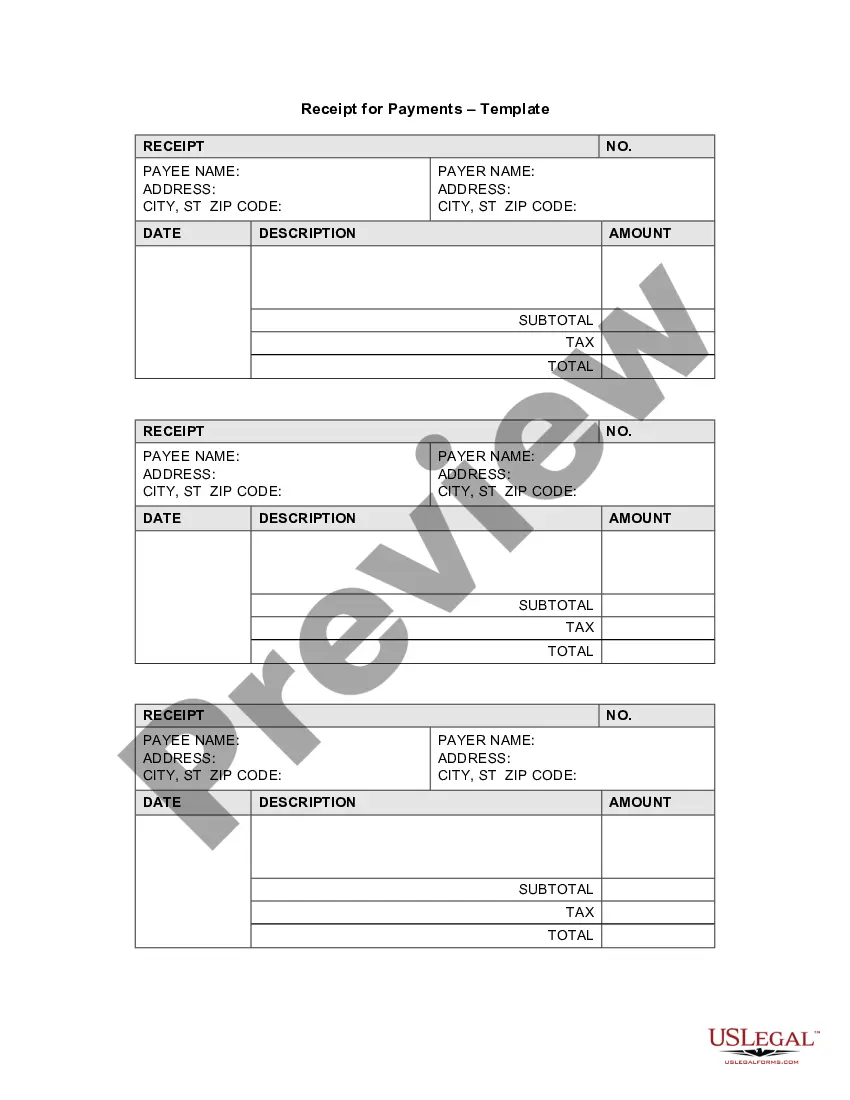
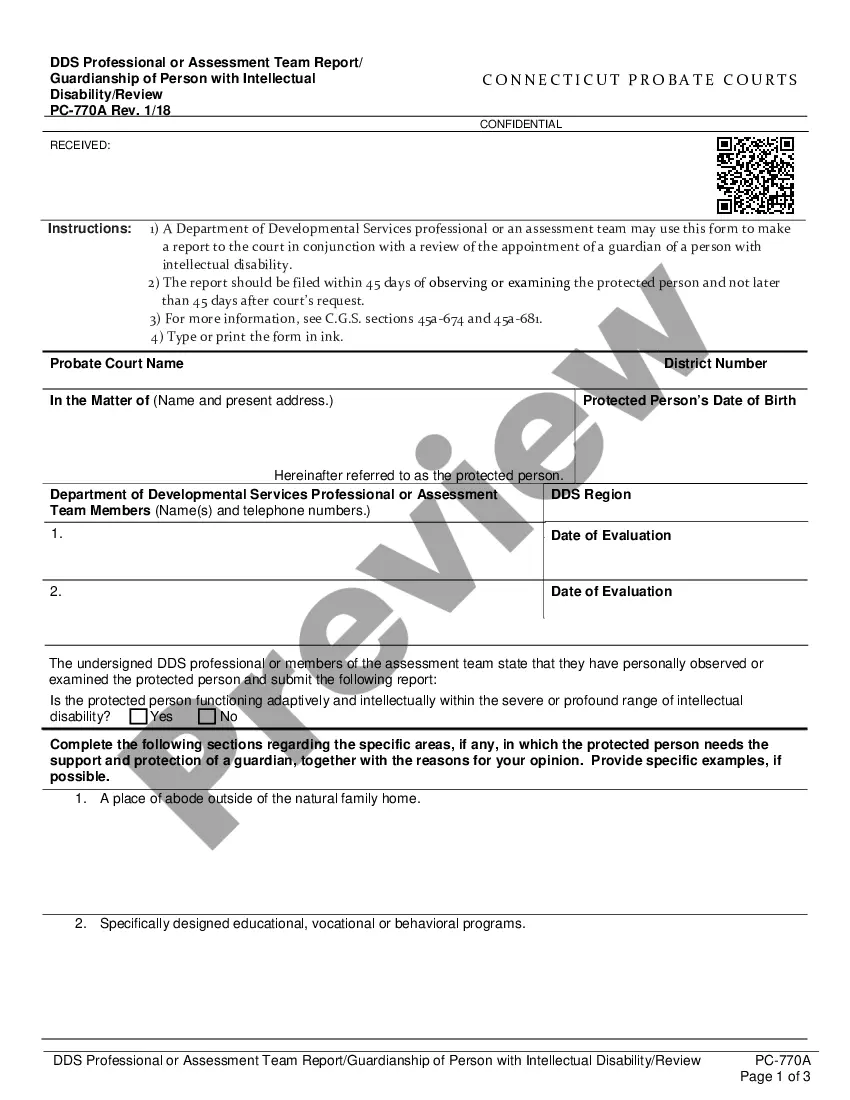
The parties have entered into an agreement whereby one party has been retained to manage and operate a certain business. Other provisions of the agreement.
All Business Purchase Formula In Franklin
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
The Revenue Multiple Method This rule attaches a value to several types of businesses based on their annual revenue or sales. The revenue multiple used often falls between 0.5 to 5 times yearly revenue depending on the industry.
Let's look at an example. You already know that when the entrepreneurs ask for their desired investment, they've placed a value on their company. For example, asking $100,000 for a 10% stake in the company implies a $1 million valuation ($100k/10% = $1M).
To accurately ascertain a business's value efficiently, calculate its total liabilities and subtract that figure from the sum of all assets—the resulting number is known as book value. This approach to calculating company worth takes into account both existing assets and any outstanding liabilities.
A less sophisticated but still popular way to determine a company's potential value quickly is to multiply the current sales or revenue of a company by a multiple "score." For example, a company with $200K in annual sales and a multiple of 5 would be worth $1 million.
To calculate book value, start by subtracting the company's liabilities from its assets to determine owners' equity. Then, exclude any intangible assets. The figure you're left with represents the value of any tangible assets the company owns.
Current Value = (Asset Value) / (1 – Debt Ratio) To quickly value a business, find its total liabilities and subtract them from the total assets. This will give you an idea of its book value. This formula estimates the worth of a business by looking at its assets and subtracting any liabilities.
To find the fair market value, it is then necessary to divide that figure by the capitalization rate. Therefore, the income approach would reveal the following calculations. Projected sales are $500,000, and the capitalization rate is 25%, so the fair market value is $125,000.
Current Value = (Asset Value) / (1 – Debt Ratio) To quickly value a business, find its total liabilities and subtract them from the total assets. This will give you an idea of its book value. This formula estimates the worth of a business by looking at its assets and subtracting any liabilities.
Add up the value of everything the business owns, including all equipment and inventory. Subtract any debts or liabilities. The value of the business's balance sheet is at least a starting point for determining the business's worth. But the business is probably worth a lot more than its net assets.