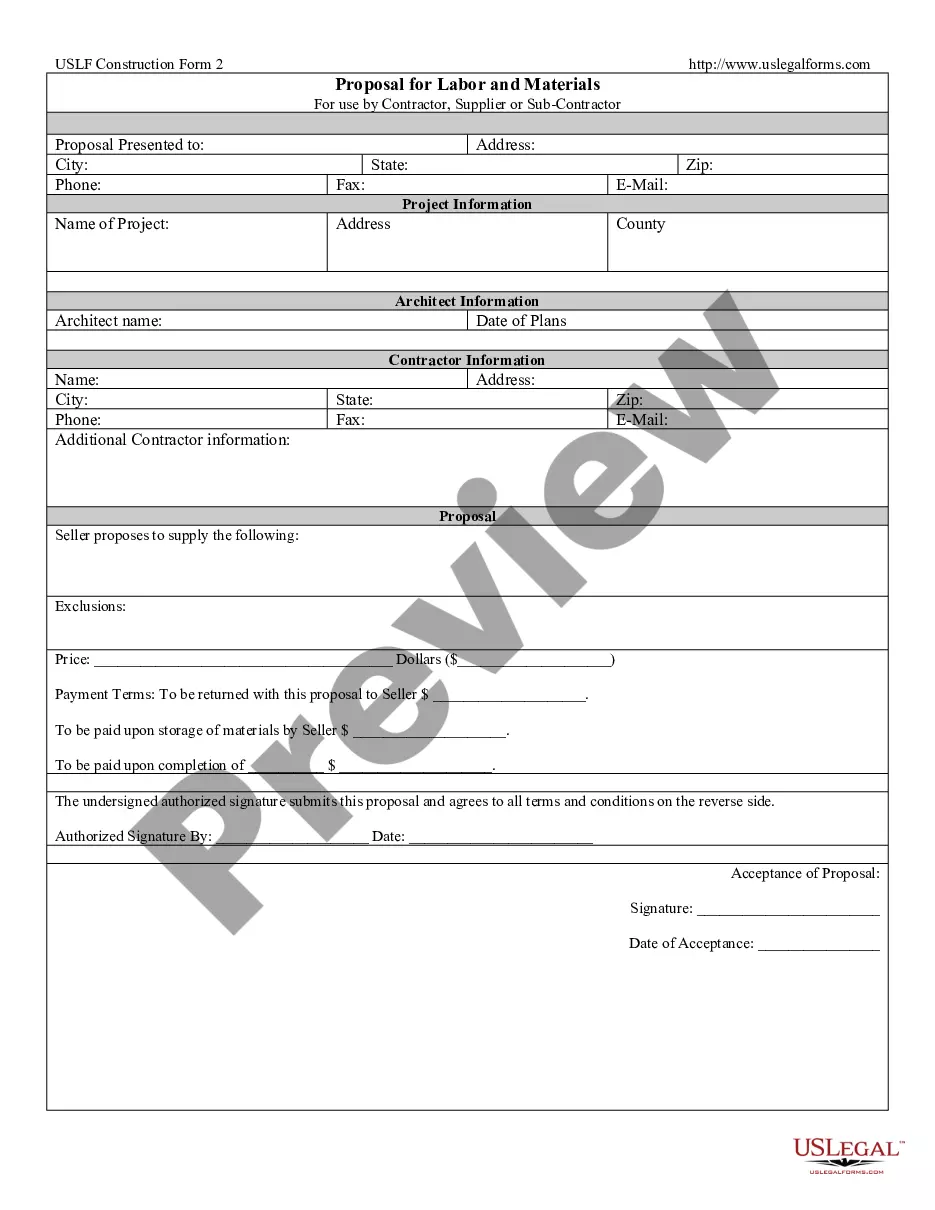
Law Book Rules In Wake
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Law in action is a legal theory, associated with legal realism, that examines the role of law, not just as it exists in the statutes and cases, but as it is actually applied in society.
The law collection currently consists of more than one million titles comprising over 2.9 million volumes, and over 3 million microform items, which can be located by searching the online catalog.
The law on the books approach to criminal justice emphasizes that during the preliminary hearing the judge decides whether there is probable cause not hold the defendant, while the law in action perspective emphasizes that in most jurisdictions there i s a strong probability that the case will proceed.
"Law in books" refers to laws and legal doctrine contained in bound volumes, such as reporters. Roscoe Pound introduced the term in 1910 in contrast to “law in action” to illustrate the difference between how laws appear in text and their real-life application.
Law-in-books describes all written-down laws, regulations and written legal customs. Contrary to legal writing in law, treaties, statues and cases, law-in-action is a legal theory that examines the role of law how it is actually applied and practiced in society.
As a result of this discrepancy between the individualism of law and the collectivism of the people, Pound tried to convince his readers, “a struggle is in progress between society and the common law.” 32 He famously contrasted the divergence between “the law in action,” reflecting “popular thought and feeling,” and “ ...
Legal Treatises, Hornbooks, and Nutshells: Legal treatises, hornbooks, and nutshells provide overviews of individual legal topics, such as contracts, criminal law and criminal procedure, civil procedure, torts, property, taxation, and other subject areas.
The United States Code is the Code of Laws of the United States of America (also referred to as Code of Laws of the United States, United States Code, U.S. Code, or U.S.C.) and is a compilation and codification of all the general and permanent Federal laws of the United States.
The Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) is an annual codification of the general and permanent rules of the executive departments and agencies of the Federal Government published by the Office of the Federal Register (OFR) in the National Archives and Records Administration (NARA) in the Federal Register.
U.S. Code (U.S.C.) This code set consists of multiple volumes of the federal laws.