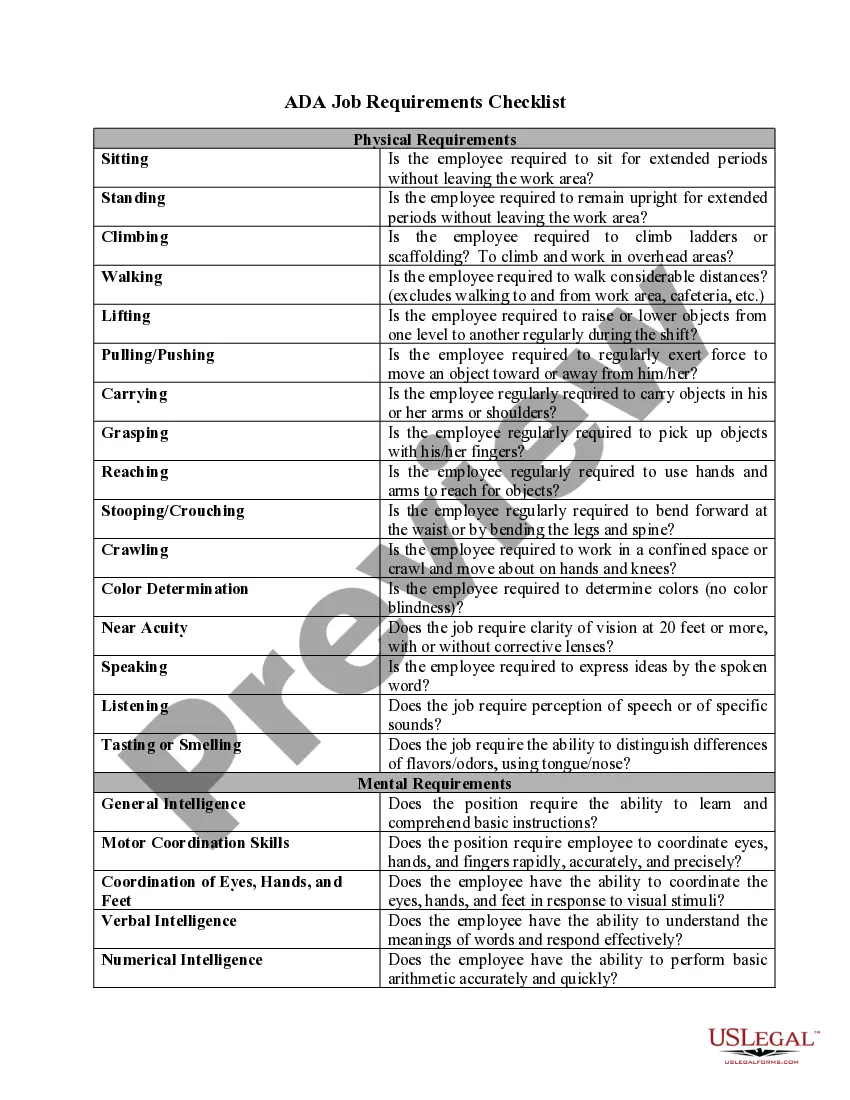
This due diligence checklist lists liability issues for future directors and officers in a company regarding business transactions.
Georgia Checklist for Potential Director and Officer Liability Issues
Description
How to fill out Checklist For Potential Director And Officer Liability Issues?
US Legal Forms - one of the largest collections of legal documents in the United States - offers a vast selection of legal form templates that you can download or print.
By using the site, you can discover thousands of forms for business and personal needs, categorized by types, states, or keywords. You can obtain the latest versions of forms like the Georgia Checklist for Potential Director and Officer Liability Issues in just a few seconds.
If you already have an account, Log In and access the Georgia Checklist for Potential Director and Officer Liability Issues from the US Legal Forms collection. The Download button will be visible on every form you view. You can access all previously downloaded forms in the My documents section of your account.
Make modifications. Fill out, edit, and print and sign the downloaded Georgia Checklist for Potential Director and Officer Liability Issues.
Every template you added to your account does not have an expiration date and is yours indefinitely. Therefore, if you wish to download or print another copy, simply visit the My documents section and click on the form you need. Access the Georgia Checklist for Potential Director and Officer Liability Issues with US Legal Forms, the most extensive collection of legal document templates. Utilize thousands of professional and state-specific templates that meet your business or personal needs.
- If you are using US Legal Forms for the first time, here are simple steps to help you begin.
- Ensure you have selected the correct form for your city/state. Click on the Preview button to examine the content of the form. Review the form summary to ensure you have chosen the correct form.
- If the form does not meet your requirements, utilize the Search field at the top of the screen to find the one that does.
- When you are satisfied with the form, confirm your choice by clicking on the Buy now button. Then, select the payment plan you prefer and provide your credentials to register for an account.
- Process the transaction. Use a credit card or PayPal account to complete the transaction.
- Select the file format and download the form to your device.
Form popularity
FAQ
The business judgment rule in Georgia protects directors and officers by allowing them to make decisions without fear of personal liability, provided those decisions are made in good faith and with reasonable care. It acknowledges that business decisions carry risks and that not all outcomes can be predicted. Understanding this rule is crucial for anyone involved in corporate governance. Check out our Georgia Checklist for Potential Director and Officer Liability Issues to learn more.
Board members can be sued for their individual actions, such as if they personally and directly injure someone, guarantee a loan on which the nonprofit defaults, do something intentionally illegal or mix the nonprofit's funds with their personal funds.
Limited liability protects shareholders, directors, officers and employees against personal liability for actions taken in the name of the corporation and corporate debts. Ordinarily, an officer of the corporation, whether also a shareholder, director or employee, cannot be held personally liable.
Typically, a corporate officer isn't held personally liable, as long as his or her actions fall within the scope of their position and the parameters of the law. An officer of a corporation may serve on the board of directors or fulfill a managerial role. A corporate officer may also be: A shareholder.
In almost every D&O policy, there must be some finding or ruling that the insured actually engaged in the prohibited conduct before the exclusion will apply; an allegation that the director or officer engaged in the bad acts listed in the exclusion (e.g. fraud or illegal personal profit) is not enough for the exclusion
D&O policies include an exclusion for losses related to criminal or deliberately fraudulent activities. Additionally, if an individual insured receives illegal profits or remuneration to which they were not legally entitled, they will not be covered if a lawsuit is brought forward due to this.
The corporate opportunity doctrine prohibits a corporate fiduciary from exploiting an opportunity related to the corporation's business unless he or she first offers that opportunity to the corporation.
Related party transactions or self-dealing is a legal concept in which a fiduciary (such as a director, or officer,) personally benefits in a transaction involving a company to which he or she owes the fiduciary duty. A common example of self-dealing occurs when a director is on both sides of a transaction.
Threefold Duties of a Director of a CorporationDuty to be diligent. Compliance with the duty of a director to act with diligence requires the exercise of reasonable care, prudence, and equate knowledge and skill.The duty to be loyal.The duty to be obedient.
The following elements must be shown to prove200b usurping: 1) the opportunity was presented to the director or officer in his or her corporate200b capacity; 2) the opportunity is related to or connected with the200b corporation's current or proposed200b business; 3) the corporation has the financial ability to take advantage of