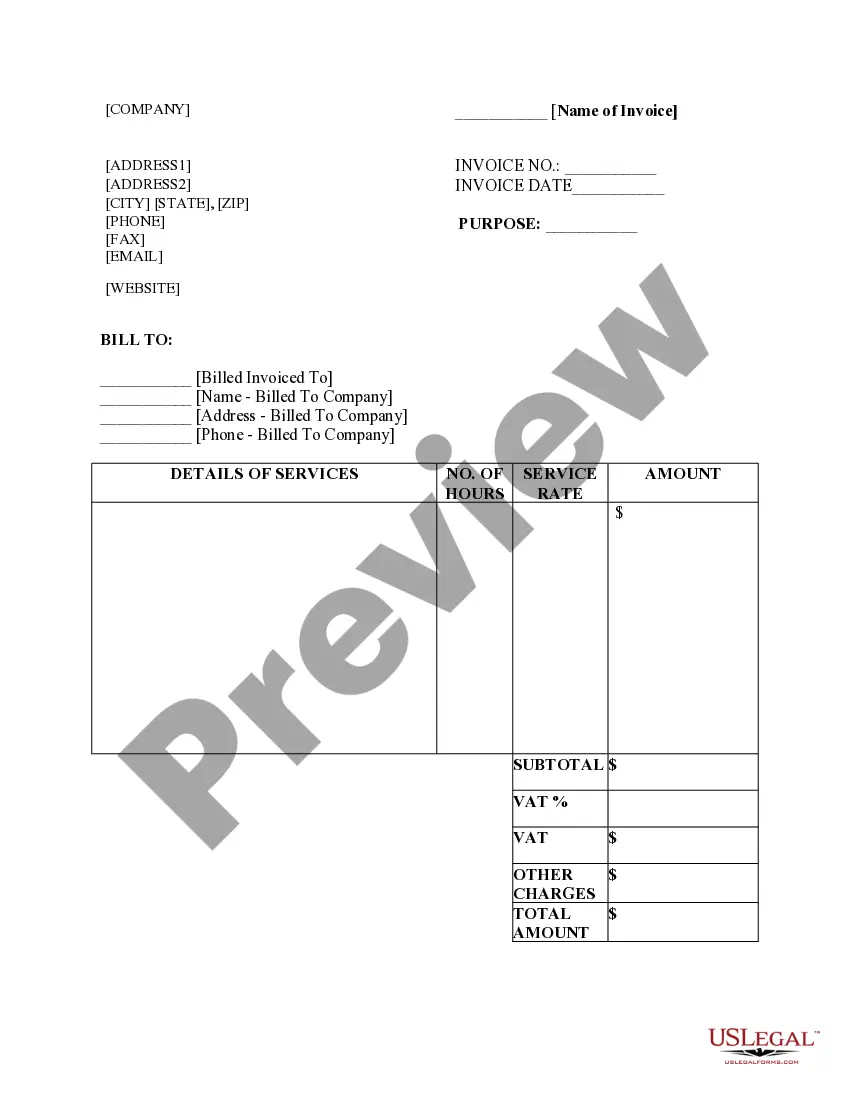
Agreement Receivable Statement With Join In King
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
The aging calculation would place Invoice A in the 0–30 days category, Invoice B in the 31–60 days category, and Invoice C in the 61–90 days category. The report would reflect these categorizations and sum the amounts for each category for a total of $1,000 owed in 0–30, $2,000 owed in 31–60, and $3,000 owed in 61–90.
An accounts receivable aging report is an accounting document that gives the business an overview of its outstanding payments from customers and how long they are past due.
An account receivable is recorded as a debit in the assets section of a balance sheet. It is typically a short-term asset—short-term because normally it's going to be realized within a year.”
Accounts receivable aging is the process of distinguishing open accounts receivables based on the length of time an invoice has been outstanding. Accounts receivable aging is useful in determining the allowance for doubtful accounts.
Aging accounts receivable involves categorizing outstanding invoices into time buckets, such as current, 1-30 days overdue, 31-60 days overdue, and so on. For example, an invoice due on March 1st that remains unpaid by April 1st would fall into the 31-60 days overdue category.