Michigan Specific Consent Form for Qualified Joint and Survivor Annuities - QJSA
Description
How to fill out Specific Consent Form For Qualified Joint And Survivor Annuities - QJSA?
If you require thorough, download, or printing legal document templates, utilize US Legal Forms, the most significant collection of legal forms available online.
Capitalize on the site’s simple and user-friendly search to find the documents you need.
Various templates for business and personal purposes are categorized by types and regions, or keywords.
Step 4. Once you have found the form you need, select the Acquire now option. Choose the payment plan you prefer and enter your details to register for an account.
Step 5. Complete the transaction. You can pay using your credit card or PayPal account to finalize the purchase.
- Use US Legal Forms to obtain the Michigan Specific Consent Form for Qualified Joint and Survivor Annuities - QJSA with just a few clicks.
- If you are already a US Legal Forms user, Log In to your account and click on the Download button to access the Michigan Specific Consent Form for Qualified Joint and Survivor Annuities - QJSA.
- You can also access forms you previously saved from the My documents section of your account.
- If this is your first time using US Legal Forms, follow the instructions below.
- Step 1. Make sure you have chosen the form for the correct city/state.
- Step 2. Utilize the Preview option to review the content of the form. Don’t forget to check the description.
- Step 3. If you are not satisfied with the form, use the Search box at the top of the screen to find other variations of the legal document template.
Form popularity
FAQ
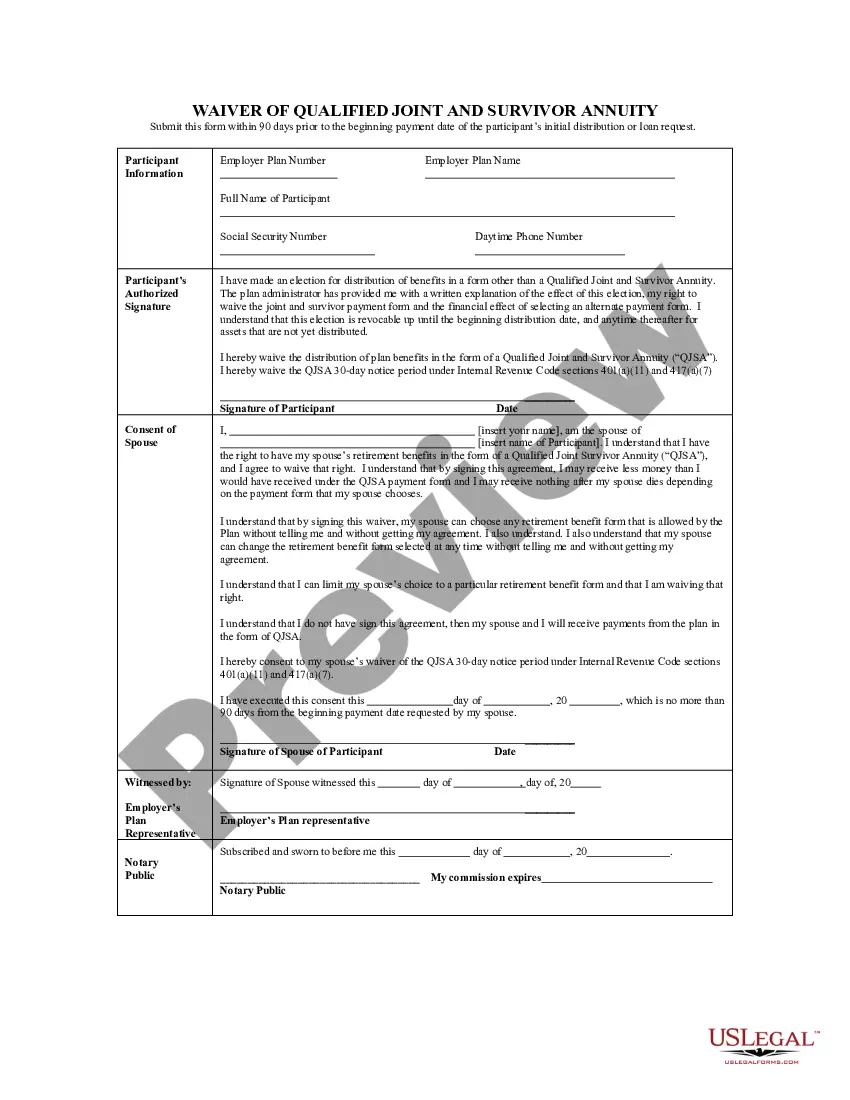
A married participant is required to obtain written spousal consent if she chooses to name a primary beneficiary other than her spouse. This rule is in effect for all qualified retirement plans, regardless of whether they are subject to the REA or designed as an REA safe harbor plan.
Spousal Waiver Form means that form established by the Plan Administrator, in its sole discretion, for use by a spouse to consent to the designation of another person as the Beneficiary or Beneficiaries under a Participant's Account.
ANSWER: Spousal consent is required if a married participant designates a nonspouse primary beneficiary and may be necessary if a 401(k) plan offers one or more annuity forms of distribution. Here is a summary of these rules and the way many 401(k) plans avoid spousal consents.
Because of these legal rights, an IRA owner subject to community property rules and wishing to leave assets to another beneficiary is required to obtain spousal consent when first electing or requesting to change the primary beneficiary to someone other than his spouse.
A QJSA is when retirement benefits are paid as a life annuity (a series of payments, usually monthly, for life) to the participant and a survivor annuity over the life of the participant's surviving spouse (or a former spouse, child or dependent who must be treated as a surviving spouse under a QDRO) following the
In most cases, the account holder can name a beneficiary, whether that's a child, another relative, or someone else other than their spouse. In community property states, though, a spouse can inherit an IRA or must approve of the account holder's designated beneficiary in writing.
A QJSA is when retirement benefits are paid as a life annuity (a series of payments, usually monthly, for life) to the participant and a survivor annuity over the life of the participant's surviving spouse (or a former spouse, child or dependent who must be treated as a surviving spouse under a QDRO) following the
Qualified Joint and Survivor Annuity (QJSA) includes a level monthly payment for your lifetime and a survivor benefit for your spouse after your death equal to the percentage designated of that monthly payment.
If you do not waive the QPSA, after your death the Plan will pay your spouse the QPSA unless your spouse elects another benefit form. The QPSA will not pay benefits to other beneficiaries after your spouse dies. If you waive the QPSA, the Plan will pay your account to your designated beneficiary.
The QJSA payment form gives your spouse, the annuitant, a retirement payment for the rest of his or her life. Under the QJSA payment form, after your spouse dies, the contract will pay you, the surviving spouse, at least 50% percent of the retirement benefit that was paid to your spouse, the annuitant.