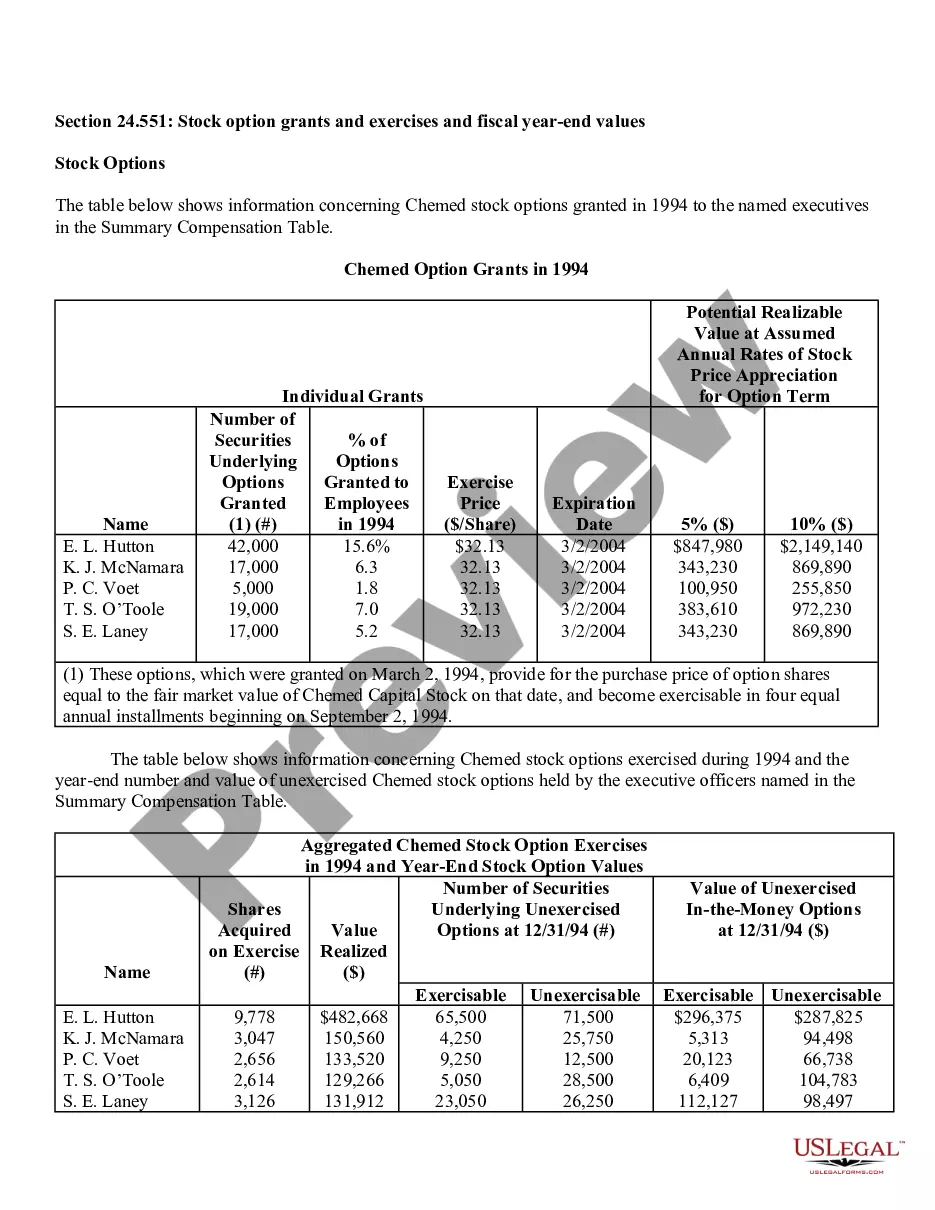
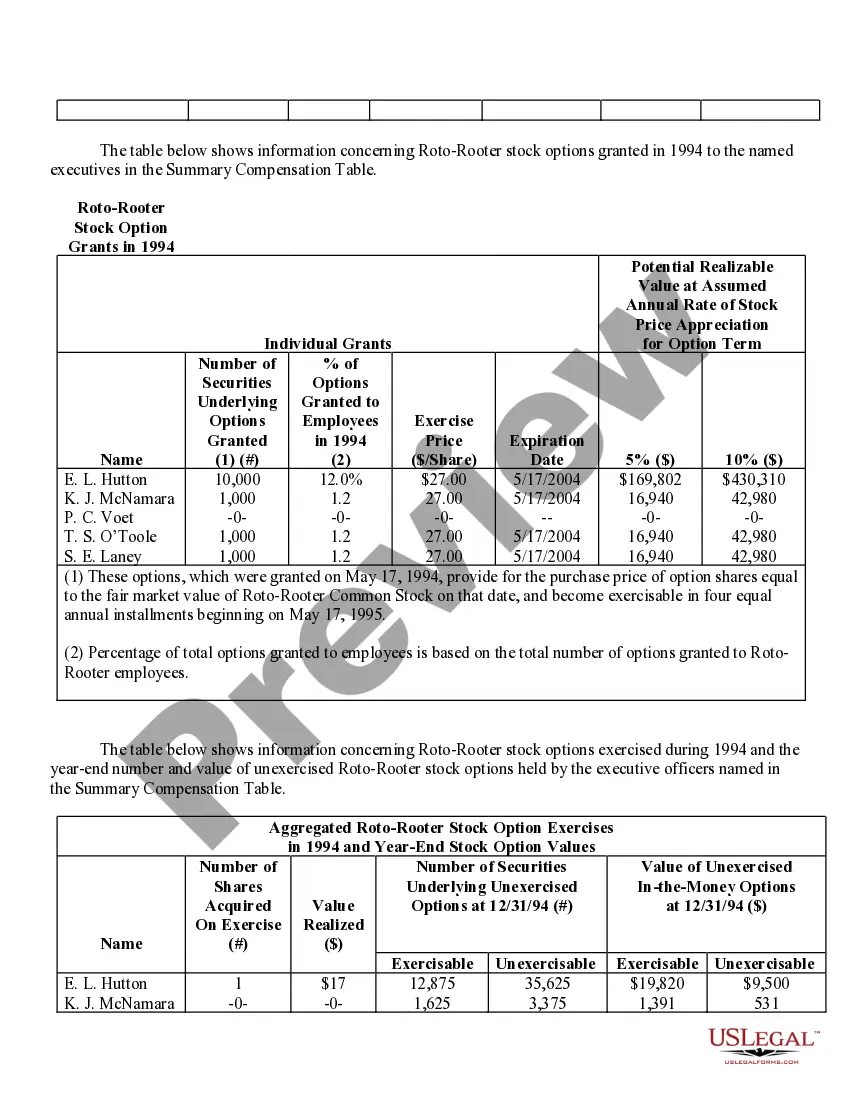
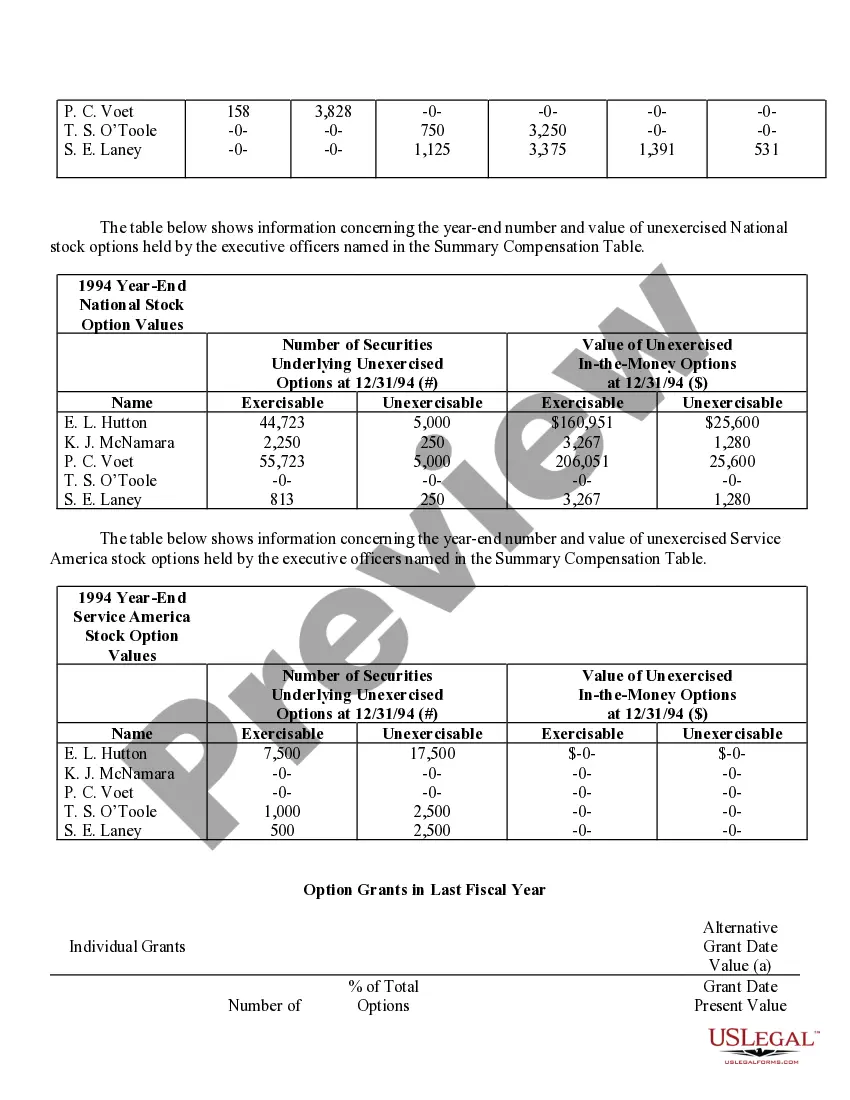
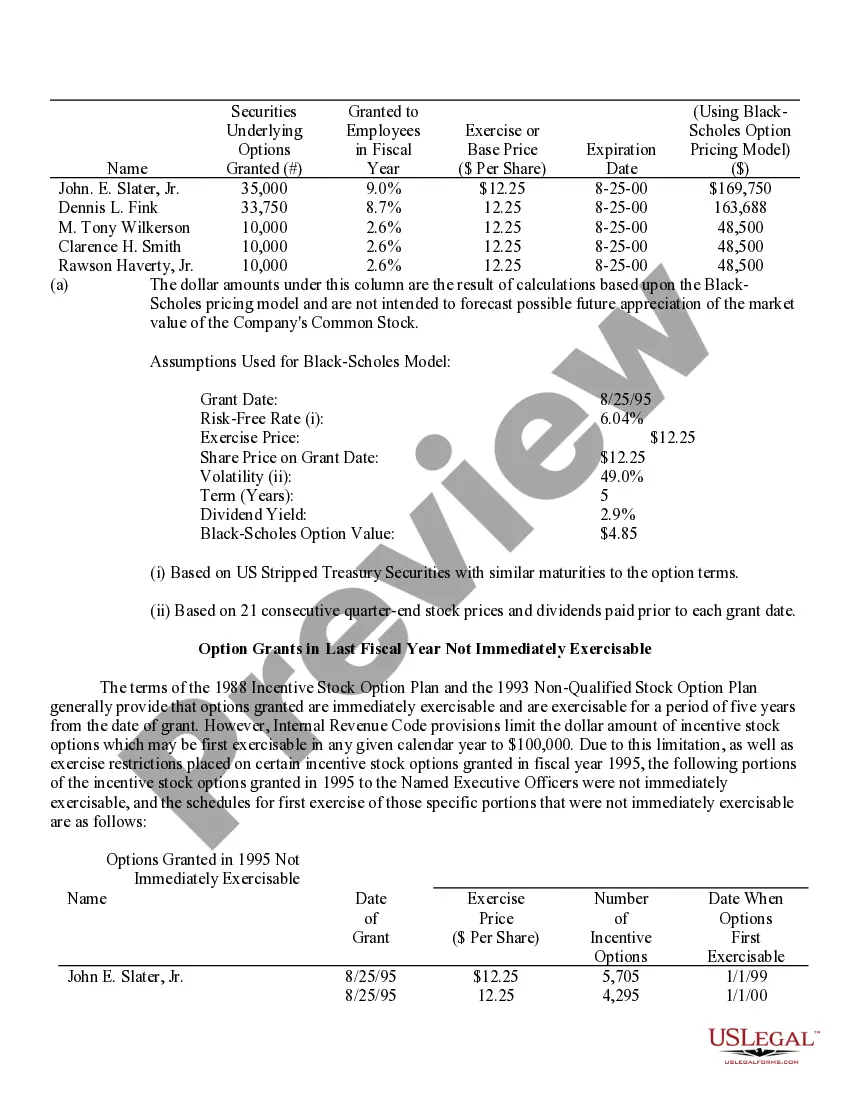
Grant Of Stock Options
Description
How to fill out Stock Option Grants And Exercises And Fiscal Year-End Values?
- Log into your US Legal Forms account if you're a returning user. Ensure that your subscription is active to access necessary templates.
- For new users, begin by exploring the vast selection of legal forms. Check the form description and preview mode to verify it fits your needs and complies with local regulations.
- If your first choice doesn't meet your requirements, use the Search feature to locate alternate templates that suit your intended purpose.
- Once you find the right document, click the 'Buy Now' button to proceed with purchasing your selected form and choose an appropriate subscription plan.
- Complete your purchase by entering your payment information, either via credit card or PayPal account.
- Download the form to your device for easy access and completion. You can also find it later in the 'My Forms' section of your account.
By utilizing US Legal Forms, you gain access to over 85,000 legal documents, ensuring you find the right template for your stock option grants. Additionally, expert assistance is available to help you with the filling process, providing confidence that your documents are accurate and legally enforceable.
Don’t wait! Start your journey towards effective stock option grants by accessing the US Legal Forms library today.
Form popularity
FAQ
Granted stock options are those that the company has given you, but you cannot use them yet. Vested stock options are the ones that you can exercise because you have met the necessary conditions set by the company. Understanding this difference is crucial, as it influences when you can take advantage of the grant of stock options. You can strategize better when you know your vesting schedule.
Accepting your company's option grant can be a smart move, but you should evaluate it carefully. Consider the potential for the stock's value to increase and whether you believe in the company's future growth. Furthermore, analyzing how this option aligns with your financial goals can help you make an informed decision. Make the most out of your grant of stock options by understanding its significance.
An example of a stock grant is when a company awards 100 shares of common stock to an employee as part of their annual bonus. These shares may come with vesting requirements, meaning the employee must stay with the company for a specific period to fully own the shares. This approach encourages employees to commit to the company, making it beneficial for both parties. Such arrangements are often part of broader compensation strategies, including the grant of stock options.
Yes, stock grants do count as income. When a company awards stock grants, the recipient typically recognizes this as taxable income. This means the value of the stock at the time of the grant is subject to income tax. Therefore, it's important to understand how these grants affect your overall tax situation, especially in relation to the grant of stock options.
Yes, a company can grant a stock option to an entity, typically under specific circumstances. Entities can include partnerships, corporations, or trusts, but the terms of the grant must comply with relevant regulations. If you are considering this approach, it may be beneficial to consult with a legal expert to ensure compliance and optimal structuring.
The $100,000 rule pertains to incentive stock options (ISOs), where only $100,000 worth of options can qualify for special tax treatment in a calendar year. Any amount exceeding this limit may be subject to different tax implications. Understanding this rule is vital for maximizing the benefits of the grant of stock options while minimizing tax liabilities.
To report stock options on your tax return, you will need to include any income recognized during the exercise of your options. For the grant of stock options that are treated as income, include this amount on your tax return under the appropriate income section. Keeping detailed records will make this process easier when tax season arrives.
Generally, the grant of stock options is not considered a taxable event. Taxes typically arise when the options are exercised or sold. It’s crucial to understand this distinction, as your financial planning around the grant of stock options can greatly affect your tax situation.
The accounting for stock grants involves recognizing the fair value of the stock options over the vesting period. This means that the expense is recorded in your company's financial statements as the options become vested. Accurate accounting of the grant of stock options is essential for financial reporting purposes.
You may be able to write off stock option losses when you sell the shares acquired through the grant of stock options. However, the rules can be complex, and it often depends on your tax situation. Consulting a tax professional can provide clarity on how to approach these deductions.