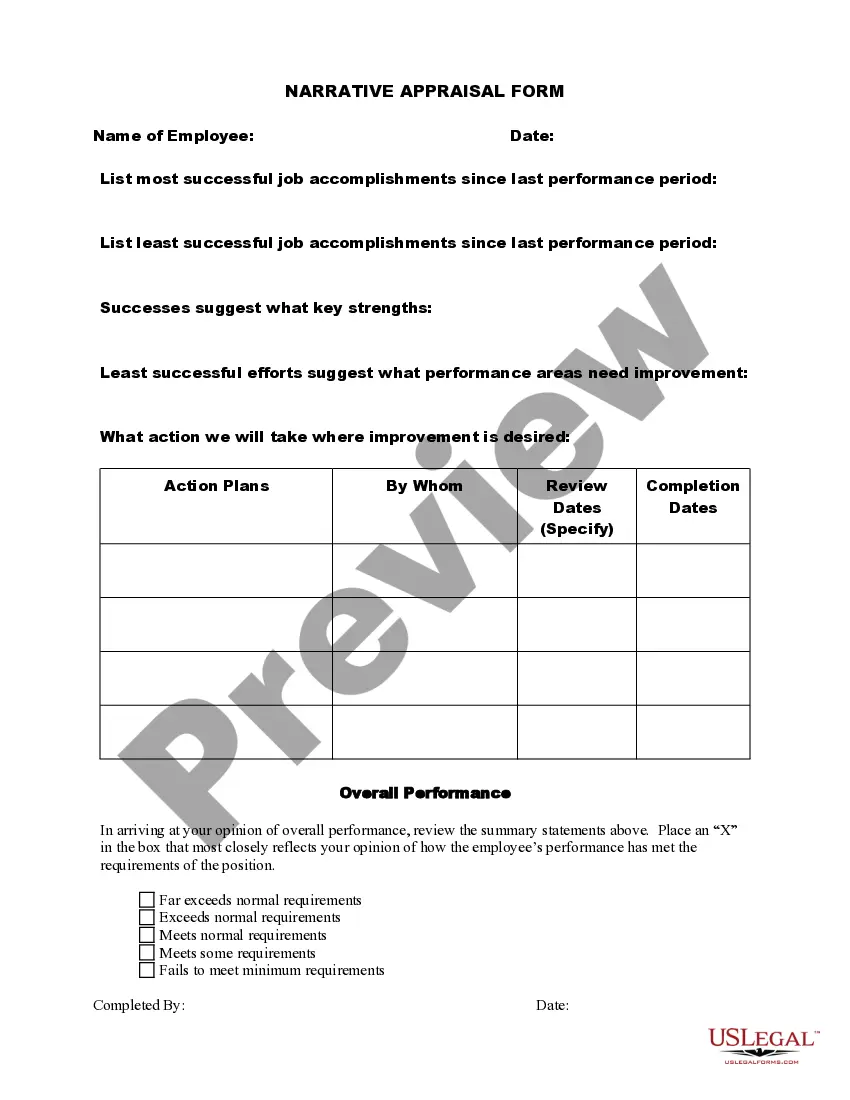
Contract Cost Plus Agreement With Gmp In Washington
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Contingency. Often a percentage of the GMP that provides the contractor with a financial buffer to account for unforeseen and unknown conditions. Allowances. An amount set aside for known unknowns related to materials, labor, and other project costs.
A contingent contract is a legal agreement in which the terms and conditions only apply or take effect if a specific event occurs. Essentially, the parties involved agree to perform actions or obligations based on the occurrence or non-occurrence of a particular event in the future.
This contingency is normally calculated as a percentage. If the phase is 100 days of effort, contingency at 20% would be another 20 days. As the project progresses, the level of risk reduces as the requirements and issues become known, so the percentage will be reduced.
The recommended percentage for a contingency fund is between 5-10% of the total budget, but this may vary depending on project complexity and past experiences.
GMP, which stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, is a system that ensures that manufactured products—such as food, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical goods—are consistently produced and controlled ing to set quality standards.
Unlike stipulated sum contracts, which hold contractors responsible for completing projects at fixed prices regardless of actual costs incurred, GMP contracts transfer this risk to the contractor by setting a limit on how much the customer will be charged.
Ing to Boundy (2012), typically, a written contract will include: Date of agreement. Names of parties to the agreement. Preliminary clauses. Defined terms. Main contract clauses. Schedules/appendices and signature provisions (para. 5).