Construction Contracts In Uk In Harris
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
What is a standard form contract? While many contracts are entirely purpose made, standard form contracts consist of standardised, pre-written terms and conditions. Because standard form contracts are familiar to people in an industry, they often function effectively without the need for much negotiation.
At a greater level of detail, JCT provides a number of subjective tests for determining if certain events give grounds for recompense to the contractor, whereas NEC generally relies on more objective tests.
The most common providers of construction contracts in the UK are: The New Engineering Contract (NEC) The Joint Contracts Tribunal (JCT)
Typically, requirements include: Accounts for the last 2 years. Insurance certificates. Health and safety policy. Quality assurance policy. Environmental policy. Equal opportunities policy. Organisation structure chart. CHAS, Constructionline, SafeContractor industry accreditations.
JCT contracts are the most commonly used in the UK, especially for building projects. They come in several forms, each designed for different project needs: Standard building contract. The standard building contract is intended for larger, more complex projects where detailed contract provisions are necessary.
Related Content. A contract where the terms and conditions are put forward by one party and the other party is not given an opportunity to negotiate or amend those terms and conditions.
Steps to Become a Contractor in the UK Set Up Your Business Structure. Decide whether to operate as a sole trader, limited company, or umbrella company. Register Your Business. Set Up Your Finances. Understand Tax Obligations. Additional Business Requirements. Find Opportunities.
Ing to Boundy (2012), typically, a written contract will include: Date of agreement. Names of parties to the agreement. Preliminary clauses. Defined terms. Main contract clauses. Schedules/appendices and signature provisions (para. 5).
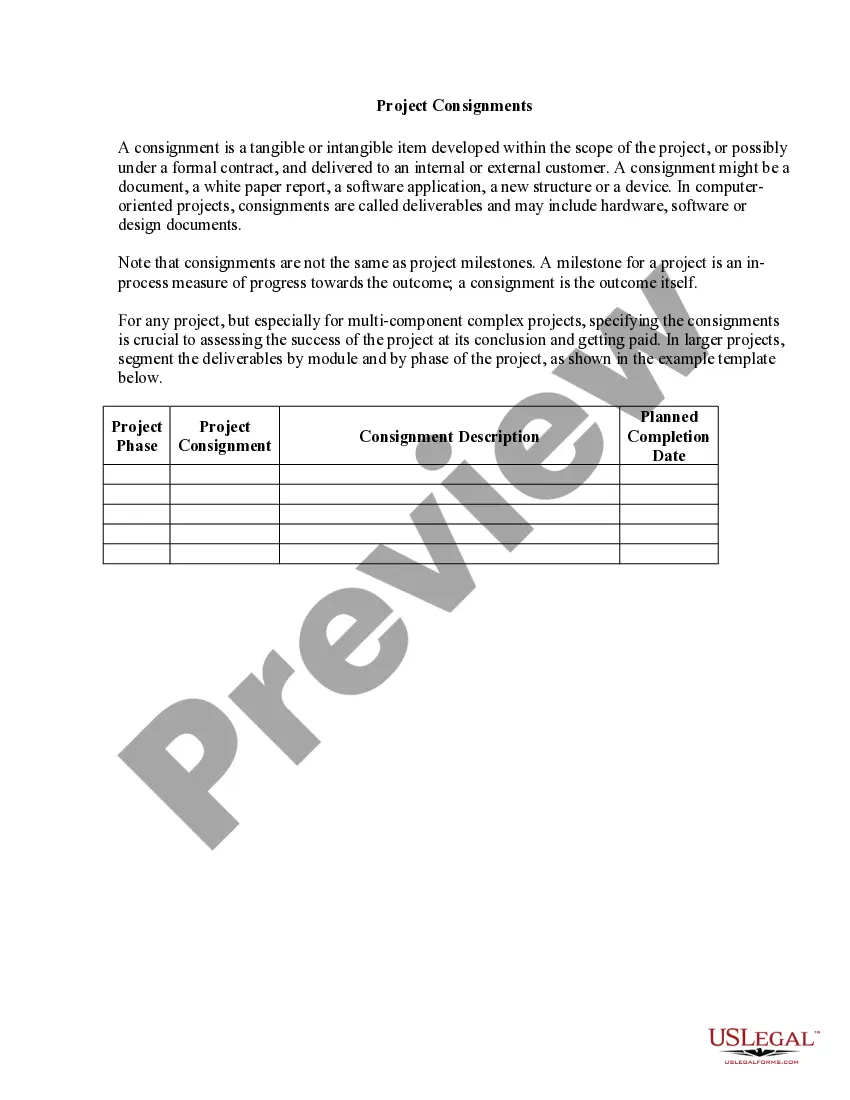
How to draft a contract in 13 simple steps Start with a contract template. Understand the purpose and requirements. Identify all parties involved. Outline key terms and conditions. Define deliverables and milestones. Establish payment terms. Add termination conditions. Incorporate dispute resolution.