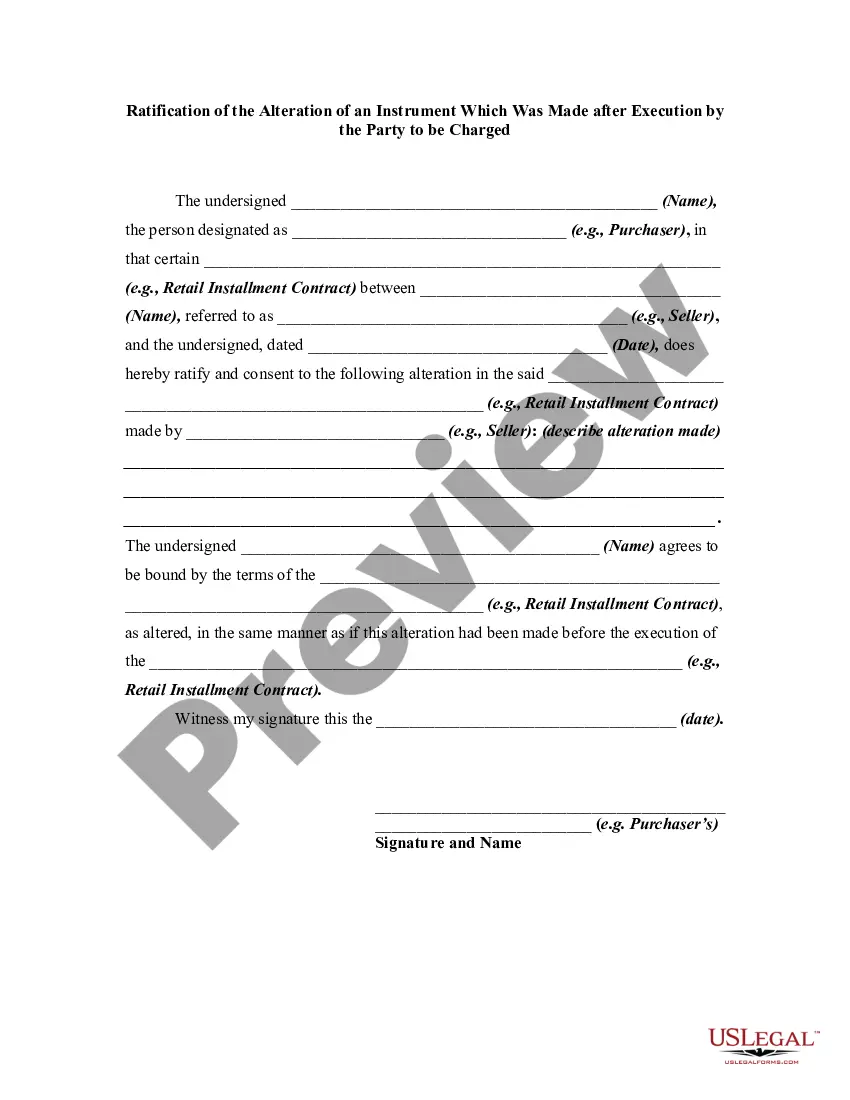
An alteration of a written instrument is a change in language of the instrument that is made by one of the parties to the instrument who is entitled to make the change. Any material alteration of a written instrument, after its execution, made by the owner or holder of the instrument, without the consent of the party to be charged, renders the instrument void as to the nonconsenting party. The party to be charged refers to that party or parties against whom enforcement of a contract or instrument is sought.
If a party consents to the alteration, the instrument will not be rendered invalid as to that party.
Maryland Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged
Description
How to fill out Ratification Of The Alteration Of An Instrument Which Was Made After Execution By The Party To Be Charged?
US Legal Forms - one of the largest collections of official templates in the U.S. - offers a wide range of legal document templates that you can download or print.
By utilizing the platform, you will obtain numerous forms for business and personal purposes, organized by categories, states, or keywords. You can find the latest versions of documents such as the Maryland Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged in moments.
If you possess a monthly subscription, Log In and download the Maryland Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged through the US Legal Forms repository. The Download button will appear on every form you look at. You can access all previously saved forms in the My documents section of your account.
Process the transaction. Use your credit card or PayPal account to finalize the transaction.
Select the format and download the form onto your device. Edit. Complete, modify, print, and sign the saved Maryland Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged. Each template you add to your account does not have an expiration date and is yours indefinitely. Thus, if you need to download or print another version, simply navigate to the My documents section and click on the form you need. Gain access to the Maryland Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged via US Legal Forms, the most extensive collection of legal document templates. Utilize numerous professional and state-specific templates that fulfill your business or personal requirements and specifications.
- Ensure you have selected the correct form for your locality/region.
- Click the Review button to examine the form's content.
- Review the form summary to confirm you have chosen the appropriate form.
- If the form does not meet your needs, use the Search bar at the top of the screen to find one that does.
- Once satisfied with the form, confirm your choice by clicking the Get now button.
- Then, choose your preferred pricing plan and provide your details to register for an account.
Form popularity
FAQ
The Maryland Property Act encompasses a variety of laws governing property rights, ownership, and transactions within the state. It serves as a foundational legal framework for real estate practices, including how instruments can be altered and ratified. A solid understanding of this Act is crucial when navigating the Maryland Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged.
The low impact landscaping law in Maryland promotes environmentally friendly practices in property management. It encourages property owners to adopt sustainable landscaping techniques, ultimately benefiting local ecosystems. Although it may not directly relate to the Maryland Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged, effective property management often intertwines with legislation and best practices.
Real Property Code 3 105 refers to the procedures surrounding property disclosures and requirements for various property transactions. Knowing this code is essential for understanding how to manage property instruments effectively. It directly relates to the Maryland Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged, providing guidance on necessary legal processes.
Article 8 402 provides rules regarding the ratification and acknowledgment of property documents in Maryland. It specifies the necessary steps to ensure that any alterations made to instruments are valid and enforceable. This is particularly relevant when discussing the Maryland Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged.
Section 2 125 outlines the acceptance and processing of property documents in Maryland. This section is vital for ensuring that alterations made to property instruments are recognized legally and effectively. In relation to the Maryland Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged, this section helps facilitate the necessary legal affirmations.
Property Code 2 119 in Maryland specifies guidelines related to the execution of property instruments, impacting how changes are made and ratified. This code assures that alterations meet legal standards and can be recognized in case of disputes. When seeking clarity on the Maryland Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged, this code provides valuable insights.
Section 14 132 of the Maryland Real Property Code deals with statutory requirements for property management and ownership transfer. It ensures that property instruments are executed and ratified properly to maintain legal validity. This is crucial in contexts involving the Maryland Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged.
Section 8 204 of the Maryland Real Property Article addresses the procedure for the ratification of certain property instruments. Specifically, it outlines how parties can affirm the validity of changes made to documents relating to property law. Understanding this section is essential when considering the Maryland Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged.
Maryland Code Real Property 3-105 deals with the requirements for recording real property documents. This code helps ensure that property transactions are recognized legally, thereby offering protection to all parties involved. For dealing with the Maryland Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged, consulting this code is advisable for anyone looking to secure their property interests.
In Maryland, the duration for a wrongful detainer case can vary, but it typically spans several weeks to months depending on the specific circumstances. If you're facing such an issue, knowing the steps involved is key, especially when relating it to the Maryland Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged. Engaging with a reliable platform like US Legal Forms can simplify navigating through these legal processes.