Sample Trust Financial Statements Format
Description
How to fill out Trust Agreement - Family Special Needs?
Creating legal documents from the ground up can frequently be somewhat daunting.
Certain cases may entail hours of exploration and substantial funds spent.
If you’re looking for a simpler and more cost-effective method for drafting Sample Trust Financial Statements Format or other documents without needing to navigate through obstacles, US Legal Forms is always accessible to you.
Our digital collection of over 85,000 current legal forms encompasses virtually every aspect of your financial, legal, and personal affairs. With just a few taps, you can swiftly obtain state- and county-compliant documents meticulously assembled for you by our legal experts.
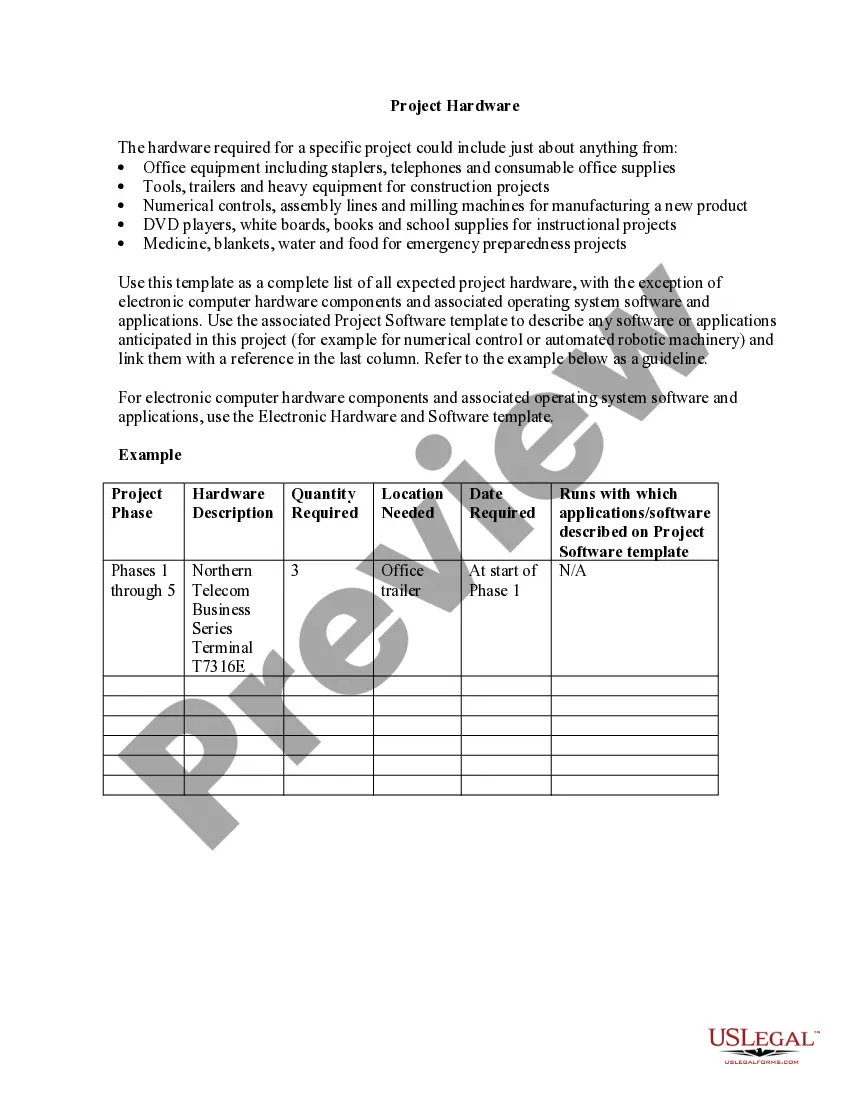
Review the document preview and descriptions to confirm that you are on the right form. Ensure the selected form meets the requirements of your state and county. Choose the most appropriate subscription plan to purchase the Sample Trust Financial Statements Format. Download the file, complete it, validate it, and print it out. US Legal Forms boasts an impeccable reputation and more than 25 years of expertise. Join us today and make document handling an effortless and efficient process!
- Utilize our platform whenever you require a dependable and trustworthy service through which you can conveniently find and download the Sample Trust Financial Statements Format.
- If you’re familiar with our website and have previously registered an account with us, simply Log In to your account, select the form, and download it now or re-download it later in the My documents section.
- Not registered yet? No problem. It requires minimal time to sign up and navigate the library.
- Before proceeding to download the Sample Trust Financial Statements Format, keep these recommendations in mind.
Form popularity
FAQ
To prepare a trust accounting, begin by gathering all financial documents, including bank statements and receipts related to the trust's income and expenses. Next, categorize the transactions and create a detailed report that outlines income, disbursements, and overall balances. Employing a sample trust financial statements format can streamline the process, ensuring that you present a clear and concise accounting that meets legal requirements and helps beneficiaries understand the trust's financial outlook.
An accounting of a trust typically includes a detailed record of all transactions, balancing income against expenses, and summarizing distributions to beneficiaries. It presents an organized view of the trust's financial activities over a certain period. Using a sample trust financial statements format can help ensure clarity and completeness, making it easier for trustees and beneficiaries to understand the trust's financial situation.
Creating a trust format starts with understanding the essential components necessary for your Sample trust financial statements format. You'll want to include a title for the trust, detailed information about the assets, and the roles of the trustee and beneficiaries. Additionally, you can use the US Legal Forms platform, where you can find templates tailored to your specific needs, ensuring that your trust format complies with legal requirements and conveys all necessary information clearly.
Yes, trusts are generally required to produce financial statements for legal and tax purposes. These statements help in assessing the financial condition of the trust and ensuring compliance with relevant laws. You can utilize a sample trust financial statements format to guide your documentation and reporting efforts efficiently.
Creating a trust requires several key documents, including a trust agreement, beneficiary list, and financial statements. These documents help outline the roles, responsibilities, and rights of all parties involved. To streamline your process, consider using a sample trust financial statements format to guide the preparation of your trust's financial records.
Trusts typically do need to prepare financial statements to comply with legal and tax requirements. By doing so, you create a reliable record of all transactions and the current value of trust assets. Utilizing a sample trust financial statements format can simplify this process and ensure you cover all necessary details.
Yes, preparing financial statements for a trust is often necessary. These statements provide a clear view of the trust's financial health and ensure accurate record-keeping. Additionally, the sample trust financial statements format can help you maintain clarity and transparency for beneficiaries and tax authorities.