Investor Term Sheet Template For Business Partnership In Orange
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
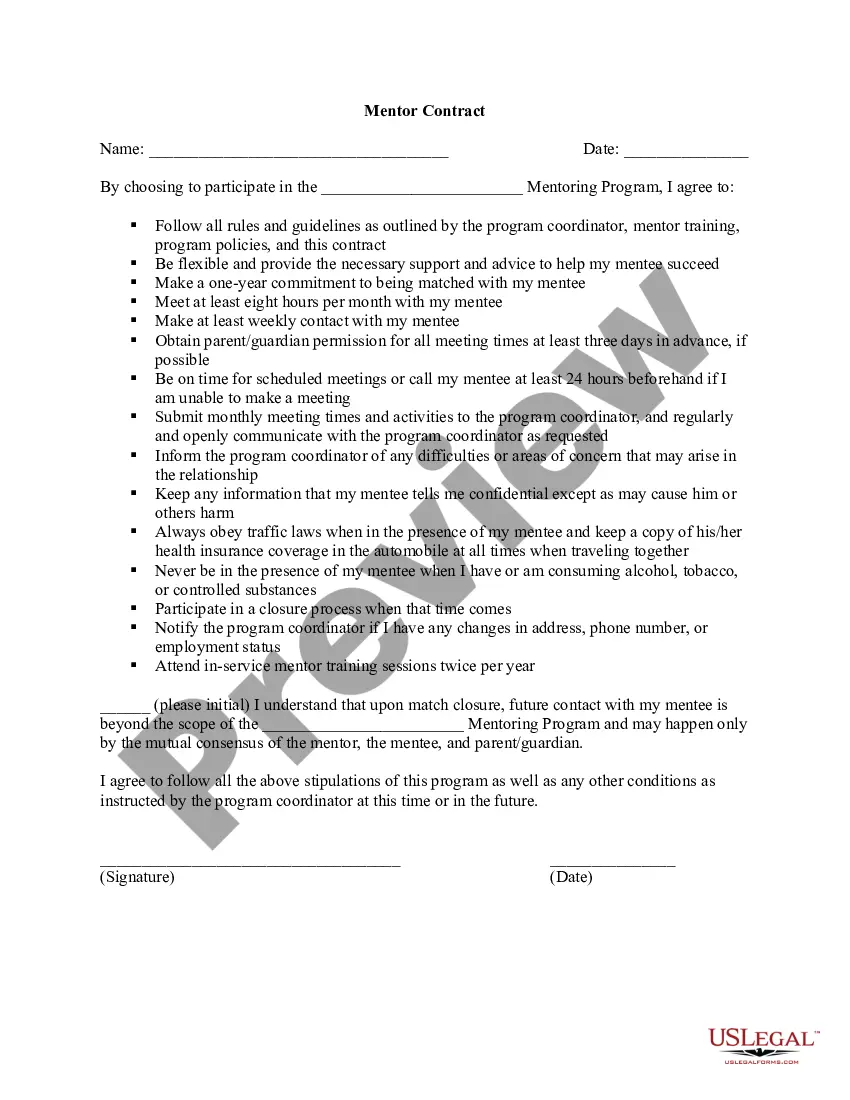
6 Tips for Writing a Term Sheet List the terms. Summarize the terms. Explain the dividends. Include liquidation preference. Include voting agreement and closing items. Read, edit and prepare for signatures.
CohnReznick's Beth Mullen looks at several important points in a deal term sheet. Credit delivery amount and timing. Guarantees. Reserves. Year 15 exit options. Implied costs for third-party reports.
A term sheet is a nonbinding bullet-point document that outlines the material terms and conditions of a potential business agreement. The purpose of a term sheet is to outline the terms upon which the venture debt provider is willing to make the investment. It's important to note that these terms are negotiable.
Under a standard four-year time-based vesting schedule with a one-year cliff, 1/4 of your shares vest after one year. After the cliff, 1/36 of the remaining granted shares (or 1/48 of the original grant) vest each month until the four-year vesting period is over.
A partnership term sheet is a non-binding agreement that outlines the key terms and conditions of a business partnership.
In as little as 500 words, a VC's term sheet lays out the financial terms of the investment, how much your startup will be worth, who will control it and who will profit the most if the company is sold or goes public. The term sheet is akin to a letter of intent.
For seed round investments, investors often provide a term sheet when offering their private investment. For loans, lending institution will often provide a term sheet to prospective borrowers.
“Term sheets”, “letters of intent”, “memoranda of understanding” and “agreements in principle” may constitute an enforceable agreement if the writing includes all the essential terms of an agreement. This is so even if “the parties intended to negotiate a 'fuller agreement'”.