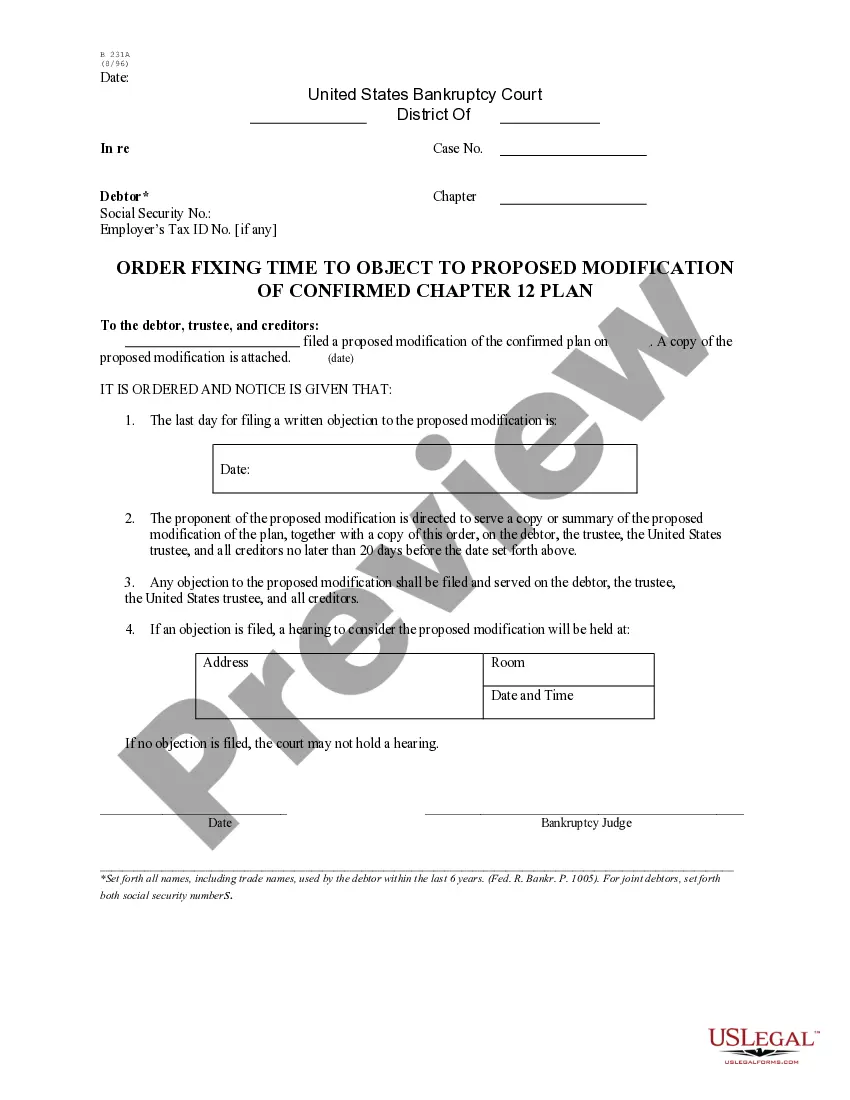
West Virginia Order Fixing Time to Object to Proposed Modification of Confirmed Chapter 13 Plan - B 231B
Description
How to fill out Order Fixing Time To Object To Proposed Modification Of Confirmed Chapter 13 Plan - B 231B?
Are you in a place that you require documents for possibly company or specific functions just about every day time? There are a variety of legitimate papers themes accessible on the Internet, but discovering kinds you can rely on isn`t easy. US Legal Forms provides a large number of form themes, such as the West Virginia Order Fixing Time to Object to Proposed Modification of Confirmed Chapter 13 Plan - B 231B, which are composed to fulfill state and federal demands.
Should you be currently familiar with US Legal Forms internet site and get a free account, basically log in. Next, you can obtain the West Virginia Order Fixing Time to Object to Proposed Modification of Confirmed Chapter 13 Plan - B 231B design.
Should you not come with an profile and wish to begin to use US Legal Forms, follow these steps:
- Obtain the form you will need and make sure it is for your proper metropolis/region.
- Make use of the Review button to analyze the shape.
- Browse the description to ensure that you have chosen the correct form.
- In case the form isn`t what you are looking for, take advantage of the Lookup area to find the form that meets your requirements and demands.
- When you find the proper form, just click Purchase now.
- Pick the rates plan you would like, complete the necessary details to create your money, and pay for the transaction making use of your PayPal or credit card.
- Pick a convenient paper structure and obtain your version.
Discover every one of the papers themes you have bought in the My Forms food list. You can get a further version of West Virginia Order Fixing Time to Object to Proposed Modification of Confirmed Chapter 13 Plan - B 231B whenever, if needed. Just click on the needed form to obtain or print the papers design.
Use US Legal Forms, by far the most comprehensive variety of legitimate varieties, in order to save time as well as steer clear of faults. The services provides skillfully manufactured legitimate papers themes that can be used for a variety of functions. Create a free account on US Legal Forms and initiate generating your life easier.
Form popularity
FAQ
If it isn't possible to resolve your financial emergency (for example, you lost your job, or your employer permanently reduced your pay), you might be able to reduce your payments by asking the court to modify the amounts paid through your repayment plan. Options if You Can't Make Your Chapter 13 Plan Payments | Nolo nolo.com ? legal-encyclopedia ? options-ca... nolo.com ? legal-encyclopedia ? options-ca...
Modification after confirmation. The court and the trustee will ask you to explain why you need to change your plan payments and provide proof of your changed circumstances (such as a job loss or a reduction in income). If satisfied, the court will order a new plan payment for the duration of your case.
To obtain a plan moratorium or modification, you must file a motion, either on your own or through counsel, with the bankruptcy court. You also must give notice of the motion to the Chapter 13 trustee, creditors, and other parties in interest in ance with the local rules for the district where you live.
A motion to modify a confirmed Chapter 13 plan (also called a motion to amend confirmed plan) is filed typically by the debtor, but these motions can also be filed by the trustee or a creditor with an allowed, unsecured proof of claim. 11 U.S.C. § 1329. Motion to Modify Chapter 13 Confirmed Plan U.S. Bankruptcy Court Middle District of Florida (.gov) ? Procedure ? M... U.S. Bankruptcy Court Middle District of Florida (.gov) ? Procedure ? M... PDF
Modification after confirmation. The court and the trustee will ask you to explain why you need to change your plan payments and provide proof of your changed circumstances (such as a job loss or a reduction in income). If satisfied, the court will order a new plan payment for the duration of your case. Modifying Your Chapter 13 Plan Payment | Nolo Nolo ? legal-encyclopedia ? modifyi... Nolo ? legal-encyclopedia ? modifyi...
The chapter 13 trustee may file an objection to the confirmation of an amended plan no later than fourteen (14) days from the date the amended plan is filed or five (5) days before the date set for the first confirmation hearing, whichever is earlier. (e) First Chapter 13 Confirmation Hearings.
Any Chapter 13 debtor who receives an objection to confirmation should first take a deep breath and relax. Then, they should pick up the phone and call their bankruptcy attorney and ask for an explanation of the objections. In the vast majority of cases, the objections can easily be fixed.
Adding debt to Chapter 13 is possible. However, it requires a motion to the court and approval from the judge overseeing the case. It is important to remember that you can only add debts incurred after you filed bankruptcy. The court won't include all creditors. Can You Add Debt to Chapter 13? - Law Offices of Robert M. Geller, P.A. attorneyfortampabay.com ? blog ? can-you-... attorneyfortampabay.com ? blog ? can-you-...