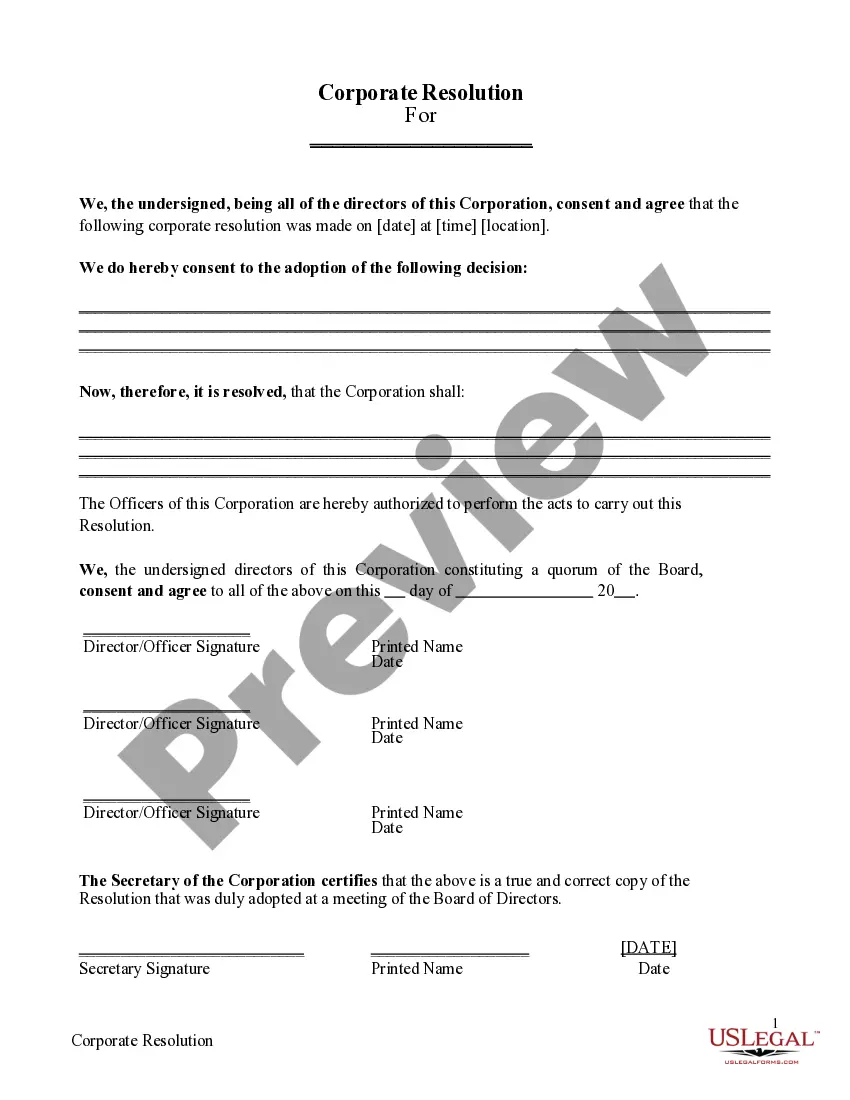
S Corporation Form In Orange
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Ownership: S corporations cannot be owned by C corporations, other S corporations (with some exceptions), LLCs, partnerships or many trusts. Stock: S corporations can have only one class of stock (disregarding voting rights), while C corporations can have multiple classes.
How to Start an S Corp in California Step 1: Check Name Availability. Step 2: Choose a Business Name. Step 3: Obtain an EIN. Step 4: File Articles of Incorporation. Step 5: Registered Agent. Step 6: Corporate Bylaws. Step 7: S Corp Director Election. Step 8: Meeting Requirements.
Choose a business name for your S corp. File articles of incorporation. Issue stock for your S corp. Elect a board of directors and appoint officers. Meet other S corp eligibility requirements. Obtain an employer identification number. Elect S corp status. Apply for state and local S corp business licenses.
To issue stock in a corporation, you can use a simple bill of sale. Stock is issued to fund the corporation—in the Articles of Incorporation, the corporation sets the number of shares the corporation is authorized to issue. The corporation then decides how many shares of stock it will initially issue.
Stock Options Corporations taxed as an s-corporation may have a Stock Option only plan. LLCs taxed as s-corporations may use contractual Option Agreements, which have similar characteristics to non-qualified stock options in a corporation.
The IRS doesn't limit S corporation income. S corporations are incorporated companies that have made an election to be taxed as a pass-through entity rather than have double taxation.
To form an S Corp in California, you must file Form 2553 (Election by a Small Business Corporation) with the IRS and then complete additional requirements with the state of California, including filing articles of incorporation, obtaining licenses and permits, and appointing directors.
Because of the one-class-of-stock restriction, an S corporation cannot allocate losses or income to specific shareholders. Allocation of income and loss is governed by stock ownership, unlike partnerships or LLCs taxed as partnerships where the allocation can be set in the partnership agreement or operating agreement.
You may or may not have heard of the S Corp Salary 60/40 rule. The guideline encourages setting reasonable compensation between 60% and 40% of the business's net profits. The IRS does not set this guideline. It should not be relied on as the only factor for deciding S corporation reasonable compensation.