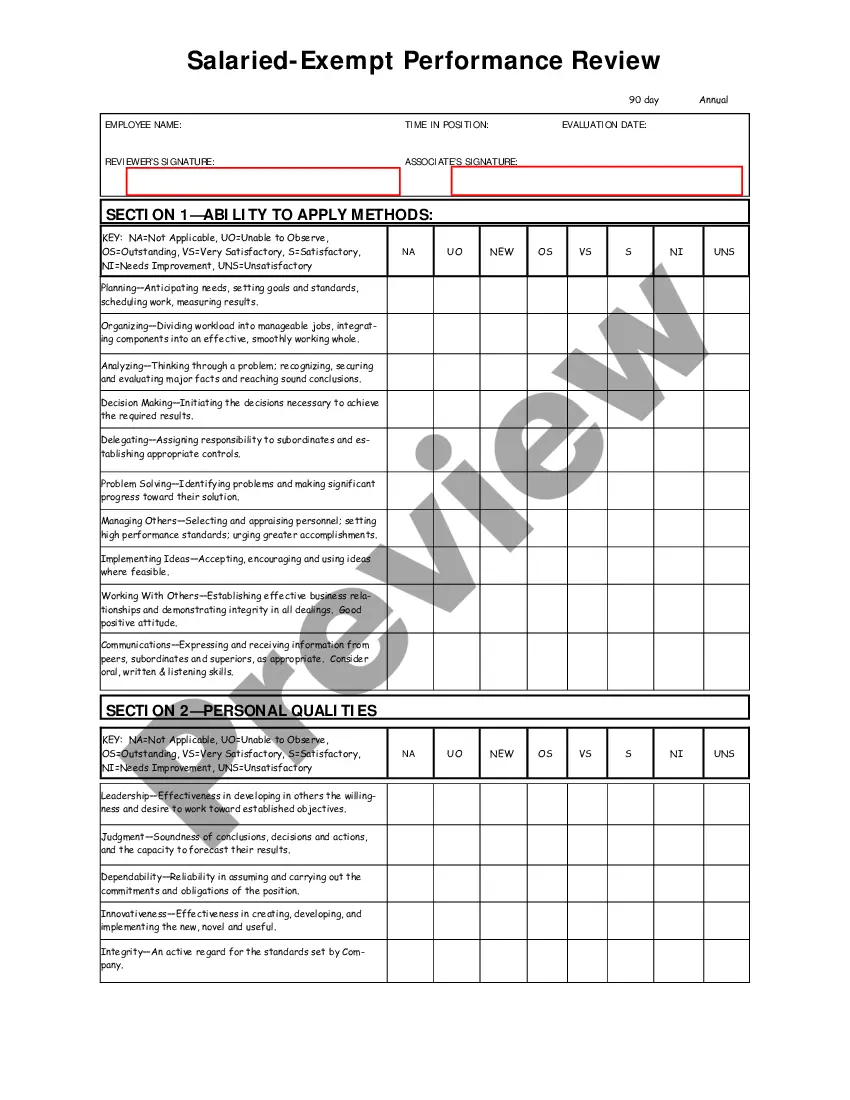
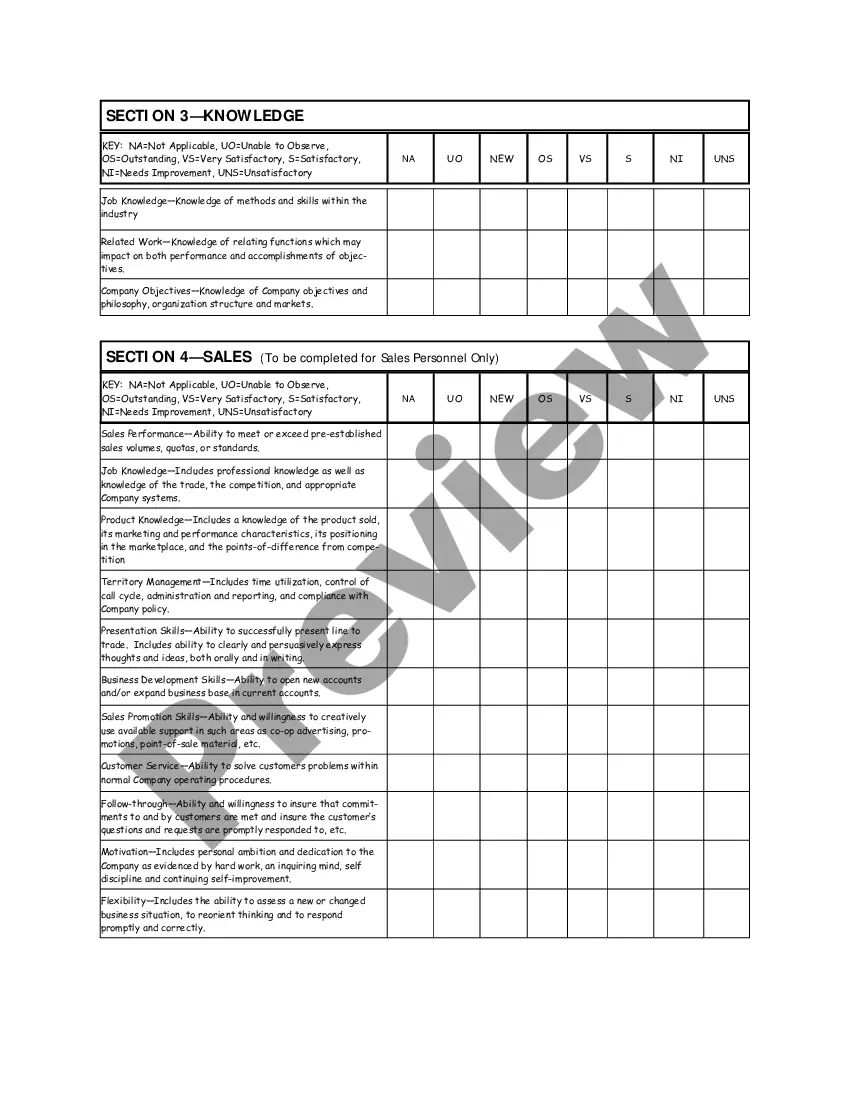
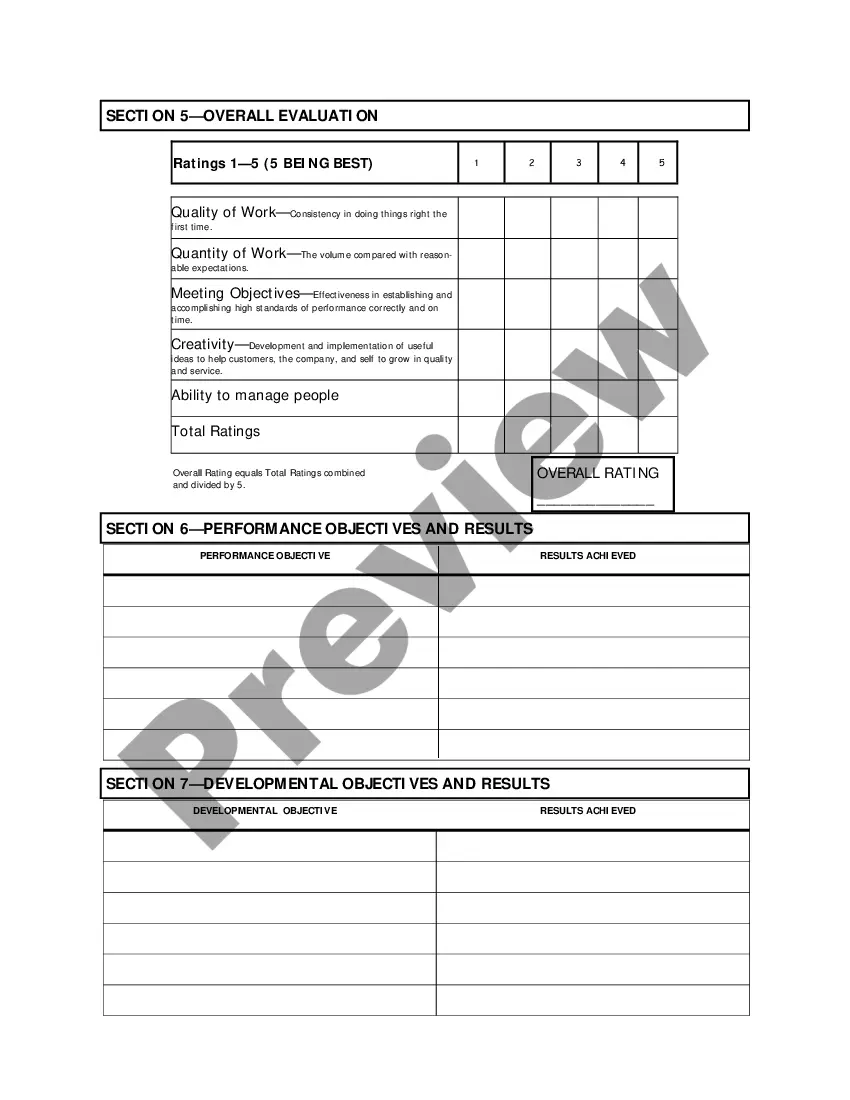
Arizona Salary - Exempt Employee Review and Evaluation Form
Description
How to fill out Salary - Exempt Employee Review And Evaluation Form?
Finding the right legitimate papers web template can be quite a have difficulties. Naturally, there are plenty of web templates available on the Internet, but how can you obtain the legitimate type you want? Utilize the US Legal Forms web site. The service offers a huge number of web templates, including the Arizona Salary - Exempt Employee Review and Evaluation Form, which can be used for company and personal demands. Every one of the types are inspected by professionals and fulfill state and federal demands.
Should you be already signed up, log in to the accounts and click the Down load option to find the Arizona Salary - Exempt Employee Review and Evaluation Form. Use your accounts to appear through the legitimate types you possess acquired in the past. Go to the My Forms tab of your accounts and get one more duplicate in the papers you want.
Should you be a fresh customer of US Legal Forms, allow me to share basic instructions for you to comply with:
- Very first, be sure you have selected the appropriate type to your metropolis/county. You can examine the form using the Review option and read the form outline to guarantee this is basically the right one for you.
- In the event the type does not fulfill your preferences, make use of the Seach field to obtain the proper type.
- When you are certain that the form is suitable, go through the Acquire now option to find the type.
- Pick the costs plan you would like and enter in the essential details. Design your accounts and buy the transaction making use of your PayPal accounts or bank card.
- Pick the file formatting and acquire the legitimate papers web template to the product.
- Complete, edit and produce and indication the acquired Arizona Salary - Exempt Employee Review and Evaluation Form.
US Legal Forms may be the biggest local library of legitimate types in which you can see a variety of papers web templates. Utilize the service to acquire expertly-created paperwork that comply with status demands.
Form popularity
FAQ
The FLSA includes these job categories as exempt: professional, administrative, executive, outside sales, and computer-related. The details vary by state, but if an employee falls in the above categories, is salaried, and earns a minimum of $684 per week or $35,568 annually, then they are considered exempt.
The federal law doesn't restrict how many hours you can be required to work in a day, although some state laws do. Hourly employees and non-exempt salaried employees must be paid overtime if they work more than 40 hours in a week. A week is defined as a fixed time period of 168 hours, or seven consecutive 24-hour days.
Maximum hours an exempt employee can be required to work The law does not provide a maximum number of hours that an exempt worker can be required to work during a week. This means that an employer could require an exempt employee to work well beyond 40 hours a week without overtime compensation.
Under federal overtime law and Texas overtime law, salaried employees must receive overtime pay for hours worked over 40 in any workweek unless two specific requirements are met: (1) the salary exceeds $455 per workweek; and (2) the employee performs duties satisfying one of the narrowly-defined FLSA overtime
Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) exempt and nonexempt testsEmployees who meet the thresholds of both the Duties and Salary tests are considered exempt from overtime pay or salaried. All other employees, with some exceptions listed below, are considered nonexempt, or eligible for overtime wages.
With few exceptions, to be exempt an employee must (a) be paid at least $23,600 per year ($455 per week), and (b) be paid on a salary basis, and also (c) perform exempt job duties. These requirements are outlined in the FLSA Regulations (promulgated by the U.S. Department of Labor).
Overtime Pay May Apply to Salaried Employees Overtime pay in Arizona is governed by federal law via The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). While salaried employees are usually exempt from overtime pay, this is not always the case.
Exempt employees are not regulated under the Fair Labor and Standards Act, which sets the federal requirements for overtime pay and minimum wage. Exempt employees must meet the Department of Labor's salary level, salary base and duties criteria.
Exempt employees' salary may fall below the minimum wage if they work enough hours and their salary is near the current $23,660, and this is legal (they are exempt). Non-exempt employees must be paid at least the minimum wage for all hours worked.
Partial Exempted Personnel from Overtime Pay.Executive Exemption.Administrative Exemption.Computer Professionals Exemption.Professional Exemption.Outside Sales Exemption.Highly Compensated Employees.