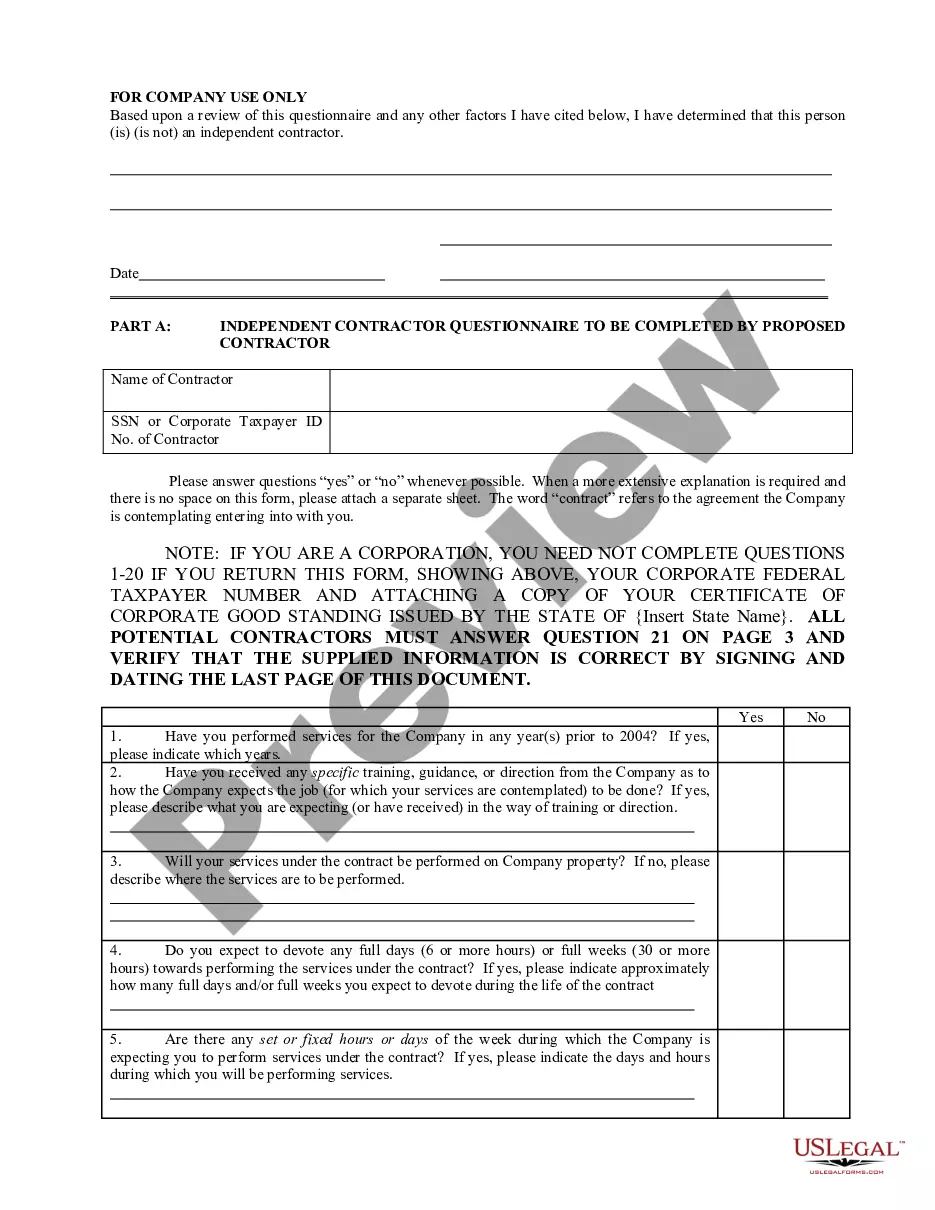
The Plugging of Wells form, the assignee shall plug all wells not capable or no longer capable of producing oil or gas in paying quantities and shall restore the lands around any such well in a manner that meets all requirements of any governmental agency having jurisdiction and the oil and gas lease on which the well is located.
Wisconsin Plugging of Wells
Description
How to fill out Plugging Of Wells?
You can spend several hours on the web trying to find the lawful record design that meets the state and federal demands you need. US Legal Forms gives a large number of lawful kinds which are analyzed by pros. You can actually download or printing the Wisconsin Plugging of Wells from our service.
If you have a US Legal Forms account, it is possible to log in and then click the Download key. Following that, it is possible to comprehensive, change, printing, or sign the Wisconsin Plugging of Wells. Each lawful record design you purchase is the one you have permanently. To have another version associated with a bought develop, proceed to the My Forms tab and then click the corresponding key.
If you work with the US Legal Forms website initially, adhere to the straightforward guidelines listed below:
- First, be sure that you have chosen the best record design for your region/town of your choosing. Browse the develop outline to make sure you have chosen the correct develop. If readily available, make use of the Review key to search through the record design too.
- If you would like discover another edition of the develop, make use of the Lookup industry to find the design that meets your needs and demands.
- When you have found the design you would like, simply click Get now to continue.
- Pick the pricing program you would like, type in your accreditations, and register for a merchant account on US Legal Forms.
- Full the financial transaction. You can use your credit card or PayPal account to cover the lawful develop.
- Pick the structure of the record and download it in your gadget.
- Make alterations in your record if required. You can comprehensive, change and sign and printing Wisconsin Plugging of Wells.
Download and printing a large number of record themes making use of the US Legal Forms website, that provides the biggest collection of lawful kinds. Use professional and state-specific themes to handle your small business or person needs.
Form popularity
FAQ
How can I find out how deep my well is? Search the database to find the WCR for your well. The report will indicate the drillhole depth and the casing depth. If you cannot find a WCR for your well, you can hire a licensed well professional to inspect the water supply system and measure the well depth for you.
The typical depth of a residential well ranges from 100 feet to 800 feet deep. Some wells are even 1,000 feet or deeper. The deeper a well is, the better the water quality.
You can measure the depth of water by lowering a wetted steel tape to into the well until the lower part of the tape is under water. A chalk coating on the last few feet of tape indicate the exact water level.
All wells must be constructed by a licensed heat exchange driller or a registered rig operator working under the supervision of a licensed driller. Obtain a Heat Exchange Construction Notification Number prior to constructing a well.
The cost of a well abandonment depends on a number of factors; the primary ones being depth of the well and whether the pump is present and needs to be pulled. A ?typical? abandonment costs $800 - $1500 but may be more or less depending on the well depth and ease with which the pump can be removed.
The typical depth of a well for a private residence ranges anywhere from 100 to 800 feet. If the geology of your region is different from that of another part of the country, you might need a well that is either deeper or shallower.
The well and pump installation must satisfy the requirements of Chapter NR 812 of the Wisconsin Administrative Code. The well must produce bacteriologically safe water; that is, the water must be free of coliform bacteria including E. coli. The well must not be cross-connected to the municipal water system.