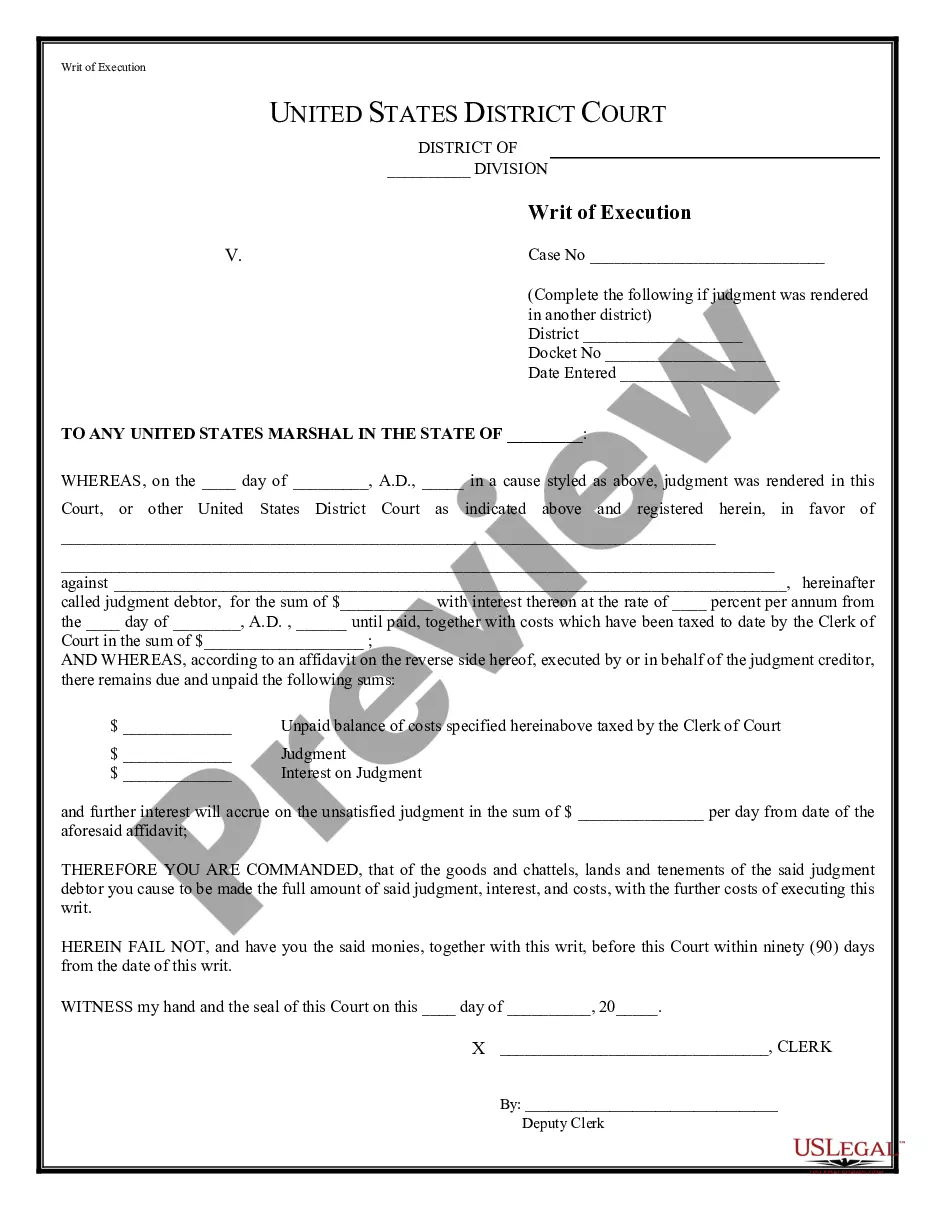
Delaware Writ of Execution to the United States Marshal - B 264
Description
How to fill out Writ Of Execution To The United States Marshal - B 264?
US Legal Forms - one of the largest libraries of lawful types in the States - offers an array of lawful record templates you can download or produce. While using site, you can find thousands of types for organization and personal reasons, sorted by categories, suggests, or keywords and phrases.You can find the most up-to-date types of types much like the Delaware Writ of Execution to the United States Marshal - B 264 within minutes.
If you have a membership, log in and download Delaware Writ of Execution to the United States Marshal - B 264 through the US Legal Forms collection. The Acquire option will appear on every single kind you perspective. You get access to all earlier downloaded types inside the My Forms tab of the profile.
In order to use US Legal Forms for the first time, listed here are straightforward recommendations to obtain started off:
- Be sure you have selected the best kind for your metropolis/region. Select the Preview option to check the form`s information. Read the kind information to ensure that you have selected the proper kind.
- In case the kind does not satisfy your needs, use the Search area towards the top of the monitor to discover the one who does.
- In case you are satisfied with the shape, confirm your decision by clicking the Buy now option. Then, select the prices strategy you want and provide your accreditations to sign up for an profile.
- Process the transaction. Make use of your Visa or Mastercard or PayPal profile to perform the transaction.
- Pick the format and download the shape in your product.
- Make changes. Fill out, edit and produce and sign the downloaded Delaware Writ of Execution to the United States Marshal - B 264.
Each format you included with your bank account lacks an expiry day and is your own permanently. So, if you would like download or produce another duplicate, just check out the My Forms segment and click on on the kind you require.
Gain access to the Delaware Writ of Execution to the United States Marshal - B 264 with US Legal Forms, the most substantial collection of lawful record templates. Use thousands of professional and express-certain templates that meet up with your business or personal requirements and needs.
Form popularity
FAQ
Execution. n. 1) the act of getting an officer of the court to take possession of the property of a losing party in a lawsuit (judgment debtor) on behalf of the winner (judgment creditor), sell it and use the proceeds to pay the judgment.
What Is a Writ of Execution? A writ of execution is a court order that puts in force a judgment of possession and directs law enforcement personnel to begin the transfer of property as the result of a legal judgment. Property may include assets, money, or real property.
A money judgment is enforced by a writ of execution, unless the court directs otherwise. The procedure on execution?and in proceedings supplementary to and in aid of judgment or execution?must with the procedure of the state where the court is located, but a federal statute governs to the extent it applies. Rule 69. Execution | Federal Rules of Civil Procedure - Law.Cornell.Edu cornell.edu ? rules ? frcp ? rule_69 cornell.edu ? rules ? frcp ? rule_69
A writ of execution is a process issued by the court directing the U.S. Marshal to enforce and satisfy a judgment for payment of money. (Federal Rules of Civil Procedure 69). Writ of Execution - U.S. Marshals Service U.S. Marshals Service (.gov) ? civil-process ? writ-of-e... U.S. Marshals Service (.gov) ? civil-process ? writ-of-e...
The term writ refers to a formal, legal document that orders a person or entity to perform or to cease performing a specific action or deed. Writs are drafted by judges, courts, or other entities that have administrative or judicial jurisdiction.
To collect money from the other side's bank account or their paycheck, you first need a filed Writ of Execution from the court. This tells the sheriff to go to the other side's bank or employer and have them give the sheriff money from the other side's bank account or paycheck to give to you. How to get a Writ of Execution | California Courts | Self Help Guide ca.gov ? after-trial ? collect-money ca.gov ? after-trial ? collect-money
A writ of attachment demands the creditor's property prior to the outcome of a trial or judgment, whereas a writ of execution directs law enforcement to begin the transfer of property as the result of the conclusion of a legal judgment.