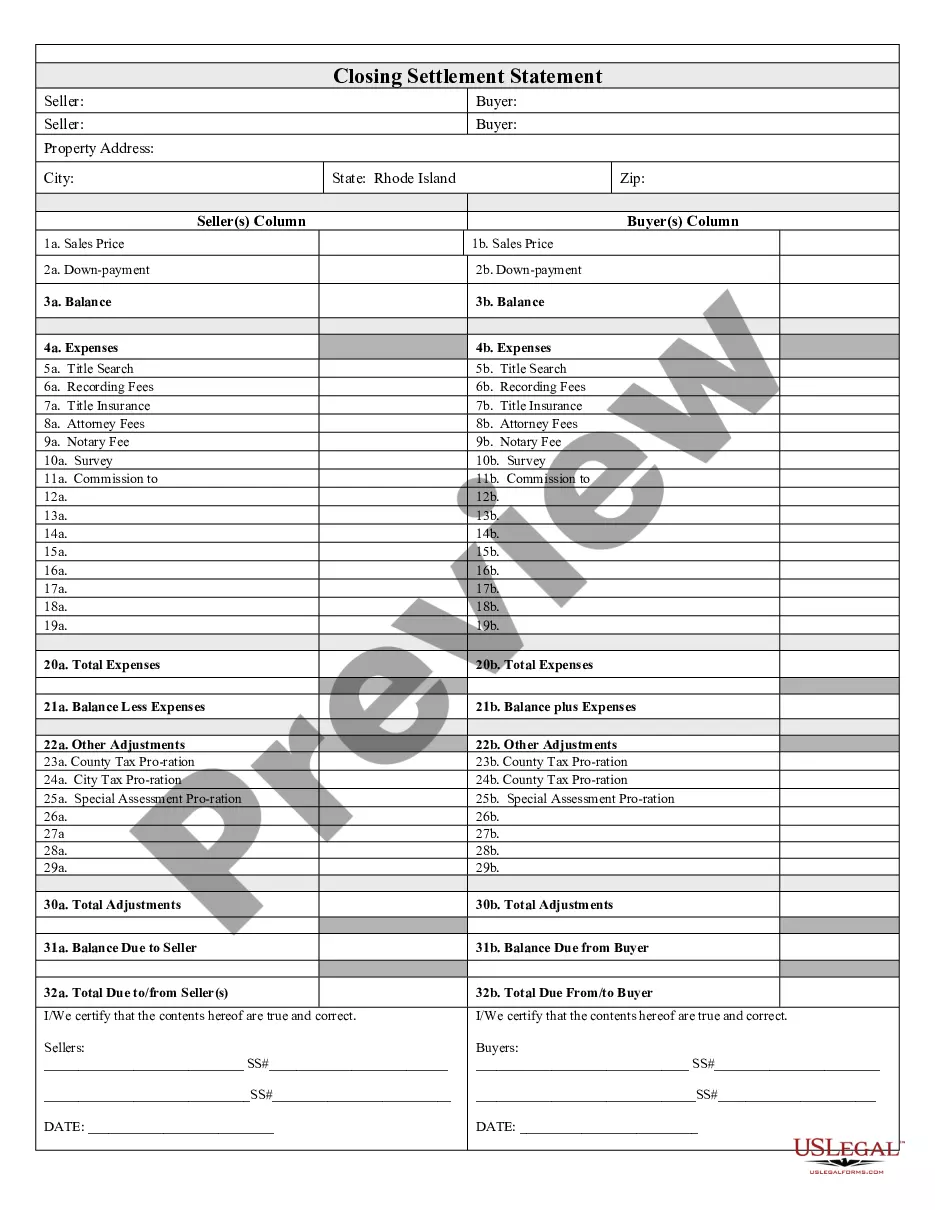
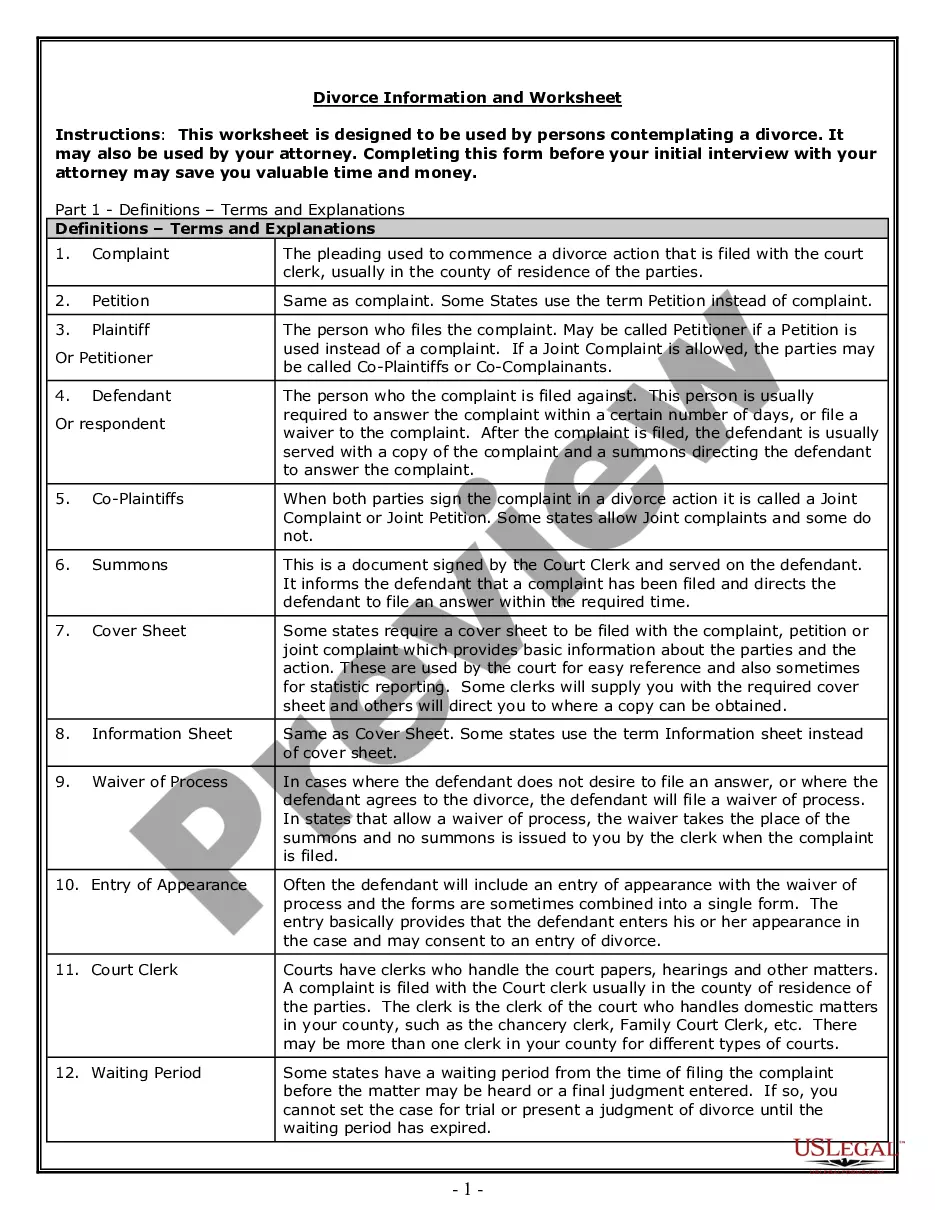
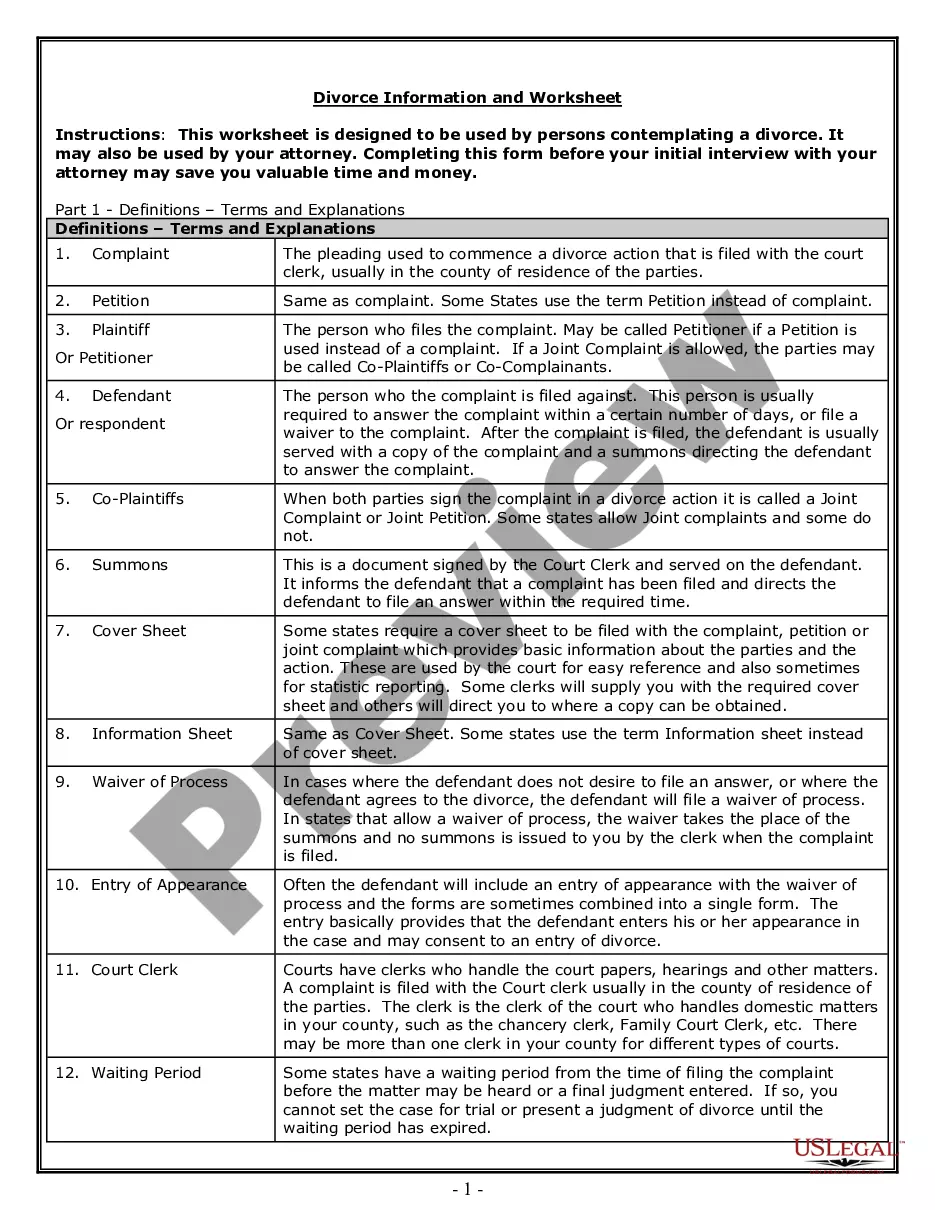
Uniquely packaged forms and information for Chapter 7 or 13 bankruptcies, including detailed instructions and other resources. Click and view the Free Preview for the latest revision dates and a complete overview of contents.
South Carolina Bankruptcy Guide and Forms Package for Chapters 7 or 13
Description
Get your form ready online
Our built-in tools help you complete, sign, share, and store your documents in one place.
Make edits, fill in missing information, and update formatting in US Legal Forms—just like you would in MS Word.
Download a copy, print it, send it by email, or mail it via USPS—whatever works best for your next step.
Sign and collect signatures with our SignNow integration. Send to multiple recipients, set reminders, and more. Go Premium to unlock E-Sign.
If this form requires notarization, complete it online through a secure video call—no need to meet a notary in person or wait for an appointment.
We protect your documents and personal data by following strict security and privacy standards.
Make edits, fill in missing information, and update formatting in US Legal Forms—just like you would in MS Word.

Download a copy, print it, send it by email, or mail it via USPS—whatever works best for your next step.

Sign and collect signatures with our SignNow integration. Send to multiple recipients, set reminders, and more. Go Premium to unlock E-Sign.
If this form requires notarization, complete it online through a secure video call—no need to meet a notary in person or wait for an appointment.
We protect your documents and personal data by following strict security and privacy standards.
Looking for another form?
How to fill out South Carolina Bankruptcy Guide And Forms Package For Chapters 7 Or 13?
Creating documents isn't the most easy process, especially for those who almost never work with legal papers. That's why we advise making use of correct South Carolina Bankruptcy Guide and Forms Package for Chapters 7 or 13 templates made by professional attorneys. It gives you the ability to prevent troubles when in court or working with official institutions. Find the documents you want on our site for top-quality forms and correct information.
If you’re a user with a US Legal Forms subscription, simply log in your account. When you’re in, the Download button will immediately appear on the file web page. Right after getting the sample, it will be saved in the My Forms menu.
Customers with no an activated subscription can easily get an account. Make use of this short step-by-step help guide to get your South Carolina Bankruptcy Guide and Forms Package for Chapters 7 or 13:
- Make certain that the sample you found is eligible for use in the state it is necessary in.
- Confirm the document. Use the Preview feature or read its description (if readily available).
- Click Buy Now if this form is what you need or utilize the Search field to get a different one.
- Choose a suitable subscription and create your account.
- Make use of your PayPal or credit card to pay for the service.
- Download your file in a preferred format.
After doing these straightforward steps, it is possible to fill out the form in your favorite editor. Double-check completed details and consider requesting a lawyer to review your South Carolina Bankruptcy Guide and Forms Package for Chapters 7 or 13 for correctness. With US Legal Forms, everything becomes much simpler. Try it out now!
Form popularity
FAQ
The potential disadvantages of bankruptcy include: Loss of credit cards. Many credit card companies automatically cancel any cards you hold when you file. You will probably receive numerous offers to apply for unsecured credit cards after filing.
In both cases, the bankruptcy court can discharge certain debts. Once a debt has been discharged, the creditor can no longer take action against the debtor, such as attempting to collect the debt or seize any collateral. Not all debts can be discharged, however, and some are very difficult to get discharged.
Chapter 7 is the most common type of bankruptcy and is often referred to as a straight bankruptcy. Under Chapter 7, you can eliminate most of your unsecured debts and some secured debts by surrendering your assets. Unsecured debts are debts not secured with collateral, including most personal loans and credit cards.
Bankruptcy is a legal status that usually lasts for a year and can be a way to clear debts you can't pay. When you're bankrupt, your non-essential assets (property and what you own) and excess income are used to pay off your creditors (people you owe money to). At the end of the bankruptcy, most debts are cancelled.