At-will Employment Example In Tarrant
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
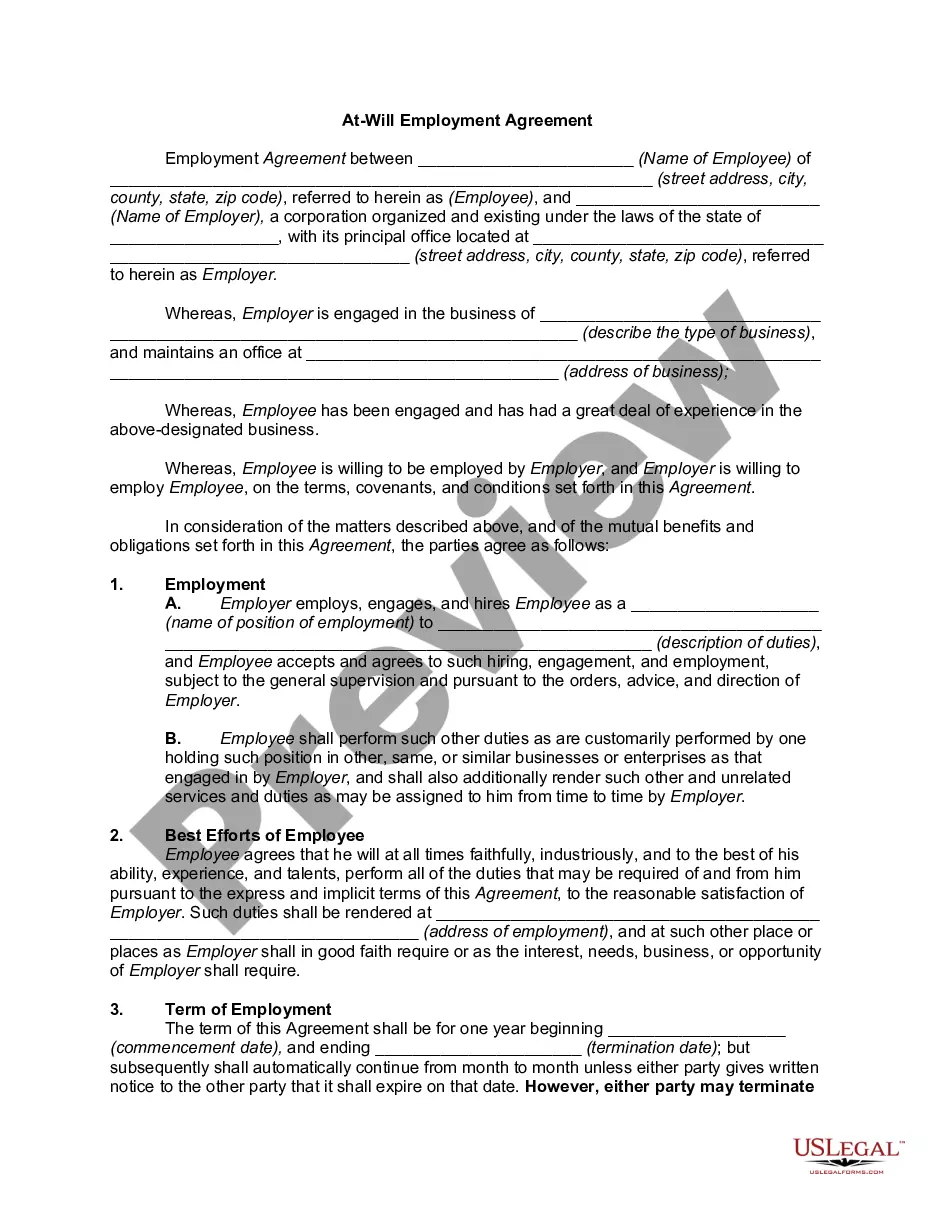
At-will employment simply means that the relationship between employer and employee can be terminated at any time, by either party, for any reason. An employer can fire an employee without giving a reason and, likewise, the employee can quit for any reason or no reason at all.
The basic rule of Texas employment law is employment at will, which applies to all phases of the employment relationship - it means that absent a statute or an express agreement (such as an employment contract) to the contrary, either party in an employment relationship may modify any of the terms or conditions of ...
To protect yourself and make sure you're doing right by your team, it's best to know the circumstances when you can't terminate at-will employees. Federal law states two main exceptions to at-will employment, which are discrimination and retaliation.
What is an “At-Will” Employment State? Since 1888, Texas has been an at-will employment state. As an at-will state, employment in Texas may be terminated by an employer or an employee for a good reason, a bad reason, or simply no reason at all, absent a specific agreement to the contrary.
For example, an employer might be in a bad mood one day, and decide to fire a random at-will employee. There is nothing inherently unlawful about doing that (even if it was an unwise business decision). As such, the fired employee probably cannot claim that they were wrongfully terminated.
At-will employment simply means that the relationship between employer and employee can be terminated at any time, by either party, for any reason. An employer can fire an employee without giving a reason and, likewise, the employee can quit for any reason or no reason at all.
While at-will employment offers freedom and flexibility, it also carries potential drawbacks such as instability and insecurity. However, with the right legal counsel, it's possible to navigate these challenges and ensure one's rights are respected.
There are five main exceptions to at-will employment in California: public policy, implied contracts, discrimination and/or retaliation, and fraud and/or misrepresentation.
Over the years, courts have carved out exceptions to the at-will presumption to mitigate its sometimes harsh consequences. The three major common law exceptions are public policy, implied contract, and implied covenant of good faith.
Executive and the Company acknowledge that this employment relationship may be terminated at any time, upon written acknowledgment that this employment relationship may be terminated at any time, upon written notice to the other party, with or without good cause or for any or no cause, at the option either of the ...