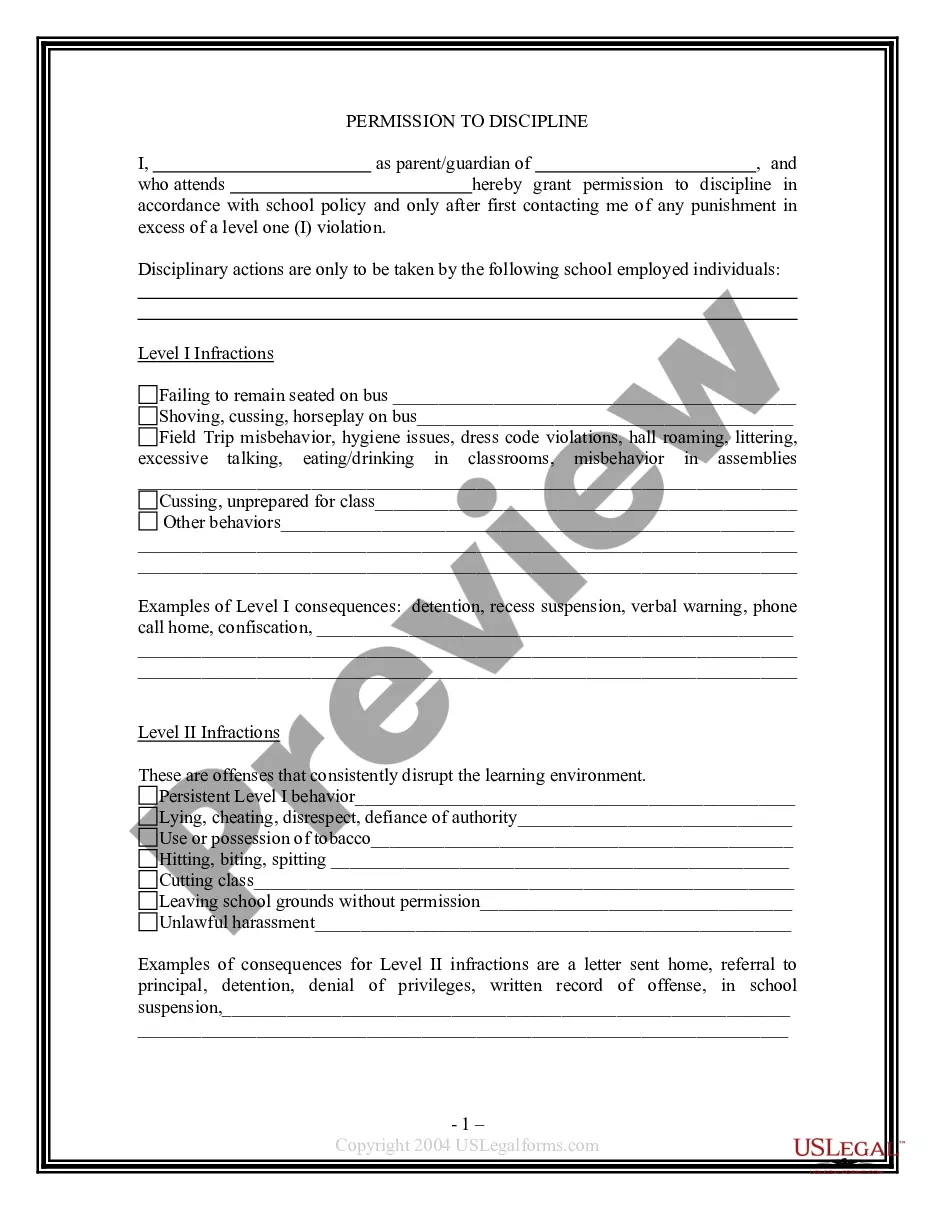
Nebraska Permission To Discipline
Description
How to fill out Permission To Discipline?
Are you currently in the position that you need paperwork for either company or person uses virtually every day time? There are plenty of authorized papers layouts accessible on the Internet, but locating kinds you can rely isn`t easy. US Legal Forms offers thousands of type layouts, like the Nebraska Permission To Discipline, that happen to be published in order to meet state and federal demands.
In case you are already familiar with US Legal Forms website and also have your account, just log in. Following that, you are able to down load the Nebraska Permission To Discipline design.
If you do not come with an account and need to start using US Legal Forms, follow these steps:
- Get the type you will need and ensure it is for that proper city/state.
- Use the Preview button to examine the shape.
- See the outline to ensure that you have chosen the correct type.
- When the type isn`t what you are trying to find, take advantage of the Look for field to discover the type that meets your needs and demands.
- When you obtain the proper type, simply click Get now.
- Select the rates strategy you would like, submit the desired details to make your bank account, and purchase the transaction making use of your PayPal or credit card.
- Pick a handy document file format and down load your copy.
Get each of the papers layouts you have bought in the My Forms food list. You can get a more copy of Nebraska Permission To Discipline at any time, if required. Just go through the needed type to down load or printing the papers design.
Use US Legal Forms, by far the most considerable collection of authorized forms, to save lots of efforts and stay away from mistakes. The support offers professionally produced authorized papers layouts that can be used for a variety of uses. Make your account on US Legal Forms and begin generating your way of life easier.
Form popularity
FAQ
(1) Any person who, by any act, encourages, causes, or contributes to the delinquency or need for special supervision of a child under eighteen years of age, so that such child becomes, or will tend to become, a delinquent child, or a child in need of special supervision, commits contributing to the delinquency of a ...
In California, the crime of contributing to the delinquency of a minor is set forth in Penal Code 272 PC. This offense is a misdemeanor punishable by up to one year in county jail and fines of up to $2500.00.
Posted on January 9, 2023. You commit the criminal offense of contributing to the delinquency of a minor when you: commit some act or fail to act in a certain way, and. the action or inaction makes a child more prone to engage in illegal activities.
Furnishing alcohol to a person under 21, aiding a minor child to possess a gun, leaving a child in an unattended car, and luring a child are all related offenses that can be charged along with contributing to the delinquency of a minor.
Use of force by person with special responsibility for care, discipline, or safety of others. (b) Such force used is not designed to cause or known to create a substantial risk of causing death, bodily harm, or extreme mental distress. Source:Laws 1972, LB 895, § 8; R.R.S.
Nevada Revised Statute section 201.110 makes clear that if any person's acts or omissions cause a person under 18 to become a delinquent child, child in need of supervision, or neglected child, that person could be found guilty of contributory neglect or contributory delinquency.
Student conduct constituting grounds for long-term suspension, expulsion, or mandatory reassignment; enumerated; alternatives for truant or tardy students.
In Nebraska, you are considered an adult for most purposes when you reach the age of 19. You will find that you have many legal rights and responsibilities when you reach 19 years of age. However, there are also some rights and responsibilities that you will want to be aware of when you turn 18.