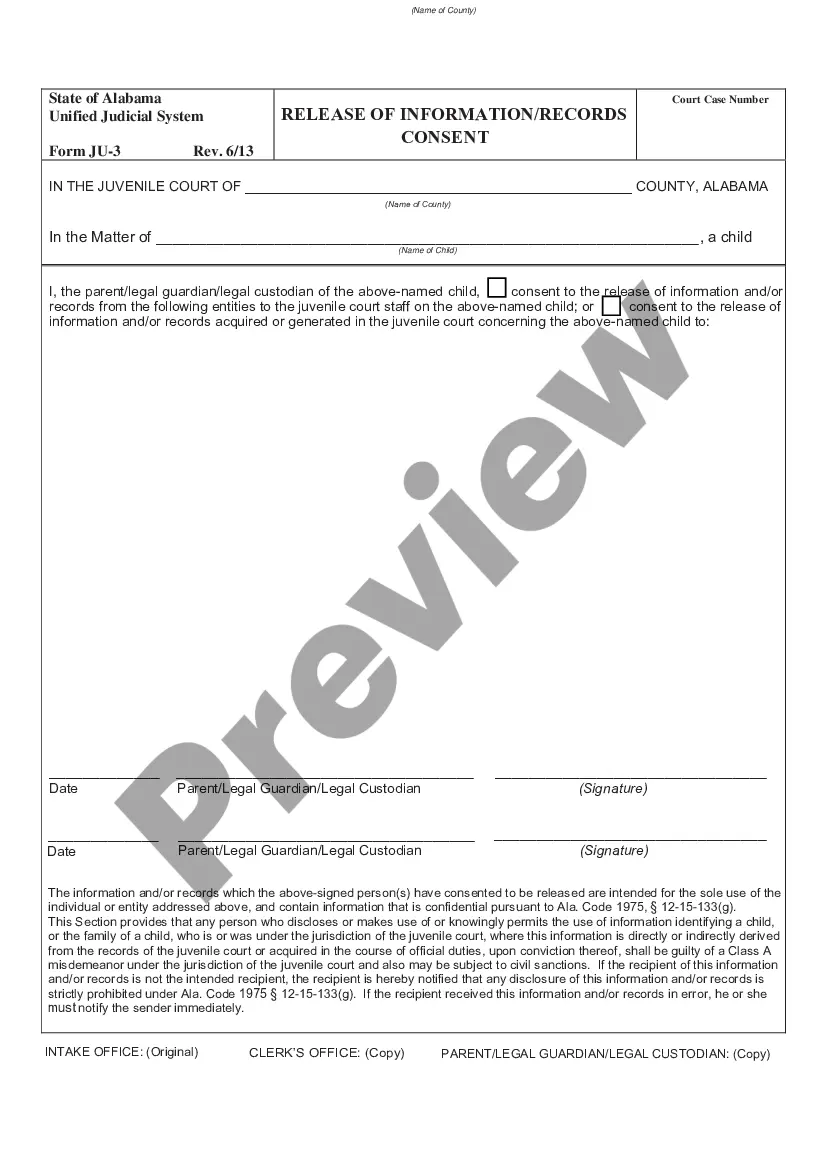
Affidavit of Plaintiff Supporting Motion for Summary Judgment by Plaintiff
Form popularity
FAQ
When it comes to summary judgment, plaintiff lawyers are often guilty of forgetting the fact that either party can file one. If you have solid evidence that can't be disputed, you may very well be able to prove your claim without going to trial.
When a motion for summary judgment is denied, the nonmoving party achieves a form of premium that enables a case to settle for an additional amount. Put simply, the settlement value of a case increases when a motion for summary judgment is denied.
(b) (1) A party may move for judgment on the pleadings.(A) If the moving party is a plaintiff, that the complaint states facts sufficient to constitute a cause or causes of action against the defendant and the answer does not state facts sufficient to constitute a defense to the complaint.
Rule 56 of the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure governs summary judgment for federal courts. Under Rule 56, in order to succeed in a motion for summary judgment, a movant must show 1) that there is no genuine dispute as to any material fact, and 2) that the movant is entitled to judgment as a matter of law.
A response must be in writing and include the same supporting documents as a motion for summary judgment. The opposition to the motion for summary judgment should also include a statement of facts showing the dispute and supporting documents.
Instead the party who believes that the undisputed facts compel a ruling in his or her favor will file a motion for summary judgment. The motion asks the court to consider the undisputed facts and apply the law to them, and argues that the law requires a judgment for the party bringing the motion.
A summary judgement occurs when, in a civil case, one party wants to move to a court decision without a trial. That only happens however, when the two parties agree to the critical facts of the issue, and the law allows summary judgement based on the undisputed facts at hand.
Completely resolve a case (e.g., entry of judgment for plaintiff or defendants) Completely resolve a claim. Completely determine the status of a particular party. Resolve a particular claim's application to a particular party. Establish a fact or ruling applicable to the case as it is further adjudicated.