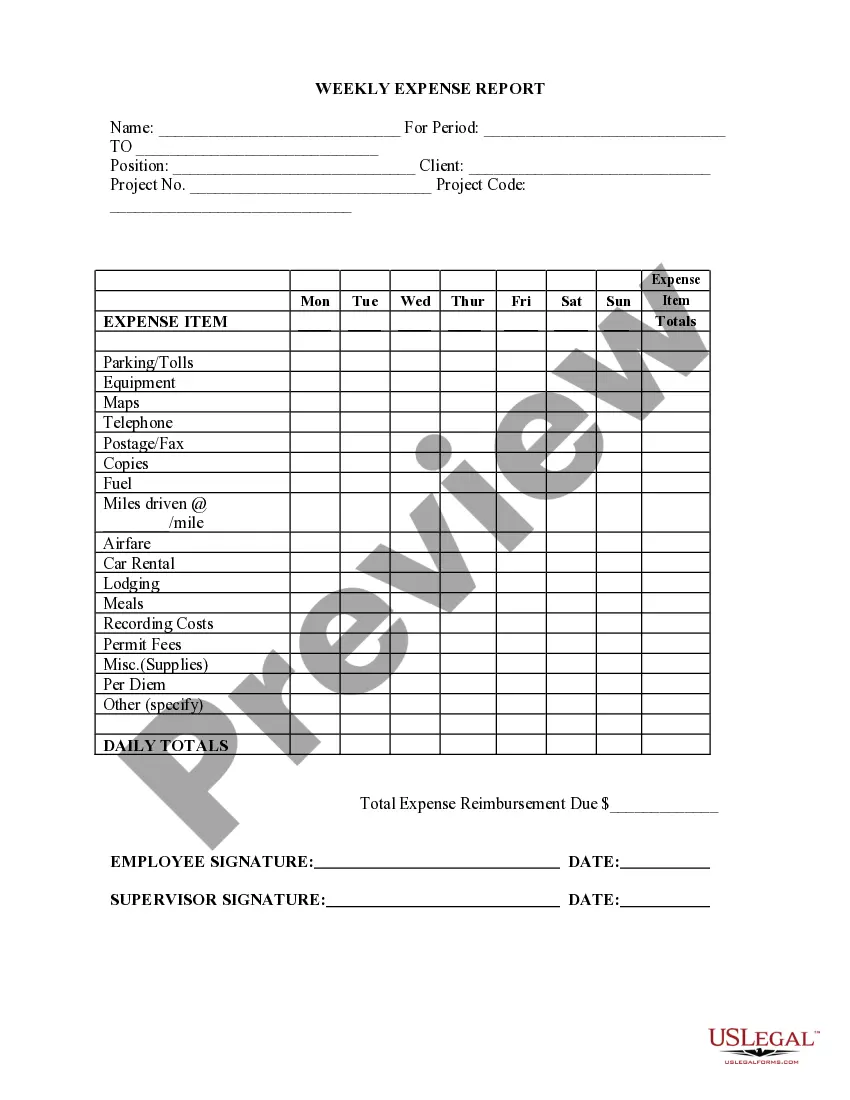
Guam Nonexempt Employee Time Report
Description
How to fill out Nonexempt Employee Time Report?
Selecting the optimal legal document template can pose a challenge.
It goes without saying that a plethora of designs can be found online, but how can you locate the legal format you need.
Leverage the US Legal Forms platform.
For new users of US Legal Forms, here are simple steps to follow: First, ensure you have selected the correct template for your city/state. You may browse the form using the Preview button and read the form description to confirm it meets your needs. If the template does not meet your expectations, utilize the Search bar to find the appropriate form. Once you are confident that the template is satisfactory, click on the Purchase Now button to obtain the form. Select your desired pricing plan and input the necessary details. Create your account and complete the purchase using your PayPal account or credit card. Choose the file format and download the legal document template to your device. Complete, modify, print, and sign the obtained Guam Nonexempt Employee Time Report. US Legal Forms hosts the largest collection of legal templates, offering various document formats. Use this service to acquire professionally crafted documents that comply with state regulations.
- The service provides thousands of templates, including the Guam Nonexempt Employee Time Report, suitable for both business and personal use.
- All templates are reviewed by professionals and comply with federal and state regulations.
- If you are already registered, Log In to your account and click the Download button to access the Guam Nonexempt Employee Time Report.
- Utilize your account to review the legal documents you have previously purchased.
- Visit the My documents section of your account to obtain another copy of the document you need.
Form popularity
FAQ
When a salary deduction from an exempt employee's salary is made, it is usually based on a daily pay rate. To find the daily pay rate, divide the employee's annual salary by 52 to compute the weekly rate. Next, divide the weekly rate by the number of days the employee is usually expected to work.
Calculating the Daily Rate Say your employee earns $50,000 a year, and she works a 40-hour week, her hourly pay is the annual amount divided by 2,080 hours (50,000/2,080 = 24.038, which you can round up to 24.04). For the employee's daily rate of pay, simply multiply 24.04 by the number of hours worked each day.
Kilo Time Zone (K) is 10 hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). This time zone is a military time zone.
The average daily rate is calculated by taking the average revenue earned from rooms and dividing it by the number of rooms sold. It excludes complimentary rooms and rooms occupied by staff.
Prorated Salary for Pay RaiseDivide the New Salary by 52 to Calculate Weekly Rate.Divide the New Weekly Rate by Number of Workdays.Subtract Previous Daily Rate from New Daily Rate.Multiply the Daily Rate Increase by the Number of Applicable Days.Add the Result from Step Four to Employee's Paycheck.
Section 7K of the FLSA is claimed, is defined as all hours worked in excess of 171 hours in a period of 28 consecutive 24-hour periods or a proportional number of hours for any other number of consecutive 24-hour periods down to seven. (42.75 hours in seven consecutive 24-hour periods.)
Exempt employees do not receive overtime pay, nor do they qualify for minimum wage. When an employee is exempt, it primarily means that they are exempt from receiving overtime pay. Exempt employees stand in contrast to nonexempt employees.
Exempt workers are exempt from overtime payso even if they work more than 40 hours in a workweek, they're not eligible for overtime pay. So, whether a salaried employee has to fill out a timesheet will come down to whether they're considered exempt or non-exempt.
At that time, Congress enacted the 207k exemption (usually referred to as 7k exemption) to allow firefighters (who commonly worked an average of 48-56 hours a week) and police officers (many of whom worked 45-48 hour schedules) to continue working those hours with minimal impact to taxpayers.
Section 7(r) of the Fair Labor Standards Act Break Time for Nursing Mothers Provision. Effective March 23, 2010, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act amended the FLSA to require employers to provide a nursing mother reasonable break time to express breast milk after the birth of her child.