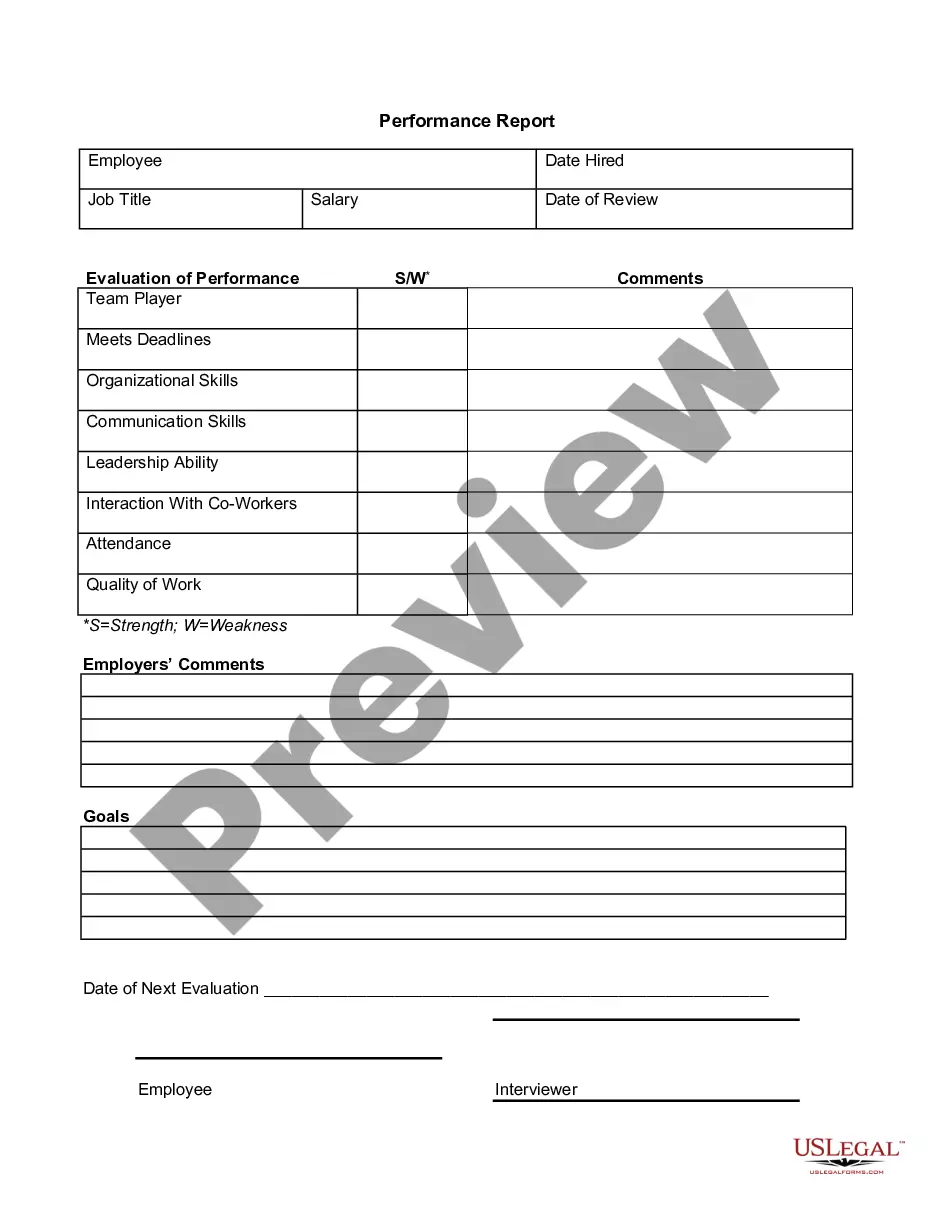
Arrest Without Probable Cause In Utah
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
“The right of the people to be secure in their persons, houses, papers, and effects, against unreasonable searches and seizures, shall not be violated, and no Warrants shall issue, but upon probable cause, supported by Oath or affirmation, and particularly describing the place to be searched, and the persons or things ...
The four elements of an arrest are the intent to arrest, authority to arrest, subjection to arrest and the understanding by the person arrested that an arrest has occured.
Probable Cause is a standard that is required for warrants, and is listed in the Fourth Amendment of the United States Constitution. It has also become standard to arrest a person without a warrant in most cases. If an officer has probable cause to believe that a person has committed a felony, the officer may arrest.
(a)(2) The arresting officer, custodial authority, or prosecutor with authority over the most serious offense for which defendant was arrested must, as soon as reasonably feasible but in no event longer than 24 hours after the arrest, present to a magistrate a sworn statement that contains the facts known to support ...
There are four categories into which evidence may fall in establishing probable cause. These include observational, circumstantial, expertise, and information: Observational evidence is based on what the officer sees, smells, or hears.
The presentation of any of these facts would allow an officer to perform a search and make an arrest. Be aware that minor traffic violations (e.g. speeding, broken tail-light, or expired registration) are not considered probable cause.
One instance where a lack of Probable Cause may arise is in prosecutions for Driving Under the Influence pursuant to California Vehicle Code Section 23152(a) VC and California Vehicle Code Section 23152(b) VC. Law enforcement is always on heightened alert for impaired drivers, especially at certain times and locations.
A search incident to arrest may only be conducted when two (2) requirements have been met. First, there must have been a lawful custodial arrest. At a minimum, this requires that (1) probable cause exist to believe that the arrestee has committed a crime and (2) an arrest is actually made.