North Carolina Chapter 7 Individual Debtors Statement of Intention - Form 8 - Post 2005
Description
How to fill out Chapter 7 Individual Debtors Statement Of Intention - Form 8 - Post 2005?
Finding the right lawful papers design could be a have a problem. Needless to say, there are a lot of themes available on the net, but how do you discover the lawful type you need? Use the US Legal Forms website. The service gives thousands of themes, including the North Carolina Chapter 7 Individual Debtors Statement of Intention - Form 8 - Post 2005, that can be used for organization and private needs. Every one of the varieties are checked by experts and satisfy state and federal needs.
Should you be previously authorized, log in for your accounts and then click the Down load button to have the North Carolina Chapter 7 Individual Debtors Statement of Intention - Form 8 - Post 2005. Utilize your accounts to appear through the lawful varieties you possess acquired earlier. Check out the My Forms tab of your accounts and acquire one more duplicate in the papers you need.
Should you be a whole new customer of US Legal Forms, here are easy guidelines so that you can follow:
- Initially, make certain you have chosen the proper type for your city/region. You are able to look through the form while using Preview button and study the form explanation to guarantee it will be the best for you.
- In the event the type will not satisfy your requirements, make use of the Seach industry to get the proper type.
- When you are positive that the form is suitable, click the Get now button to have the type.
- Choose the costs strategy you want and type in the required details. Design your accounts and pay for the order with your PayPal accounts or credit card.
- Pick the submit file format and acquire the lawful papers design for your system.
- Full, change and print and indicator the acquired North Carolina Chapter 7 Individual Debtors Statement of Intention - Form 8 - Post 2005.
US Legal Forms will be the largest library of lawful varieties where you can find a variety of papers themes. Use the service to acquire professionally-created paperwork that follow condition needs.
Form popularity
FAQ
Ultimately, if you can reasonably pay the taxes you owe as a result of your business closing after discharging all or most of your other obligations (including maybe some of the taxes), then Chapter 7 may well make more sense. Otherwise, you will probably need to file a Chapter 13 bankruptcy.
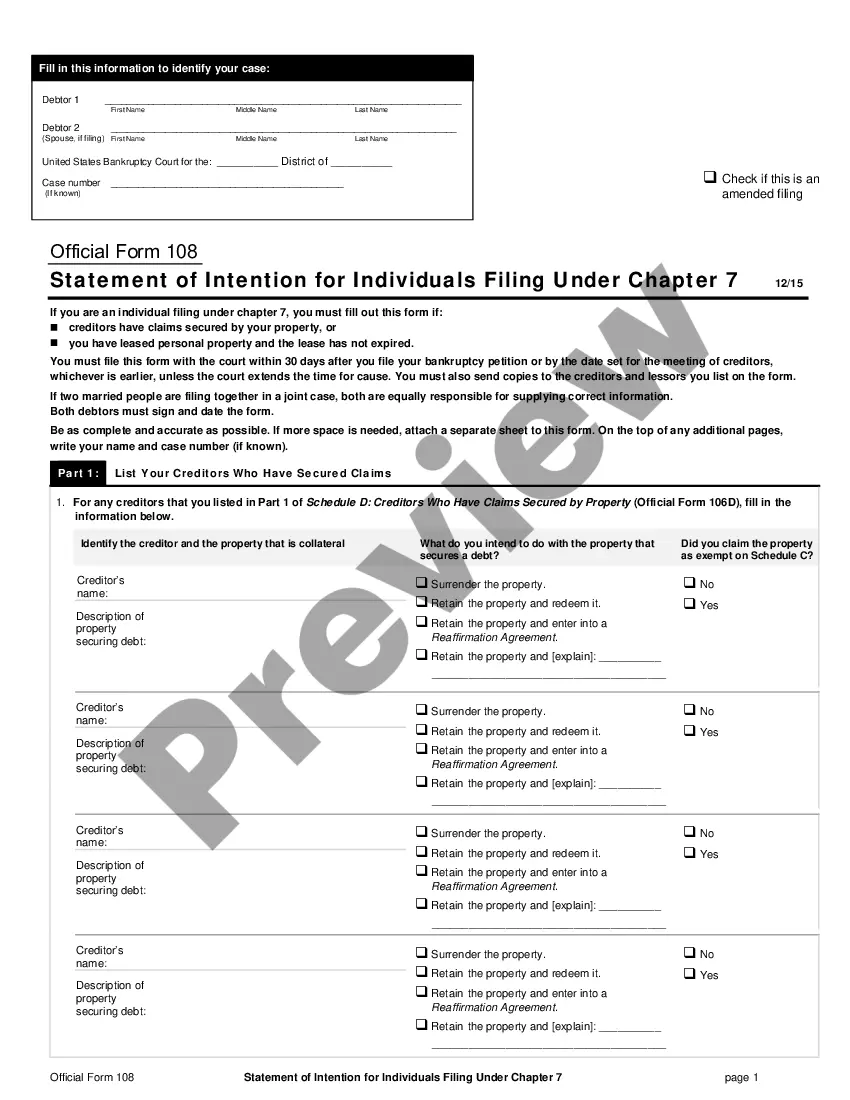
When you file for Chapter 7 bankruptcy, you will have to complete a form called the Statement of Intention for Individuals Filing Under Chapter 7. On this form, you tell the court whether you want to keep your secured and leased property?such as your car, boat, or home?or let it go back to the creditor.
While it may feel odd to pay fees to tell the courts you don't have enough money, you typically have to pay court fees to file for bankruptcy. The filing fee for a Chapter 7 bankruptcy is $338, while the filing fee for a Chapter 13 bankruptcy is $313.
A Chapter 7 bankruptcy wipes out mortgages, car loans, and other secured debts. But if you don't continue to pay as agreed, the lender will take back the home, car, or other collateralized property using the lender's lien rights.
Examples of nonexempt assets that can be subject to liquidation: Additional home or residential property that is not your primary residence. Investments that are not part of your retirement accounts. An expensive vehicle(s) not covered by bankruptcy exemptions.
You Don't Get to Keep Assets If You Fail The idea of keeping your home and car and personal belongings is an attractive part of Chapter 13. But if the case fails or is dismissed, protection for those assets disappears.
Disadvantages to a Chapter 7 Bankruptcy: If you want to keep a secured asset, such as a car or home, and it is not completely covered by your bankruptcy exemptions then Chapter 7 is not an option. The automatic stay created by filing Chapter 7 Bankruptcy only serves as a temporary defense against foreclosure.
A Chapter 13 petition for bankruptcy will likely necessitate a $500 to $600 monthly payment, especially for debtors paying at least one automobile through the payment plan. However, since the bankruptcy court will consider a large number of factors, this estimate could vary greatly.