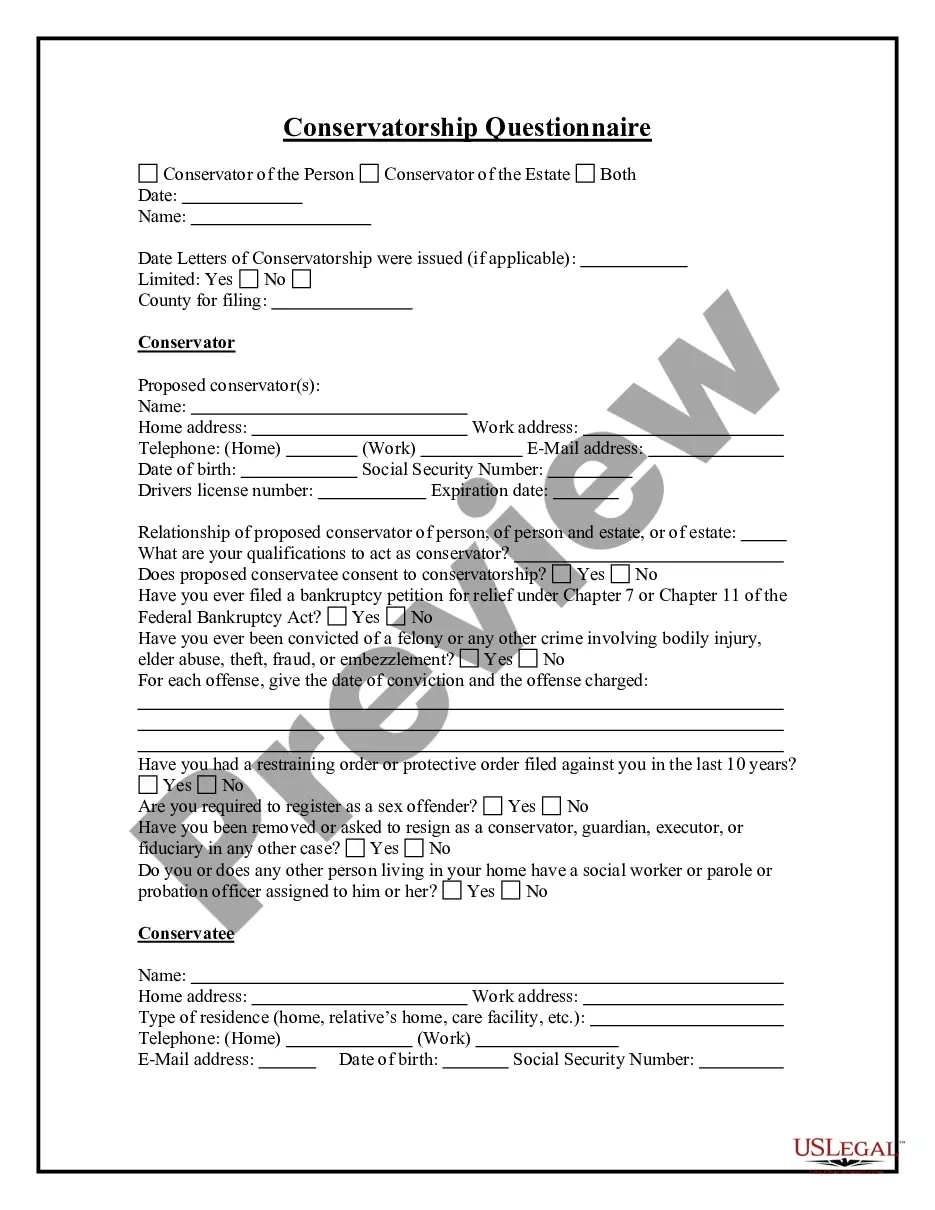
Zoning involves government-imposed restrictions on the use that may be made of land. For example, a municipality may adopt a zoning ordinance that permits the construction of only single-family houses in a designated portion of the city. Zoning is used to plan future community growth and to ensure reasonable, orderly development. A variance is an exception granted by an administrative agency such as a zoning board that permits a use of property that is inconsistent with an existing zoning ordinance.
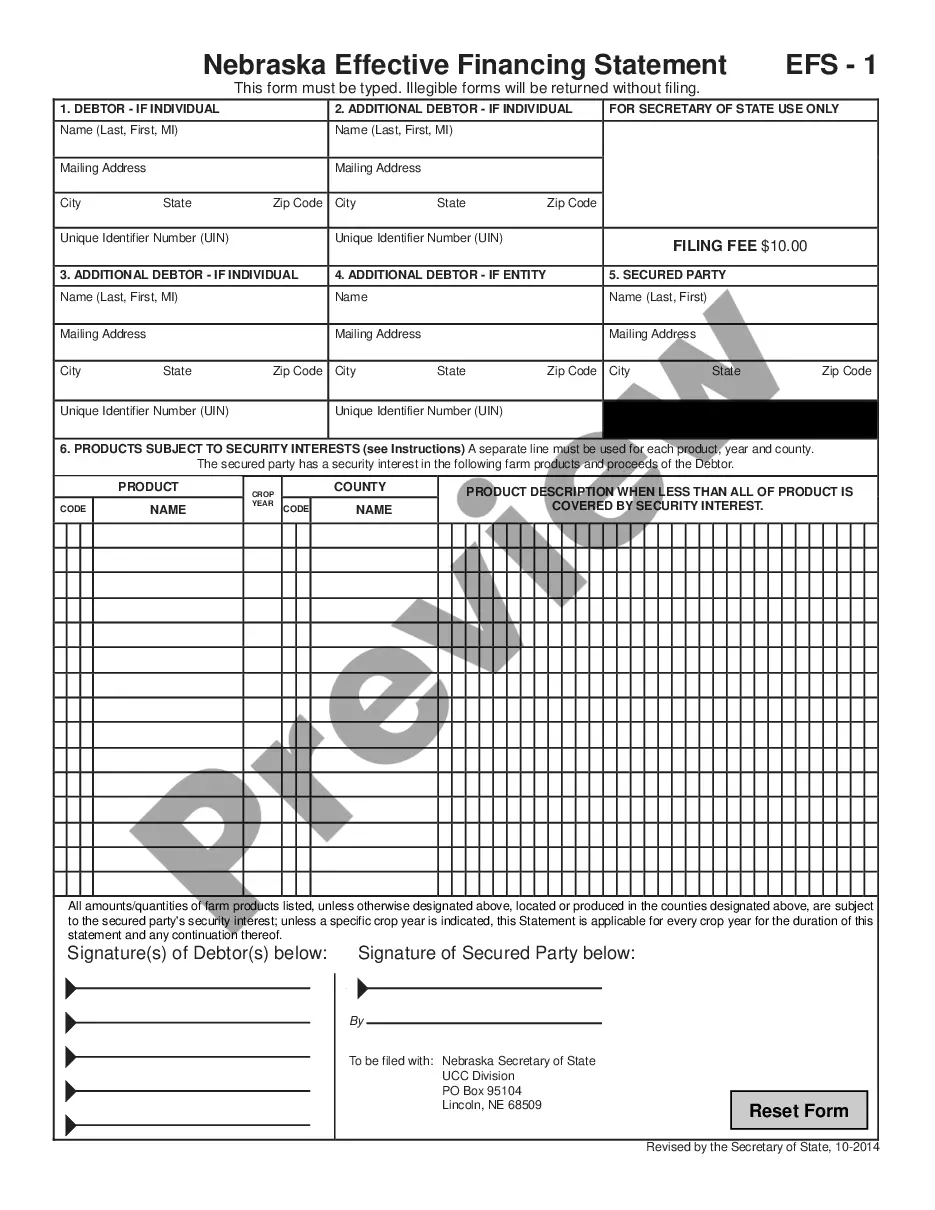
This form is a generic example that may be referred to when preparing such a form for your particular community. It is for illustrative purposes only. Local laws should be consulted to determine any specific requirements for such a form in a particular jurisdiction.